Joshua Cummins
Digestive System Lab Report
This lab report will cover the different parts and the different components that are
in those parts
within the digestive system.
Including the mouth structure and digestive system.
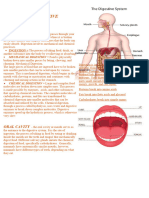
The Mouth Structure is a vital structure in our body. The use is to help digest our
food with our saliva and teeth. It is also used to import oxygen into our body to
keep our blood flowing. The mouth uses tastebuds to detect what is entering our
body by sending messages to our brain. Our mouths also use the teeth to help
break down the food.
But there is not much of a purpose of our mouth structure if did not have
our esophagus and stomach. The mouth breaks down our food and sends it
down the esophagus and down into the stomach. While in the esophagus the
food is made into a bolus and is being taken down easily because of the saliva.
Afterwards the food is entered into the stomach and the stomach uses acidic
juices, turning it into chyme. During the process of chyme the stomach is taking
in all of the nutrients from the food and goes into the small intestines. Lastly after
passing the small intestine, the chyme goes into the large intestine and made
into feces. It is held in the haustra and the large intestine sends messages to the
brain that it is ready to be release
Part I The Structure of the Mouth
Salivary Glands:
Salivary glands are filled with an enzyme called Amylase. This specific enzyme is
responsible for breaking down the amylose and amylopectin that is found in
starched goods. Amylase breaks these molecules in starch by coating and
surrounding them while they are in your mouth, then it begins to deconstruct
those molecules through a process called hydrolysis. This turns them into smaller
better managed molecules, the result of the of this conversion is called maltose
which is a type of simple carbohydrate.
Figure 1: Cracker lab
�Contribution of smell and texture:
It is a common belief that smell and texture are major parts in taste. The reason
for texture is because the tongues surface is covered with rough projections
called papillae, while some can provide friction to handle food while others are
scattered throughout the mouth to provide taste buds. The root of the tongue is
anchored to the hyoid bone in the back of the mouth towards the throat.
Mammal Teeth Structure:
The teeth is the first mechanical part of breaking down food along side the
amylase which is the first chemical part which occurs within our mouths. The
teeth do not use an enzyme to breakdown food but actually force and pressure to
split/tear apart the food and due to their hard surface it makes them easy to do
so, it can then be swallowed to go down the esophagus so the the other digestive
functions may take place. Without teeth there would be so much food that we
would not be able to consume due to the size they hold.
Figure 1.
Part II Esophagus and Stomach
But there is not much of a purpose of our mouth structure if did not have
our esophagus and stomach. The mouth breaks down our food and sends it
down the esophagus and down into the stomach. While in the esophagus the
food is made into a bolus and is being taken down easily because of the saliva.
Afterwards the food is entered into the stomach and the stomach uses acidic
�juices, turning it into chyme. During the process of chyme the stomach is taking
in all of the nutrients from the food and goes into the small intestines. Lastly after
passing the small intestine, the chyme goes into the large intestine and made
into feces. It is held in the haustra and the large intestine sends messages to the
brain that it is ready to be release
�Experimental Data
pH of stomach
Drops of fluid from
pancreatic duct
pH of fluid from main
pancreatic duct
Drops of fluid from
common bile duct
Motility of stomach
Motility of small intestine
Blood glucose level
Strength of contraction
Drops of fluid from salivary
duct
What is the effect of the effect digestive hormones?
The digestive hormones all cause a different effect because of how they react
with the body.
A lab experiment was taken place with multiple rats prepared and put into
different labs where they were injected with a different hormone to see what the
reaction is within the body and what they caused to happen. Each different
hormone affected the lab rats in a different ways for example while some
dropped the pH in the main pancreatic duct while others increased the drops of
fluid from the bile duct.
Conclusion:
Over the time within this lab report and the experiments conducted inside of it we
have come to know more about the digestive system that is inside of our body
and how it operates and what affects it has.