Professional Documents
Culture Documents
536spectrophotometry PDF
536spectrophotometry PDF
Uploaded by
pontas97Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
536spectrophotometry PDF
536spectrophotometry PDF
Uploaded by
pontas97Copyright:
Available Formats
Spectrophotometry
Fall, 2010
Spectrophotometry
Quantifies the transmission of
light through solutions
COLORIMETRY:
When chemical reaction occurs
that changes the color of the
solution, which in turn increases
the absorption of light at a
specific wavelength.
SPECTROPHOTOMETRY:
When the solution contains a specific molecule
that absorbs light at a specific wavelength (eg: NADH
@ 340 nm).
Dr. Robert A. Robergs, Ph.D., FASEP, EPC
Spectrophotometry
Fall, 2010
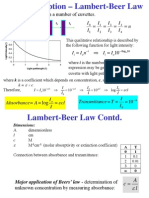
Beer-Lambert Law
Ii =
where;
= Ie
Ie = Ii e -acL
a = absorption coefficient (wavelength specific)
c = concentration of dissolved molecule
L = thickness of light path length through solution
=L
Dr. Robert A. Robergs, Ph.D., FASEP, EPC
e = 2.71828
Spectrophotometry
Fall, 2010
Beer-Lambert Law, contd.
Ie = Ii e -acL
Ie / Ii = e -acL
Transmittance = T = Ie / Ii = e -acL
ln T = ln (e -acL) = - a c L
ln (1/T) = a c L
= Absorbance
Absorbance equals the natural log of the reciprocal of transmittance
Beer-Lambert Law, contd.
Absorbance equals the natural log of the reciprocal of transmittance
ln (1/T) = a c L
= Absorbance
Absorbance = a c L
If you know the absorption coefficient for a given
wavelength, and the thickness of the path length for light
transmitted through the solution, you can calculate
concentration.
Dr. Robert A. Robergs, Ph.D., FASEP, EPC
Spectrophotometry
Fall, 2010
What wavelength of light best
distinguishes chlorophyll a
from b and carotenoids?
~ 675 nm
What wavelength of light best
distinguishes carotenoids from
chlorophyll a and b?
~ 520-530 nm
What wavelength of light best
distinguishes chlorophyll b
from a and carotenoids?
~ 650 nm
Spectrophotometers
Dr. Robert A. Robergs, Ph.D., FASEP, EPC
Spectrophotometry
Fall, 2010
Genesys 10 Spectrophotometer
Dr. Robert A. Robergs, Ph.D., FASEP, EPC
You might also like
- Spectro Photo Me TryDocument81 pagesSpectro Photo Me TrySunil100% (1)
- Optical Sources, Detectors, and Systems: Fundamentals and ApplicationsFrom EverandOptical Sources, Detectors, and Systems: Fundamentals and ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes Analytical Biochemistry: Chapter - 1 Spectrophotometry and ColorimetryDocument35 pagesLecture Notes Analytical Biochemistry: Chapter - 1 Spectrophotometry and ColorimetryHarpreet Singh100% (3)
- Spectroscopic MethodsDocument76 pagesSpectroscopic MethodsVu SangNo ratings yet
- Uv Visible SpectrosDocument6 pagesUv Visible Spectrospankajbhattb_pharmaNo ratings yet
- UV / Vis Spectroscopy: Mr. Z. ClarkeDocument41 pagesUV / Vis Spectroscopy: Mr. Z. ClarkeSash1693No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Spectroscopy MethodsDocument77 pagesChapter 1 - Spectroscopy MethodsHariss JailudinNo ratings yet
- Pka Determination Using SpectrometryDocument7 pagesPka Determination Using SpectrometryVanitha SelvarajanNo ratings yet
- Uv-VISIBLE SPECTROSDocument41 pagesUv-VISIBLE SPECTROSVansh YadavNo ratings yet
- SpectrosDocument58 pagesSpectrospaoloobiasNo ratings yet
