Professional Documents
Culture Documents
LEED Green Building Certification System
Uploaded by
api-27027563Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
LEED Green Building Certification System
Uploaded by
api-27027563Copyright:
Available Formats
LEED Green Building Certification System
What is LEED?
LEED is a third party certification program and the nationally accepted benchmark for the design,
construction and operation of high performance green buildings. Developed by the U.S. Green Building
Council in 2000 through a consensus based process, LEED serves as a tool for buildings of all types and
sizes. LEED certification offers third party validation of a project’s green features and verifies that the
building is operating exactly the way it was designed to.
What types of buildings can use LEED?
LEED certification is available for all building types including new construction and major renovation;
existing buildings; commercial interiors; core and shell; schools and homes. LEED systems for
neighborhood development, retail and healthcare are currently pilot testing. To date, there is over 4.5
billion square feet of construction space involved with the LEED system.
How does LEED work?
LEED is a point based system where building projects earn LEED points for satisfying specific green
building criteria. Within each of the seven LEED credit categories, projects must satisfy particular
prerequisites and earn points.
The five categories include Sustainable Sites (SS), Water Efficiency (WE), Energy and Atmosphere (EA),
Materials and Resources (MR) and Indoor Environmental Quality (IEQ). An additional category,
Innovation in Design (ID), addresses sustainable building expertise as well as design measures not
covered under the five environmental categories. The number of points the project earns determines the
level of LEED Certification the project receives. LEED certification is available in four progressive levels
according to the following scale:
There are 100 base points; 6 possible Innovation in Design and 4 Regional Priority points
Certified 40–49 points
Silver 50–59 points
Gold 60–79 points
Platinum 80 points and above
What are regional credits?
Regional credits are another feature of LEED and acknowledge the importance of local conditions in
determining best environmental design and construction practices. LEED projects will be able to earn
“bonus points” for implementing green building strategies that address the important environmental issues
facing their region. A project can be awarded as many as four extra points, one point each for achieving
up to four of the six priority credits. To download a region-by-region list of priority credits, visit
www.usgbc.org/leedv3.
How are LEED credits weighted?
The allocation of points is based on strategies that will have greater positive impacts on what matters
most – energy efficiency and CO2 reductions. Each credit was evaluated against a list of 13
environmental impact categories, including climate change, indoor environmental quality, resource
depletion and water intake, among many others.
Is LEED training available?
Yes, USGBC offers a variety of LEED instructor-led workshops, online courses and Webinars (live and
on-demand). To learn more about USGBC’s LEED curriculum, visit www.usgbc.org/education.
Can products be certified under LEED?
No, LEED applies to green building projects. Individual products can contribute to points under the
certification system; LEED criteria are performance-based. In attempting to meet these requirements,
LEED practitioners identify products that have desired attributes. However, some LEED criteria do require
specific product data as a part of a successful submittal.
How much does it cost to register a project?
The registration fee for a project is $450 for USGBC members and $600 for nonmembers.
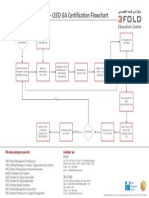
What is the process for LEED certification?
Certification is now administered by the Green Building Certification Institute (GBCI) through a network of
professional, third-party certification bodies. To register a project for LEED certification, visit
www.gbci.org.
What is the average LEED certification fee?
LEED certification fees vary by project size but the average certification cost is $2000.
What is the LEED professional credentialing program?
The LEED professional credentialing program is being managed by GBCI, and includes a multi-faceted
credentialing system that ensures that LEED professionals have the latest knowledge and understanding
of green building practices and to encourage professionals to maintain and advance their knowledge and
expertise.
Under the new program, there are three tiers of excellence for a professional to pursue: LEED Green
Associate; LEED AP with specialty; and LEED AP Fellow. To learn more about the tiers and the
professional credentialing program, visit www.gbci.org.
Does green building cost more?
No, green buildings do not have to cost a penny more. LEED certified projects to date demonstrate that
you can achieve LEED certification and reap its many benefits with a common-sense approach to design
with no additional dollars. Depending on your green building strategy and the level of certification your
project is targeting, there may be mid- and long-term ROI associated with additional green features that
merits an investment in first costs.
What are the benefits of LEED certification?
