Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pneumoniae: 4. Identification and Characterization of Streptococcus
Uploaded by
Sallie Naomi0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views2 pagesS. pneumoniae is a gram-positive lanceolate diplococcus that grows best at 35-37°C with 5% CO2. On blood agar plates, it forms small, grey, moist colonies that produce alpha-hemolysis zones. It can be identified through a combination of gram stain, catalase, optochin, and bile solubility tests. S. pneumoniae is the leading cause of meningitis in infants, children, adolescents, and older adults. Identification of streptococci involves examining hemolytic reactions on blood agar and using the Lancefield serological classification system, with S. pyogenes, S. agalactiae, and S. pneumoniae being the most significant pathogens
Original Description:
biology
Original Title
streptococcus
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentS. pneumoniae is a gram-positive lanceolate diplococcus that grows best at 35-37°C with 5% CO2. On blood agar plates, it forms small, grey, moist colonies that produce alpha-hemolysis zones. It can be identified through a combination of gram stain, catalase, optochin, and bile solubility tests. S. pneumoniae is the leading cause of meningitis in infants, children, adolescents, and older adults. Identification of streptococci involves examining hemolytic reactions on blood agar and using the Lancefield serological classification system, with S. pyogenes, S. agalactiae, and S. pneumoniae being the most significant pathogens
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views2 pagesPneumoniae: 4. Identification and Characterization of Streptococcus
Uploaded by
Sallie NaomiS. pneumoniae is a gram-positive lanceolate diplococcus that grows best at 35-37°C with 5% CO2. On blood agar plates, it forms small, grey, moist colonies that produce alpha-hemolysis zones. It can be identified through a combination of gram stain, catalase, optochin, and bile solubility tests. S. pneumoniae is the leading cause of meningitis in infants, children, adolescents, and older adults. Identification of streptococci involves examining hemolytic reactions on blood agar and using the Lancefield serological classification system, with S. pyogenes, S. agalactiae, and S. pneumoniae being the most significant pathogens
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
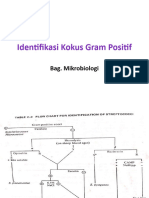
4.
Identification and Characterization of Streptococcus
pneumoniae
gram-positive lanceolate diplococci, but can also occur as single
cocci or in short chains of cocci.
growing best at 35-37C with ~5% CO2 (or in a candle-jar).
media that contain blood, but can also grow on a chocolate agar
plate (CAP).
On a blood agar plate (BAP), colonies: small, grey, moist (sometimes
mucoidal), colonies
produce a zone of alpha-hemolysis
The alpha-hemolytic property differentiates this organism from
many species, but not from the commensal alpha-hemolytic
(viridans) streptococci. Differentiating pneumococci from viridans
streptococci is difficult as young pneumococcal colonies appear
raised, similar to viridans streptococci. However, once the
pneumococcal culture ages 24-48 hours, the colonies become
flattened, and the central portion becomes depressed, which does
not occur with viridans streptococci.
S. pneumoniae can be identified using Gram stain, catalase, and
optochin tests simultaneously, with bile solubility as a confirmatory
test. S. pneumoniae is bile soluble whereas all other alphahemolytic streptococci are bile resistant.
1. Penyebab meningitis
Newborns
Group B Streptococcus, Escherichia coli, Listeria monocytogenes
Infants and Children
Streptococcus pneumoniae, Neisseria meningitidis, Haemophilus in
type b
Adolescents and Young
Adults
Neisseria meningitidis, Streptococcus pneumoniae
Older Adults
Streptococcus pneumoniae, Neisseria meningitidis, Listeria monoc
5. identifikasi streptococcus
Streptococci: Gram-positive cocci pairs and in chains of
cells. Strepococci are often grouped by hemolytic reaction on blood
agar and by serological typing using the Lancefield classification
system.
The most significant pathogens are Streptococcus pyogenes
(Lancefield Group A), Streptococcus agalactiae (Lancefield Group B)
and Streptococcus pneumoniae. Some streptococci (formerly group
D) now placed in the genus Enterococcus are of medical significance
because they are often difficult to treat because of antibiotic
resistance.
Always facultative anaerob and catalase (-).Enterococcus is
usually gamma, nonhemolytic.
