Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Redox
Uploaded by
tmoatshe96Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Redox
Uploaded by
tmoatshe96Copyright:
Available Formats
REDOX REACTIONS
This is derived from the two processes oxidation and reduction. A chemical reaction involves both
oxidation and reduction which means no oxidation occurs without reduction. Many processes are
redox. This can be explained in terms of oxygen, hydrogen, electrons and oxidation numbers.
In terms of oxygen:
When a substance combines with oxygen it is said to be oxidized: Oxidation is gain of oxygen
When a substance loses oxygen it is said to be reduced: Reduction is loss of oxygen
Gain of oxygen (oxidation)
Example: CuO + H2 Cu + H2O
Loss of oxygen (reduction)
Redox reactions can also be explained in terms of hydrogen (oxidation is loss of hydrogen while reduction is
gain of hydrogen).
Not all chemical reactions involve reactions with hydrogen or oxygen therefore the above definitions do not
cater for the majority of the reactions. To cater for such reactions they are explained in terms electron transfer.
In terms of electron transfer:
When a substance loses electrons it is oxidized (oxidation is loss of electrons)
When a substance gains electrons it is reduced (reduction is gain of electrons)
Loses 2 electrons (oxidation)
Mg + Cl2 MgCl2
Gains 1 electron
Mg is a metal and it reacts by losing 2 electrons (it is oxidized) to Mg2+ while the non metal Cl gains an electron
(it is reduced) to Cl
Redox reactions are easily shown by the use of half equations which show ionic equations for both oxidation
and reduction.
Mg Mg2+ + 2e- or Mg – 2e- Mg2+
The equations show loss of electrons (oxidation)
Cl2 + 2 e- 2Cl This shows gain of electrons (reduction)
In terms of Oxidation states
During electron transfer changes in oxidation states occur. Oxidation state is a number given to show whether
an element has been oxidized or reduced. The oxidation state of an ion is the charge on the ion. In a covalent
compound it indicates the attraction that atom has for electrons in the bonds.
Oxidation is an increase in the oxidation number
Reduction is a decrease in the oxidation number
Mg + 2HCl MgCl2 + H2
Mg + 2H+ Cl- Mg2+ Cl- + H2
Cl- is a spectator because its oxidation number remains the same during the reaction
Mg Mg2+ + 2e
The oxidation number of Mg changed from 0 to 2+ therefore Mg has been oxidized.
2H+ + 2e H2
The oxidation number of H has decreased from +1 to 0, hence reduction
Exercise
Explain why the following reactions are Redox reactions
(i) CuO + H2 Cu + H2O
(ii) Pb(NO3)2 + Zn Zn ( NO3)2 + Pb
(iii) Zn + CuO ZnO + Cu
(iv) Mn + H2O MnO + H2
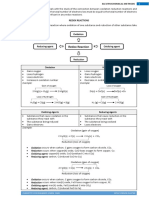
Oxidizing and Reducing agents
During redox reactions reduction is brought by a reducing agent and oxidation by an oxidizing agent. A
substance that is oxidized is the reducing agent while the reduced one is the oxidizing agent.
An oxidizing agent is a substance which;
(i) Donates oxygen to another substance
(ii) Gains electrons from another
A reducing agent is a substance which;
(i) Gains oxygen
(ii) Loses electrons
Exercise
Identify the oxidizing agent from the reactions below;
(i) 4Na + O2 2Na2O
(ii) Cu + 2AgNO3 2Ag + Cu(NO3)
(iii) 2KBr + Cl2 2KCl + Br2
(iv) Cu + 4HNO3 Cu(NO3)2 + H2O + NO2
Identify the reducing agent from the reactions below;
(i) H2 + CuO Cu + H2O
(ii) Mg + H2SO4 MgSO4 + H2
(iii) 2KI + Cl2 2KCl + I2
Examples of oxidizing and reducing agents
Oxidizing agents: conc nitric acid, conc sulphuric acid, non metals, manganese (IV) oxide, acidified potassium
manganate (vii), acidified potassium dichromate (vi), hydrogen peroxide, oxygen
Reducing agents: carbon, carbon monoxide, hydrogen, sulphur dioxide, potassium iodide, iron (ii) compound,
hydrogen sulphide.
