Professional Documents
Culture Documents
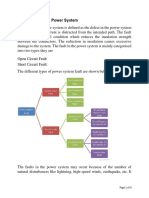
Electricalfault Condition. A Fault Condition Occurs When One or More Electrical Conductors Contact Ground And/or Each Other
Uploaded by
sandeep_chauhan3770Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Electricalfault Condition. A Fault Condition Occurs When One or More Electrical Conductors Contact Ground And/or Each Other
Uploaded by
sandeep_chauhan3770Copyright:
Available Formats
Fault Current means the electrical currentthat flows through a circuit during an
electricalfault condition. A fault condition occurs when one or more electrical conductors
contact ground and/or each other.
In an electric power system, a fault or fault current is any abnormal electric current. For example,
a short circuit is a fault in which current bypasses the normal load. An open-circuit fault occurs if a
circuit is interrupted by some failure. In three-phase systems, a fault may involve one or more
phases and ground, or may occur only between phases. In a "ground fault" or "earth fault", current
flows into the earth. The prospective short circuit current of a predictable fault can be calculated for
most situations. In power systems, protective devices can detect fault conditions and operate circuit
breakers and other devices to limit the loss of service due to a failure.
In a polyphase system, a fault may affect all phases equally which is a "symmetrical fault". If only
some phases are affected, the resulting "asymmetrical fault" becomes more complicated to analyse.
The analysis of these types of faults is often simplified by using methods such as symmetrical
components.
The design of systems to detect and interrupt power system faults is the main objective of powersystem protection
You might also like
- Realistic Faults Olted Fault: TransientDocument3 pagesRealistic Faults Olted Fault: Transientsandeep_chauhan3770No ratings yet
- Realistic Faults: Fault Current Means The Electrical Currentthat Flows Through A Circuit During AnDocument3 pagesRealistic Faults: Fault Current Means The Electrical Currentthat Flows Through A Circuit During Ansandeep_chauhan3770No ratings yet
- Fault Analysis Using Symmetrical ComponentsDocument4 pagesFault Analysis Using Symmetrical Componentssandeep_chauhan3770No ratings yet
- Realistic Faults in Electrical Systems ExplainedDocument3 pagesRealistic Faults in Electrical Systems Explainedsandeep_chauhan3770No ratings yet
- MM in Width, There Shall Be A Passage Way FromDocument4 pagesMM in Width, There Shall Be A Passage Way Fromsandeep_chauhan3770No ratings yet
- Arcing Fault: Electric ArcDocument3 pagesArcing Fault: Electric Arcsandeep_chauhan3770No ratings yet
- Arcing Fault: Three-Phase Prospective Short Circuit Current Circuit BreakersDocument3 pagesArcing Fault: Three-Phase Prospective Short Circuit Current Circuit Breakerssandeep_chauhan3770No ratings yet
- Arcing Fault: Electric ArcDocument3 pagesArcing Fault: Electric Arcsandeep_chauhan3770No ratings yet
- Per-Unit Superposition: Fault Current Means The Electrical Currentthat Flows Through A Circuit During AnDocument3 pagesPer-Unit Superposition: Fault Current Means The Electrical Currentthat Flows Through A Circuit During Ansandeep_chauhan3770No ratings yet
- Arcing Fault: Electric ArcDocument3 pagesArcing Fault: Electric Arcsandeep_chauhan3770No ratings yet
- Faults: Different Types of Faults AreDocument5 pagesFaults: Different Types of Faults AreRohit SarafNo ratings yet
- Faults in Electrical Power SystemDocument4 pagesFaults in Electrical Power Systemmaruf048No ratings yet
- Fault (In Electric Power)Document19 pagesFault (In Electric Power)kasehunNo ratings yet
- MM in Width, There Shall Be A Passage Way FromDocument4 pagesMM in Width, There Shall Be A Passage Way Fromsandeep_chauhan3770No ratings yet
- Fault Current Means The Electrical Currentthat Flows Through A Circuit During AnDocument4 pagesFault Current Means The Electrical Currentthat Flows Through A Circuit During Ansandeep_chauhan3770No ratings yet
- Realistic Faults: MM in Width, There Shall Be A Passage Way FromDocument3 pagesRealistic Faults: MM in Width, There Shall Be A Passage Way Fromsandeep_chauhan3770No ratings yet
- Realistic Faults Olted Fault: Edit EditDocument3 pagesRealistic Faults Olted Fault: Edit Editsandeep_chauhan3770No ratings yet