- Basic Principles of The InstrumentsDocument6 pagesBasic Principles of The Instrumentsdivyansh raiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 20-03-12Document36 pagesLecture 20-03-12toxiczarrar.pubgNo ratings yet
- 21 9 6 6. Chapter 13. Ultraviolet Visible Spectrophotometry 11.29Document16 pages21 9 6 6. Chapter 13. Ultraviolet Visible Spectrophotometry 11.29nekenih413No ratings yet
- Prepared by Michigan Department of Environmental Quality Operator Training and Certification UnitDocument55 pagesPrepared by Michigan Department of Environmental Quality Operator Training and Certification Unitlalitk02No ratings yet
- Beers Law NotesDocument5 pagesBeers Law NotesJerome GironNo ratings yet
- Uv Visible SpectrosDocument13 pagesUv Visible SpectrosROγALKING0CNo ratings yet
- Uv-Visible SpectrosDocument41 pagesUv-Visible SpectrosChadNo ratings yet
- Chem 137.1 - Exer 1 PostlabDocument15 pagesChem 137.1 - Exer 1 PostlabGerry Mark Gubantes100% (1)
- Lecture IDocument50 pagesLecture INofrizalNo ratings yet
- Principles of Colorimetric MeasurementsDocument8 pagesPrinciples of Colorimetric MeasurementsDipmalya Basak100% (1)
- Analysis of Samples Absorbance Susing UV-VisDocument17 pagesAnalysis of Samples Absorbance Susing UV-VisRaiwata Mertanjaya100% (2)
- Module 1 Notes 1chem Mescenotes - inDocument63 pagesModule 1 Notes 1chem Mescenotes - inHafizNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of SpectrophotometryDocument56 pagesFundamentals of SpectrophotometryNORMA PATRICIA SANCHEZ LONDOÑO100% (1)
- Fundamentals of Spectrophotometry: ColorimetryDocument33 pagesFundamentals of Spectrophotometry: ColorimetryaliNo ratings yet
- Beer's LawDocument8 pagesBeer's Lawjuser2007No ratings yet
- Lecture Notes Analytical Biochemistry: Chapter - 1 Spectrophotometry and ColorimetryDocument35 pagesLecture Notes Analytical Biochemistry: Chapter - 1 Spectrophotometry and Colorimetryhod MLSNo ratings yet
- Uv VisibleDocument13 pagesUv VisiblebushraqadriNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering Department: Adamson University College of EngineeringDocument13 pagesChemical Engineering Department: Adamson University College of EngineeringKarl RodernoNo ratings yet
- Uv Visible SpectrosDocument23 pagesUv Visible SpectrosKD LoteyNo ratings yet
- Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy - University NotesDocument29 pagesAtomic Absorption Spectroscopy - University NotesLilac44No ratings yet
- Unit 2Document59 pagesUnit 2NTGNo ratings yet
- 2 Visible Spectroscopy - GoodDocument7 pages2 Visible Spectroscopy - GoodOmSilence2651No ratings yet
- Uv-VISIBLE SPECTROSDocument41 pagesUv-VISIBLE SPECTROSneerajNo ratings yet
- Part 3 Using Light For DetectionDocument48 pagesPart 3 Using Light For DetectionJosé ClementeNo ratings yet
- SPECTROPHOTOMETER Practical Handout 2nd Year MBBSDocument7 pagesSPECTROPHOTOMETER Practical Handout 2nd Year MBBSIMDCBiochem100% (1)
- Optical-Methods Part1Document7 pagesOptical-Methods Part1Sumedha ThakurNo ratings yet
- Revised Preliminary Introduction of SpectrosDocument29 pagesRevised Preliminary Introduction of SpectrosRevathiNo ratings yet
- Lab1 SpectrophotometryDocument25 pagesLab1 SpectrophotometrynqwrgnbzhqNo ratings yet
- Blessing AssignmentDocument8 pagesBlessing AssignmentSuleiman IshaqNo ratings yet
