Professional Documents
Culture Documents
5 Cross Section Classification Handout PDF
5 Cross Section Classification Handout PDF
Uploaded by
Fatih ÇELİKEROriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
5 Cross Section Classification Handout PDF
5 Cross Section Classification Handout PDF
Uploaded by
Fatih ÇELİKERCopyright:
Available Formats
Steel Design to Eurocode 3
Local Buckling and CrossSection Classification
In Eurocode 3 you will need to refer to the following
clauses when classifying a section and determining the
cross-sectional resistance:
Clause 5.5 covers the cross section classification
Clauses 6.1 and 6.2 covers the cross-sectional
resistance
Sections with slender webs or flanges will be more
susceptible to local buckling, where the element will
fail before the design strength is reached. Eurocode 3
takes into account the effects of local through the
process of cross section classification.
Classes
Class 2 cross-sections are those which can develop
their plastic moment resistance, but have limited
rotation capacity because of local buckling.
Class 3 cross-sections are those in which the stress in
the extreme compression fibre of the steel member
assuming an elastic distribution of stresses can reach
the yield strength, but local buckling is liable to prevent
development of the plastic moment resistance.
Class 4 cross-sections are those in which local
buckling will occur before the attainment of yield stress
in one or more parts of the cross-section.
Limits
The limits between the classes depend on the factor
which is calculated using fy, the yield strength of the
steel.
Factor
BS 5950
EC3
Plastic
Class 1
Compact
Class 2
Semi-compact
Class 3
Slender
Class 4
BS 5950
EC3
= (275/py)0.5
= (235/fy)0.5
Values of are given at the bottom of Table 5.2:
fy
235
275
355
420
460
1.00
0.92
0.81
0.75
0.71
EN 1993-1-1 Table 5.2
Class 1
Class 2
Class 3
Class 4
Image
Source: http://www.steel-insdag.org/new/pdfs/Chapter8.pdf
The UK National Annex says that material properties
should be taken from the product standards.
Extract from EN 10025-2 - fy (yield strength) values for
hot rolled steel:
2
fy (N/mm )
nominal thickness of element,
t (mm)
16< t 40
40 < t 63
63 < t 80
Steel
Grade
t16
Similarly to BS 5950, cross sections will be placed into
one of four behaviour classes. Class 1 is the least
susceptible to local buckling and class 4 is the most
susceptible.
fy Yield Strength
Eurocode 3 defines the classes in Clause 5.5.2:
S 275
275
265
255
245
Class 1 cross-sections are those which can form a
plastic hinge with the rotation capacity required from
plastic analysis without reduction of the resistance.
S 355
355
345
335
325
The classification of a section will depend mainly on:
The material yield strength, fy
c/t ratio
EN 10025-2 (Table 7)
c/t Width-to-Thickness Ratio
Class 3: Semi-compact
BS 5950
EC3
Limits
The width-to-thickness ratios differ in EC3 differs from
BS 5950:
Flange
outstand
Web in
bending
Web in
compression
BS (Table 11)
EC3 (Table 5.2)
b/T = < 15
c/tf = < 14
d/t = < 120
d/tw = < 142
d/tw = < 42
Class 4: Slender
Outstand
Flange
b = B/2
c = (b tw
2 r)/2
Internal
Compressio
n
Part
d=
D2T2r
c=
h 2 tf 2 r
Appropriate values of c and t are defined at the top of
Table 5.2 for different types of sections.
Table 5.2
An element that doesnt meet the class 3 limits should
be taken as a class 4 section. Effective widths are
assigned to Class 4 compression elements to make
allowance for the reduction in resistance as a result of
local buckling
To calculate the effective width of a Class 4 section,
refer to the relevant section in the Eurocodes:
Section Type
Reference
Cold-formed sections
EN 1993-1-3
Hot-rolled and
fabricated section
EN 1993-1-5
CHS
EN 1993-1-6
Internal compression parts and outstand flanges are
assessed against the limiting width to thickness ratios
for each class. The limits are provided in table 5.2.
Overall Cross-Section Classification
Table 5.2 is made up of three sheets:
Sheet 1 Internal Compression Parts
Sheet 2 Outstand Flanges
Clause 5.5.2(6) states that a cross-section is classified
according to the highest (least favourable) class of its
compression parts.