Test for oxidizing and reducing agents
Oxidizing agents: use a reducing agent like potassium iodide which will change colour from colourless to brown
due to the production of iodine.
2I- (aq) →I2 + 2e-
This can be confirmed by using starch indicator which turns blue black
Reducing agents: Use potassium dichromate (vi) which changes colour from orange to green and potassium
manganate (vii) which changes colour from purple to colourless.
MnO4- + 8H+ +5e Mn2+ + 4H2O
7+
(purple)(Mn ) (colourless)
Fe2+ Fe3+ + e-
(green) (red brown)
Cr2O72- + 14H+ + 6e- 2Cr3+ + 7H2O
6+
(orange)(Cr ) (green)
When conc sulphuric acid acts as an oxidizing agent, sulphur dioxide is always produced.
Cu + H2SO4 (l) CuSO4 + SO2 + 2H2O
You might also like
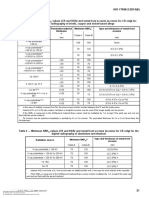
- ISO 17636-2 - 2013 Part 2 X - and Gamma-Ray Technical - Table3 & 4Document1 pageISO 17636-2 - 2013 Part 2 X - and Gamma-Ray Technical - Table3 & 4Sơn Nguyễn TháiNo ratings yet
- Oxford AQA Chemistry Paper 1 May 2023Document26 pagesOxford AQA Chemistry Paper 1 May 2023Wasiq Nabeel100% (1)
- Redox Reactions ExplainedDocument40 pagesRedox Reactions ExplainedMohamad HanifNo ratings yet
- Oxidation NumberDocument7 pagesOxidation NumberNor Faizahbaizura Abu BakarNo ratings yet
- SPM Chemistry Form 5 - Terminology and Concepts: Oxidation and Reduction (Part 1)Document18 pagesSPM Chemistry Form 5 - Terminology and Concepts: Oxidation and Reduction (Part 1)Aidah Amir100% (2)
- 9.1.1 Introduction To Oxidation and ReductionDocument23 pages9.1.1 Introduction To Oxidation and ReductionAlvin LowNo ratings yet
- Average Atomic Mass and Percent Abundance Worksheet 2 and KEYDocument2 pagesAverage Atomic Mass and Percent Abundance Worksheet 2 and KEYMaxine Taeyeon50% (4)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersNo ratings yet
- Oxidation ReductionDocument47 pagesOxidation ReductionAbdulraqeb AlawadhiNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Oxidation ReductionDocument7 pagesOxidation ReductionZul Abror Bin Ya'akopNo ratings yet
- 11.4A Redox Reaction and ElectrochemistryDocument98 pages11.4A Redox Reaction and ElectrochemistryЕлнур ИкимбаевNo ratings yet
- REDOXDocument67 pagesREDOXLeo PietroNo ratings yet
- Redox TitrationDocument23 pagesRedox TitrationSapna PandeyNo ratings yet
- Oxidation and ReductionDocument39 pagesOxidation and ReductionlisalisoNo ratings yet
- C12 Notes S RedoxDocument40 pagesC12 Notes S RedoxSiva GuruNo ratings yet
- REDOX REACTIONS: OXIDATION AND REDUCTIONDocument92 pagesREDOX REACTIONS: OXIDATION AND REDUCTIONMollel TajiriNo ratings yet
- Formats of Directed WritingDocument6 pagesFormats of Directed WritingaaleenNo ratings yet
- Stp944-Eb 1420Document146 pagesStp944-Eb 1420delta lab sangli100% (1)
- 5 6116152494587379984Document98 pages5 6116152494587379984dharwinNo ratings yet
- SPM Chemistry Form 5 – Oxidation and ReductionDocument22 pagesSPM Chemistry Form 5 – Oxidation and ReductionCk OoiNo ratings yet
- Redox Reactions ExplainedDocument17 pagesRedox Reactions ExplainedJoanne SiaNo ratings yet
- Subject: Chemistry Chapter-08: Redox Reactions Questions Carrying One MarkDocument18 pagesSubject: Chemistry Chapter-08: Redox Reactions Questions Carrying One MarkKavan KaverappaNo ratings yet
- Redox ReactionsDocument2 pagesRedox Reactionschong56No ratings yet
- Redox ReactionsDocument27 pagesRedox ReactionsRakesh SNo ratings yet