You might also like
- Hyponatremia Algorhythm Concept MapDocument2 pagesHyponatremia Algorhythm Concept Mapnursing concept mapsNo ratings yet
- Oxford Handbooks Orthopedics PDFDocument738 pagesOxford Handbooks Orthopedics PDFSallie Naomi29% (7)
- Sputum Culture TestDocument5 pagesSputum Culture TestpraveenASPNo ratings yet
- Atlas of Bacterial Growth in MediaDocument41 pagesAtlas of Bacterial Growth in MediaTamarah YassinNo ratings yet
- Blood AgarDocument4 pagesBlood Agarsyafa latifahNo ratings yet
- Mtap - Bacteriology FinalsDocument6 pagesMtap - Bacteriology FinalsMoira Pauline LibroraniaNo ratings yet
- Pre 1 MibrobiologyDocument3 pagesPre 1 MibrobiologyDeannise AnnNo ratings yet
- Bacte01 STREPTOCOCCUS ENTEROCOCCUSDocument8 pagesBacte01 STREPTOCOCCUS ENTEROCOCCUSAngelic AngelesNo ratings yet
- 3.6.8 SOP - Stool CultureDocument5 pages3.6.8 SOP - Stool CultureSemeeeJunior100% (1)
- Types of MycosesDocument8 pagesTypes of MycosesTimothy John ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Practical 7Document6 pagesPseudomonas Aeruginosa Practical 7ankitamicroNo ratings yet
- A. Staphylococcus Aureus B. Staphylococcus Epidermidis C. Staphylococcus SaprophyticusDocument8 pagesA. Staphylococcus Aureus B. Staphylococcus Epidermidis C. Staphylococcus SaprophyticusRuel MaddawinNo ratings yet
- 1 - Systemic BacteriologyDocument316 pages1 - Systemic BacteriologyAlsirNo ratings yet
- RTI Prelab 2021Document20 pagesRTI Prelab 2021youssef magdyNo ratings yet
- Pratical Two ReportDocument13 pagesPratical Two ReportMUBIRU SAMUEL EDWARDNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Colonial MorphologyDocument5 pagesBacterial Colonial MorphologyMegasonNo ratings yet
- Coagulase PlasmaDocument2 pagesCoagulase PlasmaHà Anh Minh LêNo ratings yet
- New Text DocumentDocument3 pagesNew Text Documenthari krishnaa athotaNo ratings yet
- NissuiDocument6 pagesNissuiEnda Prima Sari TariganNo ratings yet
- TCBSDocument13 pagesTCBSMohammad Aklis AzmiNo ratings yet
- PH Should Be Performed Before Placing Into The Saline Commercial PH Test Paper With A Narrow PH Range Is RecommendedDocument13 pagesPH Should Be Performed Before Placing Into The Saline Commercial PH Test Paper With A Narrow PH Range Is RecommendedJanielle Medina FajardoNo ratings yet
- 2.04.10 DermatophilDocument4 pages2.04.10 DermatophilWormInchNo ratings yet
- Streptococcus Pneumoniae MbbsDocument53 pagesStreptococcus Pneumoniae MbbsShyam MishraNo ratings yet
- Micrococcaceae and Streptococcaceae TransesDocument9 pagesMicrococcaceae and Streptococcaceae TransesaguirreangNo ratings yet
- PL850 Rabbit-Coagulase-Plasma EnglishDocument2 pagesPL850 Rabbit-Coagulase-Plasma Englishzahramaulidi28No ratings yet
- STAPHYLOCOCCUSDocument16 pagesSTAPHYLOCOCCUSSyed Mohsin NisarNo ratings yet
- Candidiasis: Sharada T Rajan Dept of Oral PathologyDocument70 pagesCandidiasis: Sharada T Rajan Dept of Oral PathologySharada GaneshNo ratings yet
- All Staph TestsDocument33 pagesAll Staph Testsalhaitham alqmeNo ratings yet
- Lab 6Document5 pagesLab 6moodyNo ratings yet
- W9 Bacte LAB Identification of StaphylococcusDocument27 pagesW9 Bacte LAB Identification of StaphylococcusAnne CabreraNo ratings yet
- Gram Positive CocciDocument34 pagesGram Positive CocciMaria Cecilia Flores50% (2)
- Week 3 - Topic 1 - Demonstration of Characteristics, Lab Diagnosis & Pathogenesis of StaphylococcusDocument24 pagesWeek 3 - Topic 1 - Demonstration of Characteristics, Lab Diagnosis & Pathogenesis of StaphylococcusTayyaba TahiraNo ratings yet
- VibrioDocument20 pagesVibrioDayana PrasanthNo ratings yet