Sheet 3 Angles and Tubular Sections
Summary
Cross-section Classification
1. Determine fy (UK NA recommends you use the
product standards)
Limits
Class 1: Plastic
Flange
outstand
Web in
bending
Web in
compression
BS (Table 11)
EC3 (Table 5.2)
b/T = < 9
c/tf = < 9
d/t = < 80
d/tw = < 72
Limits
3. Substitute the value of into the class limits in
Table 5.2 to work out the class of the flange and
web
Class 1
Flange
outstand
limiting
value, c/tf
9
Class 2
10
d/tw = < 33
Class 2: Compact
Flange
outstand
Web in
bending
Web in
compression
2. Determine from Table 5.2
BS (Table 11)
EC3 (Table 5.2)
b/T = < 10
c/tf = < 10
d/t = < 100
d/tw = < 83
d/tw = < 38
Class 3
Class 4
Web in bending
limiting value, d/tw
72
83
14
124
If it does not meet Class 3
requirements, the section is classified
as Class 4
4. Take the least favourable class from the flange
and web results
You might also like
- Portuguese Cobblestone PavementDocument37 pagesPortuguese Cobblestone PavementJohn JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Ltp150 Design GuideDocument21 pagesLtp150 Design GuideRajlić ZoranNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Ice LoadsDocument10 pagesChapter 10 Ice LoadsDan LimburgNo ratings yet
- JRC SteelDocument470 pagesJRC Steeldmardetk100% (1)
- 2 Local Buckling and Section Classification - 2011Document21 pages2 Local Buckling and Section Classification - 2011Melinda GordonNo ratings yet
- Static Design Guide LindabDocument78 pagesStatic Design Guide LindabErmal Beqiraj100% (1)
- Tes T Rep Ort: No .: D3.2 - P A RT 3Document45 pagesTes T Rep Ort: No .: D3.2 - P A RT 3Huy Dao NgocNo ratings yet
- Towers, Chimneys and Masts: Wind Loading and Structural Response Lecture 21 Dr. J.D. HolmesDocument31 pagesTowers, Chimneys and Masts: Wind Loading and Structural Response Lecture 21 Dr. J.D. HolmesZaher SharafNo ratings yet
- TC127 WG1 TG4 N135 Exap en 15254-5 240116Document23 pagesTC127 WG1 TG4 N135 Exap en 15254-5 240116Silvo ŠtihNo ratings yet
- Compendium of en 1993 1 1Document85 pagesCompendium of en 1993 1 1ahemadamNo ratings yet
- Bernt - EC3 1 5Document44 pagesBernt - EC3 1 5Rosario BlancaNo ratings yet
- Ec3 VerificcariDocument7 pagesEc3 VerificcariNeamtu NeamtuNo ratings yet
- Circular Column DesignDocument5 pagesCircular Column DesignMF YousufNo ratings yet
- Chapter05 - Plane Frame and Grid EqDocument63 pagesChapter05 - Plane Frame and Grid EqAgus BaeNo ratings yet
- RC Shell Design As Per EC - 20190521 - enDocument63 pagesRC Shell Design As Per EC - 20190521 - enGeoWest MHGeoLKNEGANo ratings yet
- Earthquake Resistant Design of Steel StructuresDocument12 pagesEarthquake Resistant Design of Steel StructuresFranklin GarciaNo ratings yet
- (Eng) Advanced Training Cold Formed 2010.0.78eDocument76 pages(Eng) Advanced Training Cold Formed 2010.0.78eTarek-Aziz BihiNo ratings yet
- Tes T Rep Ort: No .: D3.2 - P A RT 2Document177 pagesTes T Rep Ort: No .: D3.2 - P A RT 2Huy Dao NgocNo ratings yet
- On The Strength of Cast Iron ColumnsDocument25 pagesOn The Strength of Cast Iron Columnsbigduft5886No ratings yet
- User's Manual: USFOS Release 8-5 GUI Version 2.5Document66 pagesUser's Manual: USFOS Release 8-5 GUI Version 2.5Binod DhakalNo ratings yet
- EQuake Forces On Water Retaining StrsDocument4 pagesEQuake Forces On Water Retaining StrssyakurNo ratings yet
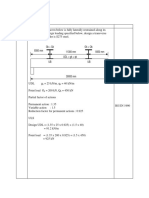
- Example 4Document4 pagesExample 4dane05No ratings yet
- Force Exerted On An Immersed BodyDocument37 pagesForce Exerted On An Immersed BodyNyi NyiNo ratings yet
- Bridge Design DataDocument1 pageBridge Design DataKw TseNo ratings yet
- CE437-Lecture 3-Wind Load CalculationDocument13 pagesCE437-Lecture 3-Wind Load CalculationNaiyaad Tanvir HossainNo ratings yet
- PDC TR-06-02 Rev 1 SBEDS Users Guide DistribADocument95 pagesPDC TR-06-02 Rev 1 SBEDS Users Guide DistribAmirko huaranccaNo ratings yet
