Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1 Reduction Oxidation Terminology Getting It Straight
1 Reduction Oxidation Terminology Getting It Straight
Uploaded by
api-2225036600 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
48 views2 pagesThe document defines oxidation and reduction terminology. Oxidation is defined as the loss of electrons or gain of oxygen, while reduction is defined as the gain of electrons or loss of oxygen. Reducing agents donate electrons and are oxidized, while oxidizing agents accept electrons and are reduced. An example reaction provided is the oxidation of magnesium and reduction of hydrogen ions.
Original Description:
Original Title
1 reduction oxidation terminology getting it straight
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document defines oxidation and reduction terminology. Oxidation is defined as the loss of electrons or gain of oxygen, while reduction is defined as the gain of electrons or loss of oxygen. Reducing agents donate electrons and are oxidized, while oxidizing agents accept electrons and are reduced. An example reaction provided is the oxidation of magnesium and reduction of hydrogen ions.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
48 views2 pages1 Reduction Oxidation Terminology Getting It Straight
1 Reduction Oxidation Terminology Getting It Straight
Uploaded by
api-222503660The document defines oxidation and reduction terminology. Oxidation is defined as the loss of electrons or gain of oxygen, while reduction is defined as the gain of electrons or loss of oxygen. Reducing agents donate electrons and are oxidized, while oxidizing agents accept electrons and are reduced. An example reaction provided is the oxidation of magnesium and reduction of hydrogen ions.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
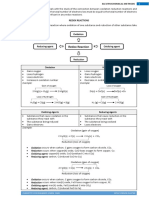
Oxidation and Reduction Terminology
Summary
Observational evidence
Chemical explanations
Terminology
Oxidation
Gain of oxygen
Loss of H
Reduction
Loss of oxygen
Gain of H
Loss of electrons
Increase in oxidation
number.
Gain of electrons
Decrease in oxidation
number.
Reducing agents are
oxidized Reducing
agents lose electrons.
Reducing agents are
reductants.
Oxidizing agents are
reduced Oxidising
agents gain electrons.
Oxidizing agents are
oxidants.
Example
Mg(s)
+ 2H+(aq)
Mg(s) loses electrons to form Mg2+(aq)
Mg2+(aq) + H2 (g)
H+(aq) gains electrons to form H2 (g)
Mg(s) is oxidized to Mg2+(aq)
H+(aq) is reduced to H2 (g)
Mg(s) is the reducing agent
H+(aq) is the oxidizing agent
Mg(s) is the reductant
H+(aq) is the oxidant
Examples of redox reactions (electron transfer)
Metal + acid
Metal Displacement reaction in solution
Electrochemical Cells (batteries)
Electrolysis
Oxidation of Metals to metal
oxides (corrosion)
Combustion of organic compounds
Reduction of Metal ores (metal oxides)
to metals
Ammonium dichromate reaction
Ammonium dichromate
(NH4)2Cr2O7(s) Cr2O3(s) + N2(g) + 4H2O (g)
Orange
to
green
ammonium chromate cromium oxide + nitrogen gas + water vapour
You might also like
- Redox ReactionDocument21 pagesRedox ReactionJenny WeeNo ratings yet
- Oxidation ReductionDocument47 pagesOxidation ReductionAbdulraqeb AlawadhiNo ratings yet
- Redox TitrationDocument23 pagesRedox TitrationSapna PandeyNo ratings yet
- Redox Titration KDBDocument45 pagesRedox Titration KDBKiranNo ratings yet
- Class 11 - Chapter 08 - Redox Reaction NotesDocument14 pagesClass 11 - Chapter 08 - Redox Reaction NotesaasifNo ratings yet
- CHE 156a REDOX ReactionsDocument62 pagesCHE 156a REDOX ReactionsJosephNo ratings yet
- SPM Chemistry Form 5 - Terminology and Concepts: Oxidation and Reduction (Part 1)Document18 pagesSPM Chemistry Form 5 - Terminology and Concepts: Oxidation and Reduction (Part 1)Aidah Amir100% (2)
- 11.4A Redox Reaction and ElectrochemistryDocument98 pages11.4A Redox Reaction and ElectrochemistryЕлнур ИкимбаевNo ratings yet
- Redox ReactionsDocument80 pagesRedox ReactionsShashwatNo ratings yet
- SPM Chemistry Form 5 - Terminology and Concepts: Oxidation and Reduction (Part 1)Document22 pagesSPM Chemistry Form 5 - Terminology and Concepts: Oxidation and Reduction (Part 1)Ck OoiNo ratings yet
- Chap 5Document11 pagesChap 5Tun Lin AungNo ratings yet
