Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 10: Solution of Triangles 10.1 Sine Rule
Uploaded by
Shafiqah Samsuri0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views4 pagesAdd Math Form 4
Original Title
Chapter 10
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentAdd Math Form 4
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views4 pagesChapter 10: Solution of Triangles 10.1 Sine Rule
Uploaded by
Shafiqah SamsuriAdd Math Form 4
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
CHAPTER 10: SOLUTION OF TRIANGLES
10.1 Sine Rule
C
a
b
A
B
c
Can be used when
Two sides and one non-included angle, or
Two angles and one opposite side are given.
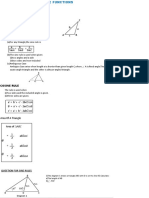
Example 1
B
70
4 cm
50
Calculate the length, in cm, of AB.
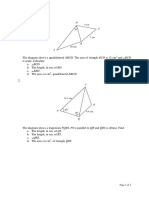
Example 2
B
26 cm
A
54
28 cm
Calculate ACB.
Page 1 of 4
Ambiguous case
C2
C1
a
A
May occur if
1. a < c.
2. A is an acute non-included angle.
The two triangles that can be formed are ABC1 and ABC2.
Example 3
B
26 cm
54
28 cm
Calculate ACB.
Page 2 of 4
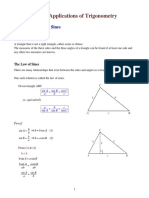
10.2 Cosine Rule
C
a
b
A
B
c
a2 = b2 + c2 2bc cos A
b2 = a2 + c2 2ac cos B
c2 = a2 + b2 2ab cos C
Can be used when
1. Two sides and the included angle, or
2. Three sides of a triangle are given.
Example 4
C
x
4 cm
B
50
A
7 cm
Calculate the length of AC, x, in cm for the triangle above.
Example 5
B
7 cm
8 cm
C
6 cm
Calculate BAC for the triangle above.
Page 3 of 4
10.3 Area of Triangles
C
a
b
A
B
c
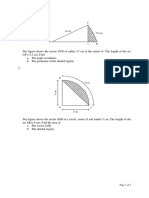
Example 6
C
7 cm
40
4 cm
A
Calculate the area of the triangle above.
Page 4 of 4
You might also like
- The Surprise Attack in Mathematical ProblemsFrom EverandThe Surprise Attack in Mathematical ProblemsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- The Sine and Cosine RuleDocument17 pagesThe Sine and Cosine RuleNur Suliana Md ZainNo ratings yet
- The Sine and Cosine RuleDocument17 pagesThe Sine and Cosine RulejustfmenotNo ratings yet
- 4 6Document2 pages4 6user09XNo ratings yet
- Solutions of TrianglesDocument19 pagesSolutions of TrianglesNoridah Binti SalmoNo ratings yet
- Mpu Egn MathDocument5 pagesMpu Egn MathF1026 AzamuddinNo ratings yet
- Solution of TriangleDocument32 pagesSolution of TriangleJr Spark100% (1)
- Lesson 9 Stem 1BDocument9 pagesLesson 9 Stem 1BJune Patricia AraizNo ratings yet
- Solving Oblique TrianglesDocument55 pagesSolving Oblique TrianglesElmer Kenneth100% (1)
- Problem in 2D and 3D-Gr12Document43 pagesProblem in 2D and 3D-Gr12Mkhongelo MkansiNo ratings yet
- 4 4 Applications Trigonometry To TrianglesDocument12 pages4 4 Applications Trigonometry To Trianglessonicdan1234No ratings yet
- Use the cosine rule to solve triangle problemsDocument6 pagesUse the cosine rule to solve triangle problemshwa5181No ratings yet
- Sine Law or Cosine LawDocument7 pagesSine Law or Cosine Lawblabdude123No ratings yet
- Make Up Chapter Test: Geometry Mathematics Course A Fall 2008: Maanvc08Document5 pagesMake Up Chapter Test: Geometry Mathematics Course A Fall 2008: Maanvc08Epic WinNo ratings yet
- The Sine and Cosine RuleDocument17 pagesThe Sine and Cosine Ruleapi-19979730No ratings yet
- Class 11 CH 17 Solution of Triangles PDFDocument4 pagesClass 11 CH 17 Solution of Triangles PDFBibhu BiswalNo ratings yet
- 14right Angle TrigonometryDocument12 pages14right Angle TrigonometryMhai MabantaNo ratings yet
- bk9 12Document18 pagesbk9 12Rahique ShuaibNo ratings yet
- Trig Lecture 4Document67 pagesTrig Lecture 4REjosh BonifacioNo ratings yet
- Wikimama Class 11 CH 17 Solution of TrianglesDocument4 pagesWikimama Class 11 CH 17 Solution of TrianglesWikimamaNo ratings yet
- TESTFILE001Document18 pagesTESTFILE001BaviThran MahendranNo ratings yet
- Chapter1 TrianglesDocument18 pagesChapter1 TrianglesSyafiiqahNo ratings yet
