Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bone Biopsy for Osteomyelitis Treatment
Uploaded by
Amirul Ashraf Bin Shukeri0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pageTo treat osteomyelitis appropriately, a bone biopsy and culture must be performed to identify the causative organism and ensure it is sensitive to antibiotics. For chronic osteomyelitis caused by gram-negative bacilli like Salmonella or Pseudomonas, oral antibiotics may be used. There is no urgency to treat chronic osteomyelitis - a biopsy can be obtained and the culture results used to guide targeted antibiotic treatment.
Otitis externa presents with itching and drainage from the external ear canal and is often difficult to examine due to swelling. It is associated with swimming and foreign objects in the ear. Treatment involves topical antibiotics like ofloxacin or polymyxin/neomycin with hydro
Original Description:
8
Original Title
8
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentTo treat osteomyelitis appropriately, a bone biopsy and culture must be performed to identify the causative organism and ensure it is sensitive to antibiotics. For chronic osteomyelitis caused by gram-negative bacilli like Salmonella or Pseudomonas, oral antibiotics may be used. There is no urgency to treat chronic osteomyelitis - a biopsy can be obtained and the culture results used to guide targeted antibiotic treatment.
Otitis externa presents with itching and drainage from the external ear canal and is often difficult to examine due to swelling. It is associated with swimming and foreign objects in the ear. Treatment involves topical antibiotics like ofloxacin or polymyxin/neomycin with hydro
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pageBone Biopsy for Osteomyelitis Treatment
Uploaded by
Amirul Ashraf Bin ShukeriTo treat osteomyelitis appropriately, a bone biopsy and culture must be performed to identify the causative organism and ensure it is sensitive to antibiotics. For chronic osteomyelitis caused by gram-negative bacilli like Salmonella or Pseudomonas, oral antibiotics may be used. There is no urgency to treat chronic osteomyelitis - a biopsy can be obtained and the culture results used to guide targeted antibiotic treatment.
Otitis externa presents with itching and drainage from the external ear canal and is often difficult to examine due to swelling. It is associated with swimming and foreign objects in the ear. Treatment involves topical antibiotics like ofloxacin or polymyxin/neomycin with hydro
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Master the Boards: USMLE Step 3
To treat osteomyelitis
appropriately, a bone
biopsy/culture must be
performed.
Gram-negative bacilli (Salmonella and Pseudomonas are the ones to consider): This is the only form of osteomyelitis that can be successfully and
reliably treated with oral antibiotics.
- You must confirm it is gram-negative with a bone biopsy.
- The organism must be sensitive to antibiotics.
- There is no urgency to treating chronic osteomyelitis. You can obtain the
biopsy, move the clock forward, and treat what you find on the culture.
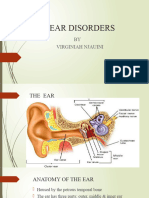
Head and Neck Infections
Otitis Externa
Presents with itching and drainage from the external auditory canal. This is a
form of cellulitis of the skin of the external auditory canal. It is often difficult
to visualize the tympanic membrane because of the swelling of the canal. It is
also painful, especially when the tragus of the ear is manipulated.
It is associated with swimming, because swimming washes out the acidic
environment normally found in the external auditory canal. Other causes
include foreign objects in the ears (e.g., repeated use of cotton swabs, hearing
aids, etc.).
Diagnostic Testing
No specific tests are necessary; diagnosis is based on exam. Do not perform a
routine culture of the ear canal.
Treatment
Topical antibiotics, such as ofloxacin or polymyxin/neomycin. Add topical
hydrocortisone to decrease swelling and itching. Adding acetic acid and
water solution to reacidify the ear can help eliminate the infection.
Malignant Otitis Externa
This is an extremely different disease from simple otitis externa. Malignant otitis externa is really osteomyelitis of the skull from Pseudomonas in a patient
with diabetes. It is an extremely serious disease, because it can lead to a brain
abscess and destruction of the skull. Treat it like osteomyelitis: x-ray, MRI,
bone biopsy/culture.