- CYN-008 SpectrosDocument56 pagesCYN-008 SpectrosharshNo ratings yet
- Visible and Ultraviolet SpectrophotometryDocument41 pagesVisible and Ultraviolet SpectrophotometryalaahamadeinNo ratings yet
- Application of Molecular Absorption SpectrosDocument52 pagesApplication of Molecular Absorption SpectrosVeliana Teta100% (1)
- Use of Isosbestic Points For Determination of Quantum Efficiency in Transient AbsorptionDocument7 pagesUse of Isosbestic Points For Determination of Quantum Efficiency in Transient AbsorptionalkimiaNo ratings yet
- (Pre-Lab) Experiment 11 - Spectrophotometric AnalysisDocument23 pages(Pre-Lab) Experiment 11 - Spectrophotometric AnalysisPATRICIA ANJELIKA ANGELESNo ratings yet
- Sample Laboratory Report - Fluorescence ActivityDocument29 pagesSample Laboratory Report - Fluorescence ActivityJames Walter Hibanada TapicNo ratings yet
- Lecture Note 16 - Electronic SpectrosDocument24 pagesLecture Note 16 - Electronic SpectrosTbsbi P.No ratings yet
- Spectrophotometric Analysis DiscussionDocument68 pagesSpectrophotometric Analysis DiscussionAldrin GeraldezNo ratings yet
- CHM 161 Spectrophotometry: Analysis of Iron (II) in An Aqueous SolutionDocument10 pagesCHM 161 Spectrophotometry: Analysis of Iron (II) in An Aqueous SolutionBowie ChongNo ratings yet
- Qleous Blumei Fadrigon - Beer Lambert LawDocument2 pagesQleous Blumei Fadrigon - Beer Lambert LawJersey Ann Reign A. GabinNo ratings yet
- All Spectro-1Document53 pagesAll Spectro-1Aliaa SalahNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Spectroscopy & Molecular Spectroscopy: Analytical Chemistry LectureDocument39 pagesAn Introduction To Spectroscopy & Molecular Spectroscopy: Analytical Chemistry Lecture陳庠廷No ratings yet
- Insmeth Lecture 2.2Document45 pagesInsmeth Lecture 2.2nofacejackNo ratings yet
- Clinical Laboratory MeasurementsDocument36 pagesClinical Laboratory MeasurementsPrasidha PrabhuNo ratings yet
- #2 Instrumental PDFDocument37 pages#2 Instrumental PDFMahmoud RedaNo ratings yet
- 16527Document22 pages16527Jaikrishna SukumarNo ratings yet
- Instrumental Methods of AnalysisDocument10 pagesInstrumental Methods of AnalysisChemistry BNMITNo ratings yet
- Comparative Photocatalytic Studies of Degradation of A Cationic and An Anionic DyeDocument4 pagesComparative Photocatalytic Studies of Degradation of A Cationic and An Anionic DyetarikulNo ratings yet
- Fourth International Conference on Non-Aqueous Solutions: Vienna 1974From EverandFourth International Conference on Non-Aqueous Solutions: Vienna 1974V. GutmannNo ratings yet
- 25th International Congress of Pure and Applied Chemistry: Plenary Lectures Presented at the 25th International Congress of Pure and Applied Chemistry, Jerusalem, Israel 6–11 July 1975From Everand25th International Congress of Pure and Applied Chemistry: Plenary Lectures Presented at the 25th International Congress of Pure and Applied Chemistry, Jerusalem, Israel 6–11 July 1975Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Macromolecular Microsymposium — 16: Main Lectures Presented at the Sixteenth Microsymposium on Macromolecules (Advances in Scattering Methods), Prague, 12 - 16 July 1976From EverandMacromolecular Microsymposium — 16: Main Lectures Presented at the Sixteenth Microsymposium on Macromolecules (Advances in Scattering Methods), Prague, 12 - 16 July 1976B. SedláčekNo ratings yet