- Concrete Slab Design Using Mathcad PDFDocument7 pagesConcrete Slab Design Using Mathcad PDFDiaconu SofiaNo ratings yet
- Ruukki Load Bearing Profiled Sheet Installation InstructionsDocument20 pagesRuukki Load Bearing Profiled Sheet Installation InstructionsEmanuel PopaNo ratings yet
- BeamExamples 368Document13 pagesBeamExamples 368Brian VisserNo ratings yet
- Bending and Compression To BS 5950 and BS en 1993-1-1Document5 pagesBending and Compression To BS 5950 and BS en 1993-1-1voegelchNo ratings yet
- Behavior of Laterally Loaded PilesDocument3 pagesBehavior of Laterally Loaded PilesVijay Dandage100% (1)
- Programme ExamplesDocument1 pageProgramme ExamplesJesús Rodríguez RodríguezNo ratings yet
- SCI PUBLICATION P387 Steel Building Desi PDFDocument106 pagesSCI PUBLICATION P387 Steel Building Desi PDFSabarishwaran SabariNo ratings yet
- Extracts From Ec3 For Students 2012Document6 pagesExtracts From Ec3 For Students 2012Alexandru MarincuNo ratings yet
- Example Plate Girder - Example 2Document11 pagesExample Plate Girder - Example 2kumutha100% (1)
- The Practical Use of Eurocode 2: LoadingDocument9 pagesThe Practical Use of Eurocode 2: Loadingpoddy102No ratings yet
- Adapt-Ptrc 2017 User ManualDocument196 pagesAdapt-Ptrc 2017 User ManualAlex JunioNo ratings yet
- Master Series Student InstallationDocument6 pagesMaster Series Student InstallationekaNo ratings yet
- Design of Composite Members and Joints PDFDocument25 pagesDesign of Composite Members and Joints PDFJózsef Tóth-Horgosi100% (1)
- Design Procedures For Profiled Metal Sheeting and DeckingDocument11 pagesDesign Procedures For Profiled Metal Sheeting and DeckingPrapa KaranNo ratings yet
- Composite Columns IDocument15 pagesComposite Columns IHeng Kimseng100% (1)
- Eurocode 8 - Design-Of-Structures-For-Earthquake-ResistanceDocument1 pageEurocode 8 - Design-Of-Structures-For-Earthquake-ResistanceDinesh JagadisanNo ratings yet
- Hkouksa VKSJ Lajpukvksa Osq Fy, Fmtkbu Yksm (Hkwdai DH Vu ) JHFR LafgrkDocument62 pagesHkouksa VKSJ Lajpukvksa Osq Fy, Fmtkbu Yksm (Hkwdai DH Vu ) JHFR LafgrkSudhakar Krishnamurthy100% (1)
- 3 EC4-2 Background Gerhard HanswilleDocument67 pages3 EC4-2 Background Gerhard Hanswilleantonio111aNo ratings yet
- C I F D: Ommercial and Ndustrial Looring EsignDocument22 pagesC I F D: Ommercial and Ndustrial Looring EsignJibbs OyawoyeNo ratings yet
- OpenSees IntroductionDocument4 pagesOpenSees IntroductionMehdi KashaniNo ratings yet
- Advanced Opensees Algorithms, Volume 1: Probability Analysis Of High Pier Cable-Stayed Bridge Under Multiple-Support Excitations, And LiquefactionFrom EverandAdvanced Opensees Algorithms, Volume 1: Probability Analysis Of High Pier Cable-Stayed Bridge Under Multiple-Support Excitations, And LiquefactionNo ratings yet
- 5 Cross Section Classification HandoutDocument2 pages5 Cross Section Classification Handoutdamquangdong1449No ratings yet
- 5 Cross Section Classification HandoutDocument2 pages5 Cross Section Classification HandoutMohan BhalmeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Classification of Cross-SectionDocument20 pagesChapter 2 - Classification of Cross-SectionMuhd Zuhairi100% (2)
- Classification of Cross SectionDocument19 pagesClassification of Cross SectionAmirul Asyraf Bin Mohd BekeriNo ratings yet
- Module 4 Member Design - Lecture 9 Local Buckling and Section ClassificationDocument17 pagesModule 4 Member Design - Lecture 9 Local Buckling and Section ClassificationSebastian Anthony TotiNo ratings yet
- Cross Section Classification HandoutDocument1 pageCross Section Classification HandoutLumi DochinNo ratings yet
- Overview of Eurocode 3Document40 pagesOverview of Eurocode 3bsitlerNo ratings yet