LEED certification is third-party validation of a building’s performance. LEED certified projects blend
environmental, economic, and occupant-oriented performance. They cost less to operate and maintain;
are energy- and water-efficient; have higher lease-up rates than conventional buildings in their markets;
are healthier and safer for occupants; and are a physical demonstration of the values of the organizations
that own and occupy them. For more information: www.usgbc.org.
You might also like
- ISO 9001:2015 Awareness Trainng Program: © ABI ConstructionDocument52 pagesISO 9001:2015 Awareness Trainng Program: © ABI ConstructionJoshuaNo ratings yet
- Iso 9001 Lead ImplementerDocument7 pagesIso 9001 Lead ImplementerwircexdjNo ratings yet
- ISO-9001 & 14001 - 2015-TrainingDocument24 pagesISO-9001 & 14001 - 2015-TrainingKranti Crank100% (1)
- Iso 9000 and Total Quality: The Relationship: Introduction To Quality Management Tell 26Document25 pagesIso 9000 and Total Quality: The Relationship: Introduction To Quality Management Tell 26Anin Asmoro100% (1)
- Guide To LEED CertificationDocument7 pagesGuide To LEED CertificationWRENDONM2012No ratings yet
- Why ISO 9001:2015? Awareness Presentation: Subtitle or PresenterDocument15 pagesWhy ISO 9001:2015? Awareness Presentation: Subtitle or PresenterMarusia TirmicanNo ratings yet
- ESSENTIAL TIME MANAGEMENT TIPSDocument39 pagesESSENTIAL TIME MANAGEMENT TIPSSonam KejriwalNo ratings yet
- Staying relevant through continuous improvementDocument53 pagesStaying relevant through continuous improvementsbtharan50% (2)
- MCB Baldrige Award CriteriaDocument20 pagesMCB Baldrige Award CriteriaAmit GuptaNo ratings yet
- Implement LEED Strategies for Conservation AgenciesDocument50 pagesImplement LEED Strategies for Conservation AgenciesktbaluNo ratings yet
- Growing The Business, The Value Proposition of The PmoDocument40 pagesGrowing The Business, The Value Proposition of The PmolglfigueiredoNo ratings yet
- Iso La: Friday, September 27, 2019 9:28 PMDocument2 pagesIso La: Friday, September 27, 2019 9:28 PMBugme 786No ratings yet
- MSD Business NegotiationDocument39 pagesMSD Business NegotiationRaj Jumani100% (1)
- BSI ISO 9001 Implementation GuideDocument16 pagesBSI ISO 9001 Implementation Guidejchristoe2613No ratings yet
- Module - 8: Change ManagementDocument14 pagesModule - 8: Change ManagementJibran BashirNo ratings yet
- 1929065493Document360 pages1929065493alecandro_900% (1)
- Quality JourneyDocument22 pagesQuality JourneyNishaThakuriNo ratings yet
- CH 2Document18 pagesCH 2suresh84123No ratings yet
- ISO 9000 - Quality ManagementDocument9 pagesISO 9000 - Quality ManagementVictor DharNo ratings yet
- Workplace Stress ManagementDocument25 pagesWorkplace Stress ManagementTasyaNo ratings yet
- PMP Prep Exam 1Document21 pagesPMP Prep Exam 1Serges Fokou100% (1)
- Implementing and Validating Quality SystemsDocument23 pagesImplementing and Validating Quality SystemsΑυτός είμαι εγώNo ratings yet
- EFQM Excellence Model TeaserDocument5 pagesEFQM Excellence Model TeaserMehmet SinanNo ratings yet
- LeadingGreen 2023 LEED Green Associate v4 TextbookDocument144 pagesLeadingGreen 2023 LEED Green Associate v4 TextbookEdmund WangNo ratings yet
- Certified ISO 9001 Lead Auditor - Two Page BrochureDocument2 pagesCertified ISO 9001 Lead Auditor - Two Page BrochurePECBCERTIFICATIONNo ratings yet
- QMS ISO 9001 2008 OverviewDocument16 pagesQMS ISO 9001 2008 Overviewvipul_gupta1835100% (1)
- EFQMTraining BrochureDocument16 pagesEFQMTraining BrochureTatjana NikolicNo ratings yet
- Vendor AssesmentDocument3 pagesVendor AssesmentRahmi Iftinan SariNo ratings yet