- Redox Reaction EDocument65 pagesRedox Reaction EKrishna RNo ratings yet
- Chap 5Document11 pagesChap 5Tun Lin AungNo ratings yet
- Redox Reactions - Lecture NotesDocument39 pagesRedox Reactions - Lecture NotespokeyballNo ratings yet
- Redox Reaction Shobhit NirwanDocument22 pagesRedox Reaction Shobhit NirwanBhavya Goyal XI Non med100% (7)
- Redox Reactions Notes for Class 11Document22 pagesRedox Reactions Notes for Class 11PROFESSOR0% (1)
- Modul Kimia Ting 5 Bab 12Document9 pagesModul Kimia Ting 5 Bab 12Chew Gee LanNo ratings yet
- 4.4 ElectrochemistryDocument20 pages4.4 Electrochemistrygabrielsiema4No ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Redox Reactions SummaryDocument42 pagesChapter 11 Redox Reactions SummaryKris DookharanNo ratings yet
- Unit 7Document3 pagesUnit 7api-282526559No ratings yet
- Redox Reactions ExplainedDocument7 pagesRedox Reactions ExplainedShaikh IradNo ratings yet
- 8oxidation Reduction ReactionsDocument50 pages8oxidation Reduction ReactionsMohamed AlQallafNo ratings yet
- RedoxDocument14 pagesRedoxsaraNo ratings yet
- Rules of Redox ReactionsDocument9 pagesRules of Redox ReactionsHamad FarooqueNo ratings yet
- Redox Titration KDBDocument45 pagesRedox Titration KDBKiranNo ratings yet
- 9.1.1 Introduction To Oxidation and ReductionDocument24 pages9.1.1 Introduction To Oxidation and ReductionPatrick AbidraNo ratings yet
- Yr 10 Chem Summer NoteDocument22 pagesYr 10 Chem Summer NoteTokoni DanielNo ratings yet
- Std.8 Module.7 Semester.2Document56 pagesStd.8 Module.7 Semester.2Md ZayedNo ratings yet
- Introductory Chemistry - SCH0201 - Lec10Document26 pagesIntroductory Chemistry - SCH0201 - Lec10Ayanthi ShashikalaNo ratings yet
- Unit 15: Redox: RED Reduction OX OxidationDocument18 pagesUnit 15: Redox: RED Reduction OX Oxidationoliver abramsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 - Redox ReactionsDocument3 pagesChapter 13 - Redox ReactionsAnosha AminNo ratings yet
- Redox ReactionsDocument4 pagesRedox Reactionsmahika gaurNo ratings yet
- Redox Reactions ExplainedDocument80 pagesRedox Reactions ExplainedShashwatNo ratings yet
- Redox Reactions: Heshani MudaligeDocument35 pagesRedox Reactions: Heshani MudaligeMary Ranjila Hordagoda FernandoNo ratings yet
- 04 Activity 1Document3 pages04 Activity 1Deocades DexinNo ratings yet
- Redox Reactions: Earning UtcomesDocument44 pagesRedox Reactions: Earning UtcomesSamoiya WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Redox Reactions (Theory) EditedDocument21 pagesRedox Reactions (Theory) EditedProfSumit LuthraNo ratings yet
- Redox Reactions ExplainedDocument5 pagesRedox Reactions ExplainedTunde DabiriNo ratings yet
- CLASS X CHEMISTRY Solution-985613Document7 pagesCLASS X CHEMISTRY Solution-985613abiniveshofficial4708No ratings yet
- Electrochemistry 2024Document62 pagesElectrochemistry 2024shellodkomaNo ratings yet
- OXIDATION AND REDUCTION REACTIONS (Autosaved)Document15 pagesOXIDATION AND REDUCTION REACTIONS (Autosaved)TeandraNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - Ch-1 NotesDocument5 pagesChemistry - Ch-1 NoteskomalNo ratings yet
- Oxidation ReductionDocument7 pagesOxidation ReductionWalu BNNo ratings yet
- Stoichiometry calculations and chemical reactionsDocument4 pagesStoichiometry calculations and chemical reactionsLei YinNo ratings yet