- Local Buckling: Classification of Cross SectionsDocument10 pagesLocal Buckling: Classification of Cross SectionsHaya BakerNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4-2-2 - Design of Compression Members NewDocument47 pagesLecture 4-2-2 - Design of Compression Members NewHarold Jackson MtyanaNo ratings yet
- Design Formula For EC2Document35 pagesDesign Formula For EC2Azim MuizNo ratings yet
- IS 802 Part-1 (2) :1992Document16 pagesIS 802 Part-1 (2) :1992Sardar. Vikramjit Singh RandhawaNo ratings yet
- 11 Continuous BeamsDocument55 pages11 Continuous BeamsMelinda GordonNo ratings yet
- Restrained Beams HandoutDocument2 pagesRestrained Beams Handoutikanyu79No ratings yet
- Session 12 CJMDocument7 pagesSession 12 CJMAbrar Hussain KhanNo ratings yet
- WD420 Washer DrierDocument32 pagesWD420 Washer Driermenderman100% (1)
- Web Methods EDIINT Module User's Guide 6.5Document98 pagesWeb Methods EDIINT Module User's Guide 6.5Sreedhar Pasarla0% (1)
- AMD CPU ChartDocument28 pagesAMD CPU Charta.dukhieNo ratings yet
- Post - Installed Rebar DesignDocument2 pagesPost - Installed Rebar DesignAsyraf ZailudinNo ratings yet
- Structural Repair Request Form: Bht-All-SrmDocument1 pageStructural Repair Request Form: Bht-All-SrmDiegoAlejandroBuitragoMartinezNo ratings yet
- Vr-Link Ecmp2 W Fss 1.1Document3 pagesVr-Link Ecmp2 W Fss 1.1cafe0sugarNo ratings yet
- Foundation Plan: Scale 1:100MDocument1 pageFoundation Plan: Scale 1:100MLady Mae BrigoliNo ratings yet
- SWD USF CSW Catalog PDFDocument20 pagesSWD USF CSW Catalog PDFChakSiuManNo ratings yet
- Geo Snimak Medijana PDFDocument10 pagesGeo Snimak Medijana PDFmaximus379No ratings yet
- Huawei IDS1000 All-In-One Container Data Center Solution BrochureDocument4 pagesHuawei IDS1000 All-In-One Container Data Center Solution BrochurelegajiusNo ratings yet
- Precedent ResearchDocument5 pagesPrecedent Researchapi-626103890No ratings yet
- Domino AdministratorDocument61 pagesDomino AdministratorPradeep MoreNo ratings yet
- Arts 9: Third Quarter - Module WEEK 3-4Document17 pagesArts 9: Third Quarter - Module WEEK 3-4Cyree ElishaNo ratings yet
- Crispy 660 Cabin Bill of MaterialsDocument2 pagesCrispy 660 Cabin Bill of MaterialsTudor GrigorasNo ratings yet
- Arch447 Presentation4Document38 pagesArch447 Presentation4Fahad RahmanNo ratings yet
- Getting Started WIth SalesForce Part IDocument33 pagesGetting Started WIth SalesForce Part IAmit Sharma0% (1)
- Manuale Hydra-Hydrahp 670703270 GBDocument56 pagesManuale Hydra-Hydrahp 670703270 GBIsaiah JohnNo ratings yet
- Eagle Catalog 2013Document31 pagesEagle Catalog 2013awarehousefulllNo ratings yet
- Manual I-24xW-S PDFDocument120 pagesManual I-24xW-S PDFMario Junior0% (1)
- Chanwar Plakhi Walon 1222Document11 pagesChanwar Plakhi Walon 1222prashanth msNo ratings yet
- Precast Concrete Accessories 0914Document28 pagesPrecast Concrete Accessories 0914Leon BruceNo ratings yet
- Techinical Interview Questions I: Good Evening SirDocument3 pagesTechinical Interview Questions I: Good Evening SirmosesaluriNo ratings yet
- STOP Solution DefinitionDocument13 pagesSTOP Solution Definitionchandrasekhar_sundarNo ratings yet
- The Artist S GazeDocument84 pagesThe Artist S Gazemanuel miranda parreño100% (1)
- 50Hz R22 Air-Cooled Modular Chiller Technical Manual20120210Document117 pages50Hz R22 Air-Cooled Modular Chiller Technical Manual20120210avouzikisNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ZigBee TechnologyDocument48 pagesIntroduction To ZigBee Technologylordi9ordinaryNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Review QuestionsDocument3 pagesChapter 5 Review QuestionsAGWIFI07No ratings yet
- LAN8720A/LAN8720Ai: Small Footprint RMII 10/100 Ethernet Transceiver With HP Auto-MDIX SupportDocument79 pagesLAN8720A/LAN8720Ai: Small Footprint RMII 10/100 Ethernet Transceiver With HP Auto-MDIX Supportapi-432313169No ratings yet
- Learn PythonDocument10 pagesLearn PythonDarien Romero LeivaNo ratings yet