- Analyzing Asymmetrical Faults in Three-Phase Power SystemsDocument3 pagesAnalyzing Asymmetrical Faults in Three-Phase Power Systemssandeep_chauhan3770No ratings yet
- Faults in Power Systems ExplainedDocument32 pagesFaults in Power Systems ExplainedGaylethunder007No ratings yet
- Voltages Currents Symmetrical Components: Subtransient Is First, and Is Associated With The Largest CurrentsDocument3 pagesVoltages Currents Symmetrical Components: Subtransient Is First, and Is Associated With The Largest Currentssandeep_chauhan3770No ratings yet
- Realistic Faults: Prospective Short-Circuit CurrentDocument3 pagesRealistic Faults: Prospective Short-Circuit Currentsandeep_chauhan3770No ratings yet
- Power System Fault Analysis Using Fault Reporting Data: What Is A Fault?Document5 pagesPower System Fault Analysis Using Fault Reporting Data: What Is A Fault?Sagar AndeNo ratings yet
- Protective Systems for Power NetworksDocument10 pagesProtective Systems for Power NetworksSoumajit PoddarNo ratings yet
- Day-30 Notes (EEE)Document1 pageDay-30 Notes (EEE)Aayush KartikNo ratings yet
- Faults in Electrical Systems Back To Basics PDFDocument2 pagesFaults in Electrical Systems Back To Basics PDFrao saniNo ratings yet
- Faults in Electrical Systems Back To Basics PDFDocument2 pagesFaults in Electrical Systems Back To Basics PDFrao saniNo ratings yet
- AC and DC Auxilliary SuplyDocument3 pagesAC and DC Auxilliary SuplykashifjuttprinceNo ratings yet
- Arcing Fault: Positive-Sequence Component, in Which The Phases Are in The Same Order As The OriginalDocument3 pagesArcing Fault: Positive-Sequence Component, in Which The Phases Are in The Same Order As The Originalsandeep_chauhan3770No ratings yet
- DeusDocument19 pagesDeusMisango EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Types of Faults in Electrical Power Systems and Their EffectsDocument20 pagesTypes of Faults in Electrical Power Systems and Their Effectstebelayhabitamu12No ratings yet
- Normal Conditions in Power SystemDocument115 pagesNormal Conditions in Power SystemAshish ShahNo ratings yet
- Ee8602 PSG Notes - New - Unit1Document20 pagesEe8602 PSG Notes - New - Unit1Vairaperumal KNo ratings yet
- Ee8602 PSG Notes - New - Unit3Document26 pagesEe8602 PSG Notes - New - Unit3Vairaperumal KNo ratings yet
- Definisi 3Document28 pagesDefinisi 3Ren SdaNo ratings yet
- Types of Faults in Power SystemDocument5 pagesTypes of Faults in Power SystemMohamed RafaatNo ratings yet
- Protection SectionDocument8 pagesProtection Sectionaam5112002No ratings yet
- Electrical Power System Faults ExplainedDocument16 pagesElectrical Power System Faults ExplainedvinaybabaNo ratings yet
- System Neutral GroundingDocument11 pagesSystem Neutral GroundingRoldzday DurezaNo ratings yet
- Protect Your Power System with Proper GroundingDocument2 pagesProtect Your Power System with Proper GroundingMujtaba HusseinNo ratings yet
- Current and Kva CalculationsDocument18 pagesCurrent and Kva CalculationsKelvin YipNo ratings yet
- 03Document194 pages03Jorge A. Perez YebraNo ratings yet
- Elements of ProtectionDocument18 pagesElements of ProtectionChetan TawarNo ratings yet
- Types of Faults in Power SystemDocument6 pagesTypes of Faults in Power Systemcollege safariNo ratings yet
- Fault Analysis in Power SystemsDocument3 pagesFault Analysis in Power SystemsdjebienNo ratings yet
- Symmetrical Fault Analysis ChapterDocument26 pagesSymmetrical Fault Analysis ChapterBelayneh TadesseNo ratings yet
- Types of FaultsDocument13 pagesTypes of FaultsRahul SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- System Protection: Section 7Document1 pageSystem Protection: Section 7imcoolmailme2No ratings yet
- Negative Phase Sequence ProtectionDocument15 pagesNegative Phase Sequence ProtectionThirumalNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Calculation and MATLAB Programming of Symmetrical and Asymmetrical Faults in Power SystemDocument4 pagesMathematical Calculation and MATLAB Programming of Symmetrical and Asymmetrical Faults in Power SystemLalbahadur MajhiNo ratings yet
- Types of Fault in Power SystemsDocument6 pagesTypes of Fault in Power SystemsSammar AbbasNo ratings yet
- ERF and ELRDocument21 pagesERF and ELRChhinPiden100% (1)
- Project On Three Phase Fault Analysis With Auto Reset On Temporary Fault and Permanent Trip OtherwiseDocument34 pagesProject On Three Phase Fault Analysis With Auto Reset On Temporary Fault and Permanent Trip OtherwiseAkashPratap2100% (21)