- L03-Project Quality ManagementDocument42 pagesL03-Project Quality ManagementMUHAMMAD AZEEM Khan100% (1)
- Chapter 3-Culture and Communication - RetailDocument22 pagesChapter 3-Culture and Communication - Retailfcleong69No ratings yet
- ISO Quality Awareness Program OverviewDocument28 pagesISO Quality Awareness Program OverviewvinothkumarNo ratings yet
- EFQM Excellence Model GuideDocument17 pagesEFQM Excellence Model GuideHeba HemdanNo ratings yet
- EFQM Excellence Model 2013 en ExtractDocument6 pagesEFQM Excellence Model 2013 en ExtractKoushik Ganguly100% (2)
- MODULE 6 Quality Service ManagementDocument7 pagesMODULE 6 Quality Service ManagementrhspampNo ratings yet
- Earn PMI, ASQ, HRCI CertificationsDocument1 pageEarn PMI, ASQ, HRCI CertificationsTariq AkhtarNo ratings yet
- 08 Project Quality ManagementDocument18 pages08 Project Quality ManagementChris GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Time and Stress Management MCQ Quiz by Dionne MahaffeyDocument26 pagesTime and Stress Management MCQ Quiz by Dionne Mahaffeyiamcalledasad100% (2)
- EFQM Knowledge Base One PageDocument2 pagesEFQM Knowledge Base One PagesamebcNo ratings yet
- Efqm ModelDocument2 pagesEfqm Modelrameshmba2398No ratings yet
- Palash Roy: Quality ManagementDocument15 pagesPalash Roy: Quality ManagementPalash RoyNo ratings yet
- All ExercisesDocument13 pagesAll ExercisesMeenal Dutt100% (1)
- EFQM Recognition BrochureDocument8 pagesEFQM Recognition Brochureشادي الاخرسNo ratings yet
- 03 - Exercises - Participant HandoutDocument33 pages03 - Exercises - Participant Handoutnandhu sampathNo ratings yet
- Succession Planning - PPT SlidesDocument34 pagesSuccession Planning - PPT SlidesPrâtèék ShâhNo ratings yet
- Manage Operational PlanDocument11 pagesManage Operational Planneha100% (1)
- Thought LeadershipDocument24 pagesThought LeadershipKevin McleanNo ratings yet
- Talaat A.Kader: QEHS Consultant/ AuditorDocument6 pagesTalaat A.Kader: QEHS Consultant/ AuditormohammedNo ratings yet
- QMS Foundation PDFDocument12 pagesQMS Foundation PDFmoha23No ratings yet
- Student Behavior RubricDocument4 pagesStudent Behavior RubricgrathwdjNo ratings yet
- ISO 14001 TestDocument3 pagesISO 14001 Testusman javaidNo ratings yet
- EDGE Practice Exam InstructionsDocument16 pagesEDGE Practice Exam InstructionsOmar LogachoNo ratings yet
- Group Exercises - Case StudiesDocument3 pagesGroup Exercises - Case StudiesNew ManNo ratings yet
- Strategic Planning & SHRMDocument73 pagesStrategic Planning & SHRMkrizzymark10No ratings yet
- Week Na 05 – Quality Management ProcessesDocument32 pagesWeek Na 05 – Quality Management ProcessessamuelpacahualaNo ratings yet
- TRUE Advisor Module 3Document13 pagesTRUE Advisor Module 3Sarthak ShuklaNo ratings yet
- IsoDocument47 pagesIsofree2dreamsNo ratings yet
- Optimize Process Improvement with Global StandardizationDocument24 pagesOptimize Process Improvement with Global StandardizationWe strategistNo ratings yet
- White Paper ISO 14001 2015 1 PDFDocument6 pagesWhite Paper ISO 14001 2015 1 PDFwaleedNo ratings yet
- ISO 20700 A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionFrom EverandISO 20700 A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- 2008 California Green Building Standards CodeDocument89 pages2008 California Green Building Standards Codeapi-27027563No ratings yet
- Draft 2010 Cal Green CodeDocument197 pagesDraft 2010 Cal Green CodeJerry MonteroNo ratings yet
- SHP Leading DesignDocument4 pagesSHP Leading Designapi-27027563No ratings yet
- BuildingsuccessDocument1 pageBuildingsuccessapi-27027563No ratings yet