- Trigon Bearing ClassifiedDocument35 pagesTrigon Bearing ClassifiedShaaminiNo ratings yet
- Solving Oblique TrianglesDocument3 pagesSolving Oblique TrianglesNikko CarismaNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry 2Document5 pagesTrigonometry 2Laura ChandraNo ratings yet
- Mathematics ss2 Exams QuestionsDocument7 pagesMathematics ss2 Exams Questionsstephen Emmanuel0% (1)
- 3RD Term S2 MathematicsDocument31 pages3RD Term S2 MathematicsAdelowo DanielNo ratings yet
- Solution of Triangle (MT)Document31 pagesSolution of Triangle (MT)mann123456789No ratings yet
- MCQ on Taking Out Quantities & Detailed Estimate for Civil EngineeringDocument9 pagesMCQ on Taking Out Quantities & Detailed Estimate for Civil EngineeringShinde vishal100% (1)
- TrigonometryDocument3 pagesTrigonometryShang Divina Ebrada50% (2)
- Math and Science Basics 1 / Mathematics 2 Homework 10.9.2013Document2 pagesMath and Science Basics 1 / Mathematics 2 Homework 10.9.2013rickytuan1991No ratings yet
- Solution of TrianglesDocument10 pagesSolution of TrianglesMohd HarrisNo ratings yet
- Topic: 3.0 Trigonometric Functions Subtopic: 3.1 Solving A Triangle by Using Sine and Cosine Formula and Area of Triangle. Learning: OutcomesDocument9 pagesTopic: 3.0 Trigonometric Functions Subtopic: 3.1 Solving A Triangle by Using Sine and Cosine Formula and Area of Triangle. Learning: OutcomesnirnanurfazianaismailNo ratings yet
- Fieldwork No. 02 Measuring and Laying Out Horizontal Angles With TapeDocument4 pagesFieldwork No. 02 Measuring and Laying Out Horizontal Angles With TapeHeliosNo ratings yet
- Refresher MATH Part5Document2 pagesRefresher MATH Part5Lionel LapuzNo ratings yet
- MC Ty Triangleformulae 2009 1Document13 pagesMC Ty Triangleformulae 2009 1lakshminivas PingaliNo ratings yet
- Submitted By: Gianne Denise C. Dueñas IV-VanadiumDocument24 pagesSubmitted By: Gianne Denise C. Dueñas IV-VanadiumalyssajeanneNo ratings yet
- Mathematics For Site EngineeringDocument16 pagesMathematics For Site EngineeringAde PutraNo ratings yet
- Fundamental of Engineering Mathematics Final ExamDocument3 pagesFundamental of Engineering Mathematics Final ExamrowelNo ratings yet
- Cosine Law 1Document5 pagesCosine Law 1Sinead Audrey VallesteroNo ratings yet
- MaDNVC02 Trigonometry VT2004Document3 pagesMaDNVC02 Trigonometry VT2004Epic WinNo ratings yet
- How To Use The AbacusDocument4 pagesHow To Use The AbacusHeinz Justine IbasanNo ratings yet
- Cosine LawDocument16 pagesCosine LawMary Kate BacongaNo ratings yet
- 18 3-D Geometry: 18.1 Using Pythagoras' Theorem and Trigonometry in Three DimensionsDocument12 pages18 3-D Geometry: 18.1 Using Pythagoras' Theorem and Trigonometry in Three DimensionsperwinsharmaNo ratings yet
- Constructions: Sample Question 1Document4 pagesConstructions: Sample Question 1Ayush JaiswalNo ratings yet
- FW 1 Measuring and Laying Out Horizontal Angles With TapeDocument3 pagesFW 1 Measuring and Laying Out Horizontal Angles With TapeAshTzy OfficialNo ratings yet
- 4.5 Applications of Trigonometric Functions: EmcgkDocument1 page4.5 Applications of Trigonometric Functions: EmcgkreacharunkNo ratings yet
- Maths 11 3Document17 pagesMaths 11 3api-230427224No ratings yet
- Task 2Document15 pagesTask 2Muruli KrishanNo ratings yet
- The Law of CosinesDocument4 pagesThe Law of Cosinesapi-213604106No ratings yet
- Math 17 4.7Document25 pagesMath 17 4.7jiiNo ratings yet
- Add Math Solution of TriangleDocument10 pagesAdd Math Solution of Trianglekamil muhammadNo ratings yet
- Chapter1 TrianglesDocument18 pagesChapter1 TrianglesahfNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Fourth Period Mathematics - Grade 10 NAME: - DATE: - / - / - GRADINGDocument2 pagesFinal Exam Fourth Period Mathematics - Grade 10 NAME: - DATE: - / - / - GRADINGJulio Cèsar GarcìaNo ratings yet