- Types of Faults and Their Effects in Electrical Power SystemsDocument6 pagesTypes of Faults and Their Effects in Electrical Power SystemsMohammed FaizanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction To Power System ProtectionDocument65 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To Power System Protectionjaved kazim100% (1)
- Short Circuit CalculationsDocument15 pagesShort Circuit CalculationsJessica RibeiroNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Power System ProtectionFrom EverandIntroduction to Power System ProtectionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Power Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 4: Electromagnetic CompatibilityFrom EverandPower Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 4: Electromagnetic CompatibilityNo ratings yet
- It Is Quite Another Electricity: Transmitting by One Wire and Without GroundingFrom EverandIt Is Quite Another Electricity: Transmitting by One Wire and Without GroundingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- FilterDocument4 pagesFiltersandeep_chauhan3770No ratings yet
- Fault Current Means The Electrical Currentthat Flows Through A Circuit During AnDocument4 pagesFault Current Means The Electrical Currentthat Flows Through A Circuit During Ansandeep_chauhan3770No ratings yet
- Realistic Faults Olted Fault: Edit EditDocument3 pagesRealistic Faults Olted Fault: Edit Editsandeep_chauhan3770No ratings yet
- Per-Unit Superposition: Fault Current Means The Electrical Currentthat Flows Through A Circuit During AnDocument3 pagesPer-Unit Superposition: Fault Current Means The Electrical Currentthat Flows Through A Circuit During Ansandeep_chauhan3770No ratings yet
- Realistic Faults: MM in Width, There Shall Be A Passage Way FromDocument3 pagesRealistic Faults: MM in Width, There Shall Be A Passage Way Fromsandeep_chauhan3770No ratings yet
- MM in Width, There Shall Be A Passage Way FromDocument4 pagesMM in Width, There Shall Be A Passage Way Fromsandeep_chauhan3770No ratings yet
- Arcing Fault: Electric ArcDocument3 pagesArcing Fault: Electric Arcsandeep_chauhan3770No ratings yet
- Fault CurrentDocument3 pagesFault Currentsandeep_chauhan3770No ratings yet
- FilterDocument3 pagesFiltersandeep_chauhan3770No ratings yet
- Per-Unit Superposition: Fault Current Means The Electrical Currentthat Flows Through A Circuit During AnDocument3 pagesPer-Unit Superposition: Fault Current Means The Electrical Currentthat Flows Through A Circuit During Ansandeep_chauhan3770No ratings yet
- Fault CurrentDocument3 pagesFault Currentsandeep_chauhan3770No ratings yet
- Analyzing Asymmetrical Faults in Three-Phase Power SystemsDocument3 pagesAnalyzing Asymmetrical Faults in Three-Phase Power Systemssandeep_chauhan3770No ratings yet
- Fault CurrentDocument3 pagesFault Currentsandeep_chauhan3770No ratings yet
- Arcing Fault: Three-Phase Prospective Short Circuit Current Circuit BreakersDocument3 pagesArcing Fault: Three-Phase Prospective Short Circuit Current Circuit Breakerssandeep_chauhan3770No ratings yet
- Arcing Fault: Electric ArcDocument3 pagesArcing Fault: Electric Arcsandeep_chauhan3770No ratings yet
- Fault CurrentDocument3 pagesFault Currentsandeep_chauhan3770No ratings yet
- Arcing Fault: Electric ArcDocument3 pagesArcing Fault: Electric Arcsandeep_chauhan3770No ratings yet
- Realistic Faults: Prospective Short-Circuit CurrentDocument3 pagesRealistic Faults: Prospective Short-Circuit Currentsandeep_chauhan3770No ratings yet
- Arcing Fault: Positive-Sequence Component, in Which The Phases Are in The Same Order As The OriginalDocument3 pagesArcing Fault: Positive-Sequence Component, in Which The Phases Are in The Same Order As The Originalsandeep_chauhan3770No ratings yet
- Fault CurrentDocument3 pagesFault Currentsandeep_chauhan3770No ratings yet
- Fault CurrentDocument2 pagesFault Currentsandeep_chauhan3770No ratings yet
- Fault CurrentDocument2 pagesFault Currentsandeep_chauhan3770No ratings yet
- Transient Recovery VoltageDocument1 pageTransient Recovery Voltagesandeep_chauhan3770No ratings yet
- Voltages Currents Symmetrical Components: Subtransient Is First, and Is Associated With The Largest CurrentsDocument3 pagesVoltages Currents Symmetrical Components: Subtransient Is First, and Is Associated With The Largest Currentssandeep_chauhan3770No ratings yet