- Praktikum 3Document24 pagesPraktikum 3ALFEARA YUNIARNo ratings yet
- Streptococcus and EnterococcusDocument7 pagesStreptococcus and EnterococcusSharmaine TrangiaNo ratings yet
- Gram Positive Cocci The Staphylococci CharacteristicsDocument15 pagesGram Positive Cocci The Staphylococci CharacteristicsKyle PicocNo ratings yet
- Identification and Characterization of Neisseria MeningitidisDocument15 pagesIdentification and Characterization of Neisseria MeningitidisRaffaharianggaraNo ratings yet
- 81139.1613396781micro 1 FinalDocument27 pages81139.1613396781micro 1 FinalDiptangshu PalNo ratings yet
- Lab-5-Staphylococci: BY Dr. Shnyar Hamid QadirDocument24 pagesLab-5-Staphylococci: BY Dr. Shnyar Hamid QadirHanaNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Microbiology - Basic Principles of Bacteriology 2014ADocument10 pages1.1 Microbiology - Basic Principles of Bacteriology 2014AkimianfernanNo ratings yet
- Labmed32 0368Document8 pagesLabmed32 0368shennie anteNo ratings yet
- A Gram Stain Is Performed From The Sputum of The Infected PatientDocument1 pageA Gram Stain Is Performed From The Sputum of The Infected PatientMohamad NassirNo ratings yet
- BACTE m6Document9 pagesBACTE m6Gerald SorianoNo ratings yet
- Clinical Bacteriology Finals 2.0: Gram Positive BaciliDocument13 pagesClinical Bacteriology Finals 2.0: Gram Positive BaciliEzra LonodNo ratings yet
- StaphylococcusDocument23 pagesStaphylococcussajad abasNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Gram Positive CocciDocument9 pages1.1 Gram Positive CocciJustine Mel Concepcion IlardeNo ratings yet
- Strepto Cocci PDFDocument34 pagesStrepto Cocci PDFMustafa SaßerNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Diagnosis of Gram Positive Non Spore Forming BacilliDocument26 pagesLaboratory Diagnosis of Gram Positive Non Spore Forming BacillialmlalyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 - الملارياDocument5 pagesLecture 6 - الملارياAhmed Qassim MadhloomNo ratings yet
- Gram Positive Cocci StaphylococciDocument41 pagesGram Positive Cocci StaphylococciZainab ElgehaniNo ratings yet
- Laboratory # 3 Biochemical Differentiation of Some Medically ImportantDocument34 pagesLaboratory # 3 Biochemical Differentiation of Some Medically ImportantSirine AjourNo ratings yet
- Additional Notes For CM AscpDocument4 pagesAdditional Notes For CM AscpAry OuiNo ratings yet
- CryptococcusDocument57 pagesCryptococcusማላያላም ማላያላምNo ratings yet
- 20 Macalisang Bacte Lec Ola (3rd Shifting)Document7 pages20 Macalisang Bacte Lec Ola (3rd Shifting)Era Dawn MacalisangNo ratings yet
- Approach Considerations MALARIADocument3 pagesApproach Considerations MALARIAAnonymous hvOuCjNo ratings yet
- CoagulaseDocument2 pagesCoagulaseJiki LaluNo ratings yet
- Practical Session Two Guide-1Document9 pagesPractical Session Two Guide-1Andrease WandazNo ratings yet
- Staphylococci & MicrococciDocument52 pagesStaphylococci & Micrococcihoneylemon.coNo ratings yet
- PneumococcusDocument29 pagesPneumococcusThe tooth fairyNo ratings yet
- Chapter15 StreptococciDocument66 pagesChapter15 StreptococciNursheda Abangon AzisNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Media Tests PicturesDocument26 pagesMicrobiology Media Tests Picturesthu_vu_29No ratings yet
- Guidelines For The Use of Potassium ChlorideDocument2 pagesGuidelines For The Use of Potassium ChlorideSallie NaomiNo ratings yet
- Etiologi MeningitisDocument6 pagesEtiologi MeningitisSallie NaomiNo ratings yet
- Dampak Terhadap KesehatanDocument1 pageDampak Terhadap KesehatanSallie NaomiNo ratings yet