8
SUBASH KC/NMC-15
You might also like
- Ear Infection Assessment and ManagementDocument8 pagesEar Infection Assessment and ManagementArt Christian Ramos100% (1)
- CholesteatomaDocument2 pagesCholesteatomaOvamelia JulioNo ratings yet
- Acuite Otitis Media Final PresentationDocument26 pagesAcuite Otitis Media Final Presentationmohamedkallon1996No ratings yet
- 01 Congenital Diseases of The External and Middle Ear-1Document39 pages01 Congenital Diseases of The External and Middle Ear-1cabdinuux32No ratings yet
- Cholesteatoma: Causes, Symptoms and Treatment of this Ear TumorDocument4 pagesCholesteatoma: Causes, Symptoms and Treatment of this Ear TumorLeny AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Otitis Externa GuideDocument6 pagesOtitis Externa GuideranmiNo ratings yet
- Clinical Manual of OtolaryngologyDocument49 pagesClinical Manual of Otolaryngologygamecockusc1992100% (3)
- Assessing The Ears and HearingDocument22 pagesAssessing The Ears and HearingGrace RamosNo ratings yet
- 4Document11 pages4eka waraNo ratings yet
- Ear Pathology GuideDocument34 pagesEar Pathology Guidenagham hamdanNo ratings yet
- Infections of The EarDocument9 pagesInfections of The Earrumaisyah alkatiriNo ratings yet
- Drugs and Substance AbuseDocument75 pagesDrugs and Substance Abuseseline sherylNo ratings yet
- Group 11 MastoiditisDocument23 pagesGroup 11 MastoiditisYen-Naah AdamsNo ratings yet
- Presentation Otitis ExternaDocument24 pagesPresentation Otitis ExternaRichard GunawanNo ratings yet
- COM FinalDocument10 pagesCOM FinalCeelin RoblesNo ratings yet
- Penyebab Otalgia 2010Document11 pagesPenyebab Otalgia 2010siska tiaraNo ratings yet
- Ear Pain Causes and TreatmentsDocument11 pagesEar Pain Causes and TreatmentsnotpentingNo ratings yet
- Doctor Franke OtitisDocument6 pagesDoctor Franke OtitisMelanie McguireNo ratings yet
- Congenital MalformationsDocument16 pagesCongenital MalformationsJohn Christopher LucesNo ratings yet
- Acute Otitis MediaDocument16 pagesAcute Otitis Mediaadrianne18sNo ratings yet
- Nur 218 Peds Exam 1 Study Guide Role of The Pediatric NurseDocument9 pagesNur 218 Peds Exam 1 Study Guide Role of The Pediatric NurseNurseme13No ratings yet
- Discharge From The Ear: Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media: Abc of Ent LudmanDocument2 pagesDischarge From The Ear: Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media: Abc of Ent LudmanPipipNo ratings yet
- Cholesteatoma, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandCholesteatoma, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- EaracheDocument5 pagesEaracheclubsanatateNo ratings yet
- Ear: Anatomy, Common Conditions, and Clinical EvaluationDocument19 pagesEar: Anatomy, Common Conditions, and Clinical EvaluationleeNo ratings yet
- Understanding Otitis Media: Causes, Symptoms and Treatment of Ear InfectionsDocument98 pagesUnderstanding Otitis Media: Causes, Symptoms and Treatment of Ear InfectionsLody Lean CruzNo ratings yet
- Acute Diffuse Otitis ExternaDocument36 pagesAcute Diffuse Otitis ExternaIlham Isnin Dolyanov HasibuanNo ratings yet
- Otitis Media and ExternaDocument22 pagesOtitis Media and ExternaLhanz CayingNo ratings yet