- Rearrangement InequalityDocument3 pagesRearrangement Inequalitypontas970% (1)
- Solution To Problem Set 4 Question No. 2 (I) : ProgramDocument1 pageSolution To Problem Set 4 Question No. 2 (I) : Programpontas97No ratings yet
- Solution To Problem Set 4 Question No. 1 (I) : ProgramDocument2 pagesSolution To Problem Set 4 Question No. 1 (I) : Programpontas97No ratings yet
- MSC BtechDocument4 pagesMSC Btechpontas97No ratings yet
- Name: Soumya Mukherjee Course: B.Sc. Statistics (Honours) Semester: 2 ROLL NO.: 449 Topic: Assignment For Foundation CourseDocument1 pageName: Soumya Mukherjee Course: B.Sc. Statistics (Honours) Semester: 2 ROLL NO.: 449 Topic: Assignment For Foundation Coursepontas97No ratings yet
- Solution To Question No.7: ProgramDocument1 pageSolution To Question No.7: Programpontas97No ratings yet
- Solution To Problem Set 4 Question No. 1 (Ii) : ProgramDocument2 pagesSolution To Problem Set 4 Question No. 1 (Ii) : Programpontas97No ratings yet
- Solution To Problem Set 4 Question No. 2 (I) : ProgramDocument1 pageSolution To Problem Set 4 Question No. 2 (I) : Programpontas97No ratings yet
- Solution To Problem Set 5 Question No. 1 (A) : ProgramDocument2 pagesSolution To Problem Set 5 Question No. 1 (A) : Programpontas97No ratings yet
- Probability Theory 1-An OutlineDocument1 pageProbability Theory 1-An Outlinepontas97No ratings yet
- Solution To Question No.3: ProgramDocument1 pageSolution To Question No.3: Programpontas97No ratings yet
- Solution To Question No.6: ProgramDocument1 pageSolution To Question No.6: Programpontas97No ratings yet
- Solution To Question No.8: ProgramDocument1 pageSolution To Question No.8: Programpontas97No ratings yet
- Solution To Question No.4: ProgramDocument1 pageSolution To Question No.4: Programpontas97No ratings yet
- Solution To Problem Set 2 Question No.2: ProgramDocument1 pageSolution To Problem Set 2 Question No.2: Programpontas97No ratings yet
- Solution To Problem Set 1 Question No.7: ProgramDocument1 pageSolution To Problem Set 1 Question No.7: Programpontas97No ratings yet
- Solution To Problem Set 1 Question No.8: ProgramDocument1 pageSolution To Problem Set 1 Question No.8: Programpontas97No ratings yet
- Solution To Problem Set 1 Question No.6: ProgramDocument1 pageSolution To Problem Set 1 Question No.6: Programpontas97No ratings yet
- Name: Soumya Mukherjee Course: B.Sc. Statistics (Honours) Semester: 1 ROLL NO.: 449 Topic: Assignment For Foundation CourseDocument6 pagesName: Soumya Mukherjee Course: B.Sc. Statistics (Honours) Semester: 1 ROLL NO.: 449 Topic: Assignment For Foundation Coursepontas97No ratings yet
- Name: Soumya Mukherjee Semester: I ROLL NO.: 449 Subject: C Programming (Problem Sets 1 and 2)Document1 pageName: Soumya Mukherjee Semester: I ROLL NO.: 449 Subject: C Programming (Problem Sets 1 and 2)pontas97No ratings yet
- Students' Activity:2015-16: Co-Curricular Activities of The StudentsDocument3 pagesStudents' Activity:2015-16: Co-Curricular Activities of The Studentspontas97No ratings yet
- St. Xavier'S College: (Autonomous)Document2 pagesSt. Xavier'S College: (Autonomous)pontas97No ratings yet