- CLASS X CHEMISTRY Solution-988010Document4 pagesCLASS X CHEMISTRY Solution-988010abiniveshofficial4708No ratings yet
- Redox Reactions and Oxidation NumbersDocument47 pagesRedox Reactions and Oxidation Numbersabdirizak Haji MohammedNo ratings yet
- Oxidation and ReductionDocument4 pagesOxidation and ReductionInnocent EbilNo ratings yet
- Redox (REDOX) Reactions ExplainedDocument50 pagesRedox (REDOX) Reactions ExplainedElvis NgandweNo ratings yet
- Oxidation n ElectrochemistryDocument57 pagesOxidation n ElectrochemistryolamidelatubosunNo ratings yet
- 1 Electrochemical MethodsDocument17 pages1 Electrochemical MethodsJames BombitaNo ratings yet
- Chem F5 Chapter 3 (2020)Document39 pagesChem F5 Chapter 3 (2020)JΞτΗασ0% (1)
- Moral Cover PageDocument1 pageMoral Cover Pagetmoatshe96No ratings yet
- Social StudiesDocument4 pagesSocial Studiestmoatshe96No ratings yet
- Igcse Geo Cover 1 SkyDocument2 pagesIgcse Geo Cover 1 Skytmoatshe96No ratings yet
- Business Idea AffidavitDocument1 pageBusiness Idea Affidavittmoatshe96No ratings yet
- Botswana General Certificate OF Secondary Education: Teaching SyllabusDocument26 pagesBotswana General Certificate OF Secondary Education: Teaching SyllabusMpaphiNo ratings yet
- Ep Jco p1 2015 SampleDocument20 pagesEp Jco p1 2015 Sampletmoatshe96No ratings yet
- Block 3Document80 pagesBlock 3tmoatshe96No ratings yet
- Physical Ed FinalDocument18 pagesPhysical Ed Finaltmoatshe96No ratings yet
- Existing Company Shareholders ConsentDocument2 pagesExisting Company Shareholders Consenttmoatshe96No ratings yet
- Religious Education: Botswana General Certificate of Secondary Education Teaching SyllabusDocument21 pagesReligious Education: Botswana General Certificate of Secondary Education Teaching Syllabustmoatshe96No ratings yet
- Organs Concerned Factors Controlled: EpidermisDocument4 pagesOrgans Concerned Factors Controlled: EpidermisKekeletsoNo ratings yet
- Form 2 Revision WorksheetDocument147 pagesForm 2 Revision Worksheettmoatshe96No ratings yet
- Geo Quiz ReviewDocument3 pagesGeo Quiz Reviewtmoatshe96No ratings yet
- WAREHOUSING + AdvertisingDocument2 pagesWAREHOUSING + Advertisingtmoatshe96No ratings yet
- Timetable 2024Document1 pageTimetable 2024tmoatshe96No ratings yet
- DescriptiveWriting 000Document2 pagesDescriptiveWriting 000Chaitanya RkNo ratings yet
- Animal Nutrition Sda EditedDocument12 pagesAnimal Nutrition Sda Editedtmoatshe96No ratings yet
- PHY - NOTES PDFDocument264 pagesPHY - NOTES PDFThutoNo ratings yet
- Mega Lecture: Wave Speed Frequency X WavelengthDocument1 pageMega Lecture: Wave Speed Frequency X WavelengthShaade91No ratings yet
- Notes On Measurements1Document9 pagesNotes On Measurements1tmoatshe96No ratings yet
- Nutrition AnimalDocument10 pagesNutrition Animaltmoatshe96No ratings yet
- Agric Quiz Up To Soil FertilityDocument3 pagesAgric Quiz Up To Soil Fertilitytmoatshe96No ratings yet
- Sample Formal Letter 1Document2 pagesSample Formal Letter 1tmoatshe96No ratings yet
- Transport in AnimalsDocument7 pagesTransport in Animalstmoatshe96No ratings yet
- Electrolysis Notes For SdaDocument13 pagesElectrolysis Notes For Sdatmoatshe96No ratings yet
- GP1 Physical Quantities & MeasurementDocument7 pagesGP1 Physical Quantities & MeasurementMamelang MoatsheNo ratings yet
- Chem 2011Document12 pagesChem 2011tmoatshe96No ratings yet
- Hormonal CoordinationDocument2 pagesHormonal Coordinationtmoatshe96No ratings yet