- Tindakbalas Redok: Pengoksidaan Dan PenurunanDocument18 pagesTindakbalas Redok: Pengoksidaan Dan PenurunanNURUL ASYIKINNo ratings yet
- Redox Application FinalDocument65 pagesRedox Application FinalHemanth HegdeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20 Oxidation-Reduction ReactionsDocument43 pagesChapter 20 Oxidation-Reduction ReactionsTegar MaulanaNo ratings yet
- Using Oxidation States To Describe Redox Changes in A Given Reaction EquationDocument22 pagesUsing Oxidation States To Describe Redox Changes in A Given Reaction EquationkushanNo ratings yet
- Contents:: Oxidation and Reduction Oxidizing and Reducing Agent Process of OxidationDocument12 pagesContents:: Oxidation and Reduction Oxidizing and Reducing Agent Process of OxidationMUHAMMAD NABEEL ARIFNo ratings yet
- Redox ReactionsDocument27 pagesRedox ReactionsRakesh SNo ratings yet
- Unit 7Document3 pagesUnit 7api-282526559No ratings yet
- Unit 5 - Part 2: Redox Reactions and ElectrochemistryDocument37 pagesUnit 5 - Part 2: Redox Reactions and ElectrochemistryBibha KumariNo ratings yet
- Class XI Chemistry Unit-8 Redox Reactions: TopicDocument60 pagesClass XI Chemistry Unit-8 Redox Reactions: TopicBaljit Singh100% (1)
- Redoxmain REDOXDocument47 pagesRedoxmain REDOXabdirizak Haji MohammedNo ratings yet
- REDOX REACTIONS NOTES-Unit 8Document13 pagesREDOX REACTIONS NOTES-Unit 8muralidharhegdenorthsquareNo ratings yet
- Combination ReactionsDocument7 pagesCombination Reactionstaurus_nikita4484No ratings yet
- MetalsDocument56 pagesMetalsTariq MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Acid and MetalDocument2 pagesAcid and MetalMariaNo ratings yet
- Redox Reaction Shobhit NirwanDocument22 pagesRedox Reaction Shobhit NirwanBhavya Goyal XI Non med100% (7)
- Ch5 Redox Reaction Shobhit NirwanDocument22 pagesCh5 Redox Reaction Shobhit NirwanPROFESSOR0% (1)
- 1 Electrochemical MethodsDocument17 pages1 Electrochemical MethodsJames BombitaNo ratings yet
- Redox Chemistry Unit 2Document51 pagesRedox Chemistry Unit 2Nicola NguyenNo ratings yet
- Reactivity Series of Metals: Reactions of Metals Effect of Heat On Metal CarbonatesDocument24 pagesReactivity Series of Metals: Reactions of Metals Effect of Heat On Metal CarbonatesCarl Agape DavisNo ratings yet
- Modul Kimia Ting 5 Bab 12Document9 pagesModul Kimia Ting 5 Bab 12Chew Gee LanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Oxidation and ReductionDocument0 pagesIntroduction To Oxidation and ReductionAdnan ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document25 pagesChapter 7FaithNo ratings yet
- C12 Notes S RedoxDocument40 pagesC12 Notes S RedoxSiva GuruNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis. Olevel ChemistryDocument53 pagesElectrolysis. Olevel ChemistrySaraYasinNo ratings yet
- Extraction (提煉) of Metal s from Metal Ores (礦石)Document53 pagesExtraction (提煉) of Metal s from Metal Ores (礦石)manish932No ratings yet
- Oxidizing and Reducing AgentsDocument2 pagesOxidizing and Reducing AgentsKenneth D. LigutomNo ratings yet
- CHEMICAL REACTIONS AND EQUATIONS Notes 1710928665Document11 pagesCHEMICAL REACTIONS AND EQUATIONS Notes 1710928665Chinmayi mamathaNo ratings yet
- Unit 15: Redox: RED Reduction OX OxidationDocument18 pagesUnit 15: Redox: RED Reduction OX Oxidationoliver abramsNo ratings yet
- Unit 12 Redox Reactions NotesDocument20 pagesUnit 12 Redox Reactions Notesedna padreNo ratings yet
- RedoxDocument2 pagesRedoxtmoatshe96No ratings yet
- Oxidation and ReductionDocument28 pagesOxidation and ReductionCharlene LowNo ratings yet
- What Are Redox Reactions?: Chemical ReactionDocument8 pagesWhat Are Redox Reactions?: Chemical ReactionReal RuchitNo ratings yet
- Curian Science Tutors Chem NotesDocument6 pagesCurian Science Tutors Chem NotesMunashe BinhaNo ratings yet
- Redox Reaction - Chemical Reactions in Which Both Oxidation and Reduction Occur SimultaneouslyDocument17 pagesRedox Reaction - Chemical Reactions in Which Both Oxidation and Reduction Occur SimultaneouslyJoanne SiaNo ratings yet
- Oxidation NumberDocument7 pagesOxidation NumberNor Faizahbaizura Abu BakarNo ratings yet
- Review Lesson:: Redox ReactionsDocument36 pagesReview Lesson:: Redox ReactionsHnut hinorNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6.1 Redox and ElectrolysisDocument15 pagesChapter 6.1 Redox and ElectrolysisdawsontangxyNo ratings yet