- Solution of TrianglesDocument35 pagesSolution of TrianglesSankar RanjanNo ratings yet
- Solving Partial Differential Equation Applications with PDE2DFrom EverandSolving Partial Differential Equation Applications with PDE2DNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document22 pagesChapter 2Shafiqah SamsuriNo ratings yet
- Exercise Chapter 11Document3 pagesExercise Chapter 11Shafiqah SamsuriNo ratings yet
- When y A, Then Dy DX When y X, Then Dy DX NX When y Ax, Then Dy DX A When y A X, Then Dy DX Anx When y X, Then Dy DX N X When y A X, Then Dy DX A XDocument1 pageWhen y A, Then Dy DX When y X, Then Dy DX NX When y Ax, Then Dy DX A When y A X, Then Dy DX Anx When y X, Then Dy DX N X When y A X, Then Dy DX A XShafiqah SamsuriNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document7 pagesChapter 3Shafiqah SamsuriNo ratings yet
- Exercise Chapter 11Document3 pagesExercise Chapter 11Shafiqah SamsuriNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11: Index Number 11.1 Index Number Price Index: Page 1 of 3Document3 pagesChapter 11: Index Number 11.1 Index Number Price Index: Page 1 of 3Shafiqah SamsuriNo ratings yet
- Exercise Chapter 10Document2 pagesExercise Chapter 10Shafiqah SamsuriNo ratings yet
- Exercise Chapter 7Document2 pagesExercise Chapter 7Shafiqah SamsuriNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6: Coordinate Geometry 6.1 Distance Between Two PointsDocument11 pagesChapter 6: Coordinate Geometry 6.1 Distance Between Two PointsShafiqah SamsuriNo ratings yet
- Exercise Chapter 6Document4 pagesExercise Chapter 6Shafiqah SamsuriNo ratings yet
- Exercise Chapter 5Document1 pageExercise Chapter 5Shafiqah SamsuriNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7: Statistics 7.1 Measures of Central Tendency 7.1.1 MeanDocument13 pagesChapter 7: Statistics 7.1 Measures of Central Tendency 7.1.1 MeanShafiqah Samsuri100% (1)
- Exercise Chapter 8Document5 pagesExercise Chapter 8Shafiqah SamsuriNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8: Circular Measure 8.1 Radian: Length of ArcDocument3 pagesChapter 8: Circular Measure 8.1 Radian: Length of ArcShafiqah SamsuriNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 ExerciseDocument1 pageChapter 3 ExerciseShafiqah SamsuriNo ratings yet
- Solve Simultaneous Equations & Geometry ProblemsDocument2 pagesSolve Simultaneous Equations & Geometry ProblemsShafiqah SamsuriNo ratings yet
- When A Real Number A Is Multiplied by Itself in N Times, The Result Is The A To The Power of N. in GeneralDocument9 pagesWhen A Real Number A Is Multiplied by Itself in N Times, The Result Is The A To The Power of N. in GeneralShafiqah SamsuriNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Quadratic Functions 3.1 Quadratic Functions and Their Graphs General Form of Quadratic FunctionDocument4 pagesChapter 3: Quadratic Functions 3.1 Quadratic Functions and Their Graphs General Form of Quadratic FunctionShafiqah SamsuriNo ratings yet
- Kertas 1 Pep BK1 SPM Terengganu 2016 - SoalanDocument35 pagesKertas 1 Pep BK1 SPM Terengganu 2016 - SoalanShafiqah SamsuriNo ratings yet
- Exercise Chapter 4Document1 pageExercise Chapter 4Shafiqah SamsuriNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document6 pagesChapter 2Shafiqah SamsuriNo ratings yet
- Exercise Chapter 1Document4 pagesExercise Chapter 1Shafiqah SamsuriNo ratings yet
- Choocoby Snack Company ReportDocument54 pagesChoocoby Snack Company ReportShafiqah Samsuri100% (1)
- OSHA Process Safety ManagementDocument18 pagesOSHA Process Safety ManagementShafiqah Samsuri100% (1)
- Fundamentals of Fires and ExplosionsDocument4 pagesFundamentals of Fires and ExplosionsShafiqah SamsuriNo ratings yet
- Functions ChapterDocument7 pagesFunctions ChapterShafiqah SamsuriNo ratings yet