- Alkanes Alkenes Alcohols Cracking and PolymersDocument46 pagesAlkanes Alkenes Alcohols Cracking and Polymerstmoatshe96No ratings yet
- Perhitungan Index Pencemaran Kualitas AirDocument27 pagesPerhitungan Index Pencemaran Kualitas AirFaitur RahmiNo ratings yet
- ALS Geochemistry Fee Schedule 2016 USD PDFDocument42 pagesALS Geochemistry Fee Schedule 2016 USD PDFmario22740% (1)
- New Rich Text DocumentDocument17 pagesNew Rich Text DocumentATUL ARYANNo ratings yet
- Important Questions Class 10 Science Chapter 1Document21 pagesImportant Questions Class 10 Science Chapter 1Darshuram DudheNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry Chapter 11 QuestionsDocument2 pagesIGCSE Chemistry Chapter 11 QuestionsRajeshNo ratings yet
- The Richest Man in BabylonDocument126 pagesThe Richest Man in BabylonMikheil FoniavaNo ratings yet
- KSSM Science Form 3 Notes on Reactivity of Metals and ThermochemistryDocument8 pagesKSSM Science Form 3 Notes on Reactivity of Metals and ThermochemistryRem HentaiNo ratings yet
- ASTM D1126 Durezas en AguaDocument4 pagesASTM D1126 Durezas en AguafamturboNo ratings yet
- Metals MCQ PDFDocument21 pagesMetals MCQ PDFMunshatia Islam MerryNo ratings yet
- Decompisition of Baking Soda: Lab Report - Bruno Moulheres, Michael Branas, Daniel Deleon, Melanie MoronDocument2 pagesDecompisition of Baking Soda: Lab Report - Bruno Moulheres, Michael Branas, Daniel Deleon, Melanie MoronFrosty BR100% (1)
- CHB102 Pracical 1st Year Mohr Salt SatyenSahaDocument5 pagesCHB102 Pracical 1st Year Mohr Salt SatyenSahaPrateek Tyagi100% (2)
- Casting Repairs and Rebuild Procedure Rev.02Document13 pagesCasting Repairs and Rebuild Procedure Rev.02sboergertNo ratings yet
- Naming Oxyanion CompoundsDocument2 pagesNaming Oxyanion CompoundsPatricia TasarraNo ratings yet
- Selling SilverDocument10 pagesSelling Silverapi-455146513No ratings yet
- API SPEC 5CT 10TH 2018 Table C4Document1 pageAPI SPEC 5CT 10TH 2018 Table C4Johanes GigihNo ratings yet
- Asme Sec Ii C Sfa-5.21Document20 pagesAsme Sec Ii C Sfa-5.21Hashim GTNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table JEE Advanced - 10.06.2023Document3 pagesPeriodic Table JEE Advanced - 10.06.2023bishtarjun32No ratings yet
- Link E-Katalog Refill Reagen Sankit Dan Kesling KitDocument3 pagesLink E-Katalog Refill Reagen Sankit Dan Kesling KitWahdi FifiNo ratings yet
- 26 AsiaDocument8 pages26 AsiaRhaiza PabelloNo ratings yet
- 9.1.01 AOAC Official Method 986.15 Arsenic, Cadmium, Lead, Selenium, and Zinc in Human and Pet FoodsDocument3 pages9.1.01 AOAC Official Method 986.15 Arsenic, Cadmium, Lead, Selenium, and Zinc in Human and Pet FoodsNguyễn Khang LuânNo ratings yet
- DPPS-2 P-Block ElementsDocument2 pagesDPPS-2 P-Block ElementsAalokNo ratings yet
- Chem (Soln) CH 8Document27 pagesChem (Soln) CH 8RahulMittalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Chemical Formulas & EquationsDocument10 pagesChapter 3: Chemical Formulas & EquationsSarah WongNo ratings yet
- State of the Art in Steel Mill Dust RecyclingDocument6 pagesState of the Art in Steel Mill Dust RecyclingCeyhun TatarNo ratings yet
- Improving weld test pass rates for stainless to mild steel jointsDocument4 pagesImproving weld test pass rates for stainless to mild steel jointscarlospalacioeNo ratings yet
- Exam-Questions-Pg-169-172 2Document26 pagesExam-Questions-Pg-169-172 2MolemoNo ratings yet