- Ear Emergencies: Thomas Morrissey and John B. LissowayDocument11 pagesEar Emergencies: Thomas Morrissey and John B. LissowayFajriah SaraswatiNo ratings yet
- Chronic Suppurative Otitis MediaDocument11 pagesChronic Suppurative Otitis MediaaditiarrtuguNo ratings yet
- Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media: Drhpsingh Additional ProfessorDocument44 pagesChronic Suppurative Otitis Media: Drhpsingh Additional ProfessorIndieNo ratings yet
- Otitis Media (Acute) : Middle Ear DisordersDocument6 pagesOtitis Media (Acute) : Middle Ear DisordersFernando BudimanNo ratings yet
- Otitis Externa A Practical Guide 2001Document10 pagesOtitis Externa A Practical Guide 2001hanumzniiNo ratings yet
- CSOMDocument50 pagesCSOMFurqan MirzaNo ratings yet
- Ears, Nose and Throat Diseases: Prepared By: Hannelli BelingonDocument103 pagesEars, Nose and Throat Diseases: Prepared By: Hannelli BelingonPatricia Kamille I. PawidNo ratings yet
- 11 - Otitis - PrecDocument6 pages11 - Otitis - PrecRhaina KhairaniNo ratings yet
- Differential Diagnosis Ear ConditionsDocument8 pagesDifferential Diagnosis Ear ConditionsOtaku ZONENo ratings yet
- Ear Infection Essentials Understanding, Treating, and PreventingFrom EverandEar Infection Essentials Understanding, Treating, and PreventingNo ratings yet
- Externa Otitis FinalDocument11 pagesExterna Otitis Finalmalika.hirachan007No ratings yet
- Homoeopathic Study & Managment of Chronic Suppurative Otitis MediaDocument52 pagesHomoeopathic Study & Managment of Chronic Suppurative Otitis MediaVANSHRAJ AMALIYARNo ratings yet
- Chronic Suppurative Osteomyelitis of The Mandible CaseDocument4 pagesChronic Suppurative Osteomyelitis of The Mandible Caseporsche_cruiseNo ratings yet
- Ear MedicationDocument15 pagesEar MedicationPascalina Monts'onyaneNo ratings yet
- External Otitis (Otitis Externa)Document16 pagesExternal Otitis (Otitis Externa)Amit MartinNo ratings yet
- Guide to Diagnosing and Treating Ear Canal InfectionsDocument11 pagesGuide to Diagnosing and Treating Ear Canal InfectionsNikita Rizky ArimamiNo ratings yet
- Ent1 18Document45 pagesEnt1 18talya.oliveNo ratings yet
- Otitis Media AkutDocument30 pagesOtitis Media Akutindah sariNo ratings yet
- MASTOIDECTOMY Written OutputDocument3 pagesMASTOIDECTOMY Written OutputJoe RealNo ratings yet
- CASE ANALYSIS - Chronic TympanomastoiditisDocument5 pagesCASE ANALYSIS - Chronic TympanomastoiditisTerry Mae Atilazal SarciaNo ratings yet
- ENT MCQforstudents AnswersDocument30 pagesENT MCQforstudents AnswersOlaNo ratings yet
- MastoiditisDocument3 pagesMastoiditisPrincess GyasiNo ratings yet
- Otits MediaDocument68 pagesOtits MediaSaidi EdwardNo ratings yet
- ENT Quick ReviewDocument6 pagesENT Quick ReviewWadeNo ratings yet
- Remota 170426124830Document34 pagesRemota 170426124830Lolo TotoNo ratings yet
- Chronic Otitis Media GuideDocument50 pagesChronic Otitis Media GuideKhalid MahidaNo ratings yet
- Types of Disease: Chronic Purulent Otitis MediaDocument8 pagesTypes of Disease: Chronic Purulent Otitis MediaAshutoshNo ratings yet
- Referat OtitisDocument20 pagesReferat OtitisBercea AndraNo ratings yet
- The Homeopathic Treatment of Ear Infections PDFDocument104 pagesThe Homeopathic Treatment of Ear Infections PDFdipgang7174No ratings yet