- Types of ReactionDocument7 pagesTypes of ReactionAdeola OmoniyiNo ratings yet
- Redox ReactionsDocument2 pagesRedox Reactionschong56No ratings yet
- Redox Reactions NotesDocument13 pagesRedox Reactions NotesmoiiifitbituserNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - CHEM Notes: Chemistry (Higher School Certificate (New South Wales) )Document7 pagesModule 3 - CHEM Notes: Chemistry (Higher School Certificate (New South Wales) )norbetNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry 2024Document62 pagesElectrochemistry 2024shellodkomaNo ratings yet
- 01-Basics of CorrosionDocument31 pages01-Basics of Corrosion이선엽No ratings yet
- OXIDATION AND REDUCTION REACTIONS (Autosaved)Document15 pagesOXIDATION AND REDUCTION REACTIONS (Autosaved)TeandraNo ratings yet
- Explanation Text: By: Dwiyanti Octaviani Farrah Nabila F Malik Farhan Nazhara Ardhan Roikhan Azhari Syifa FauziahDocument28 pagesExplanation Text: By: Dwiyanti Octaviani Farrah Nabila F Malik Farhan Nazhara Ardhan Roikhan Azhari Syifa Fauziahsyifa fauziahNo ratings yet
- Chemical ReactionDocument27 pagesChemical ReactionMary Rose JasminNo ratings yet
- 9th Class ElectrochemistryDocument18 pages9th Class ElectrochemistryCh NajamNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersNo ratings yet
- Carbon Cycle Facilitates Energy FlowDocument2 pagesCarbon Cycle Facilitates Energy Flowapi-222503660No ratings yet
- 2018 01 Organic Chemistry Introductory AnalysisDocument1 page2018 01 Organic Chemistry Introductory Analysisapi-222503660No ratings yet
- Investigation Design TemplateDocument4 pagesInvestigation Design Templateapi-222503660No ratings yet
- 2018 Task 3Document1 page2018 Task 3api-222503660No ratings yet
- 2018 Assess Task 2 Writing Ecosystem TaskbriefDocument2 pages2018 Assess Task 2 Writing Ecosystem Taskbriefapi-222503660No ratings yet
- 2018 01 Labskills Solution TransferDocument2 pages2018 01 Labskills Solution Transferapi-222503660No ratings yet
- 2018 Assess Task 2 Ecosystem FieldnotesDocument4 pages2018 Assess Task 2 Ecosystem Fieldnotesapi-222503660No ratings yet
- Nitrogencyclebuilds ProteinsDocument3 pagesNitrogencyclebuilds Proteinsapi-222503660No ratings yet
- 2017 Assessmenttask12 Designchemicalreactiondemonstration Taskbrief NoimagesDocument2 pages2017 Assessmenttask12 Designchemicalreactiondemonstration Taskbrief Noimagesapi-222503660No ratings yet
- Dear Wa Science TeachersDocument1 pageDear Wa Science Teachersapi-222503660No ratings yet
- 2018 Integratedscience Program Semester 1 Y11 2017Document10 pages2018 Integratedscience Program Semester 1 Y11 2017api-222503660No ratings yet
- 2017 Integratedscience Physics Program Y11 2017 Sem2Document1 page2017 Integratedscience Physics Program Y11 2017 Sem2api-222503660No ratings yet
- Task 16 Planetarty Pasta Rover Build and TestDocument2 pagesTask 16 Planetarty Pasta Rover Build and Testapi-222503660No ratings yet
- 2017 Assessmenttask2 Design Portable Worm Farm TaskbriefcompleteDocument6 pages2017 Assessmenttask2 Design Portable Worm Farm Taskbriefcompleteapi-222503660No ratings yet
- Task 15 Planetary RoversDocument2 pagesTask 15 Planetary Roversapi-222503660No ratings yet
- Tripling or Tritosing The TablesDocument3 pagesTripling or Tritosing The Tablesapi-222503660No ratings yet
- Integrated-Science-Y11-Syllabus-General-2016editedfor Litaeracy FocusDocument3 pagesIntegrated-Science-Y11-Syllabus-General-2016editedfor Litaeracy Focusapi-222503660No ratings yet
- 2017-03-22 JC Stemskills Full Stem Ahead-ShortenedDocument18 pages2017-03-22 JC Stemskills Full Stem Ahead-Shortenedapi-222503660No ratings yet
- 2017 Assessmenttask3and4 Designcellorganelle TaskbriefDocument5 pages2017 Assessmenttask3and4 Designcellorganelle Taskbriefapi-222503660No ratings yet
- 2017 Assessmenttask3and4 Designcellorganelle TaskbriefDocument5 pages2017 Assessmenttask3and4 Designcellorganelle Taskbriefapi-222503660No ratings yet
- 01 CellstructurefunctionDocument18 pages01 Cellstructurefunctionapi-222503660No ratings yet
- 2017 Stem Assessmenttask Design A Portable Worm Farm Taskbrief RelevantsyllabusstatementsDocument1 page2017 Stem Assessmenttask Design A Portable Worm Farm Taskbrief Relevantsyllabusstatementsapi-222503660No ratings yet