- Prof - Dr. Mohamed Talaat EL - GhonemyDocument33 pagesProf - Dr. Mohamed Talaat EL - Ghonemyadel madanyNo ratings yet
- Phase 3B General Anaesthesia Preparing For Intubation: HistoryDocument1 pagePhase 3B General Anaesthesia Preparing For Intubation: HistoryAmirul Ashraf Bin ShukeriNo ratings yet
- A 2Document1 pageA 2Amirul Ashraf Bin ShukeriNo ratings yet
- At The Time of PublicationDocument2 pagesAt The Time of PublicationAmirul Ashraf Bin ShukeriNo ratings yet
- Retinopathies: Hypertensive RetinopathyDocument3 pagesRetinopathies: Hypertensive RetinopathyAmirul Ashraf Bin ShukeriNo ratings yet
- Describe The Steps of Intubation?Document1 pageDescribe The Steps of Intubation?Amirul Ashraf Bin ShukeriNo ratings yet
- Opthal MEQDocument1 pageOpthal MEQAmirul Ashraf Bin ShukeriNo ratings yet
- William Herring MD, FACR: Book ChapterDocument1 pageWilliam Herring MD, FACR: Book ChapterAmirul Ashraf Bin ShukeriNo ratings yet
- 7 ContentDocument1 page7 ContentAmirul Ashraf Bin ShukeriNo ratings yet
- References: Author: DR Declan HylandDocument1 pageReferences: Author: DR Declan HylandAmirul Ashraf Bin ShukeriNo ratings yet
- Need PDFDocument1 pageNeed PDFAmirul Ashraf Bin ShukeriNo ratings yet
- Branchial Cyst Definition, Types, Presentation and TreatmentDocument3 pagesBranchial Cyst Definition, Types, Presentation and TreatmentAmirul Ashraf Bin ShukeriNo ratings yet
- M: Mallampati Classification: Preoperative MedicationDocument1 pageM: Mallampati Classification: Preoperative MedicationAmirul Ashraf Bin ShukeriNo ratings yet
- Wrong Order Items Replacement RequestDocument1 pageWrong Order Items Replacement RequestAmirul Ashraf Bin ShukeriNo ratings yet
- Neoplasm Presentation NotesDocument7 pagesNeoplasm Presentation NotesAmirul Ashraf Bin ShukeriNo ratings yet
- An Explanation of The Truth of MonotheismDocument16 pagesAn Explanation of The Truth of MonotheismAmirul Ashraf Bin ShukeriNo ratings yet
- ARMDDocument3 pagesARMDAmirul Ashraf Bin ShukeriNo ratings yet
- Understand DementiaDocument2 pagesUnderstand DementiaAmirul Ashraf Bin ShukeriNo ratings yet
- Obstructive Sleep Apnoea (Notes)Document4 pagesObstructive Sleep Apnoea (Notes)Amirul Ashraf Bin ShukeriNo ratings yet
- Normal ChildDocument3 pagesNormal ChildAmirul Ashraf Bin ShukeriNo ratings yet
- Menstrual Cycle IrregularitiesDocument2 pagesMenstrual Cycle IrregularitiesAmirul Ashraf Bin ShukeriNo ratings yet
- AsdfsadfDocument12 pagesAsdfsadf1qQ1qQNo ratings yet
- Brain AgingDocument2 pagesBrain AgingAmirul Ashraf Bin ShukeriNo ratings yet
- Derma EmergencyDocument2 pagesDerma EmergencyAmirul Ashraf Bin ShukeriNo ratings yet
- Neuro OphthalmologyDocument2 pagesNeuro OphthalmologyAmirul Ashraf Bin ShukeriNo ratings yet
- Quick Reference MDDDocument8 pagesQuick Reference MDDyus97No ratings yet
- Brain DefectDocument2 pagesBrain DefectAmirul Ashraf Bin ShukeriNo ratings yet
- Falls in The ElderlyDocument2 pagesFalls in The ElderlyAmirul Ashraf Bin ShukeriNo ratings yet
- AmenorheaDocument7 pagesAmenorheaAmirul Ashraf Bin ShukeriNo ratings yet
- Psychodynamicpsychotherapy PDFDocument2 pagesPsychodynamicpsychotherapy PDFAmirul Ashraf Bin ShukeriNo ratings yet