Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Com +Nursing+Care+Plan+Typhoid+Fever
Com +Nursing+Care+Plan+Typhoid+Fever
Uploaded by
Aj Miranda0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
28 views2 pagesOriginal Title
com +Nursing+Care+Plan+Typhoid+Fever
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
28 views2 pagesCom +Nursing+Care+Plan+Typhoid+Fever
Com +Nursing+Care+Plan+Typhoid+Fever
Uploaded by
Aj MirandaCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
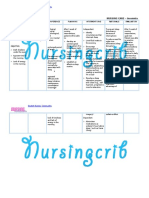
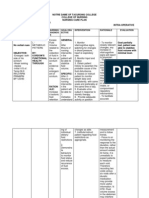
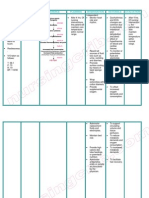
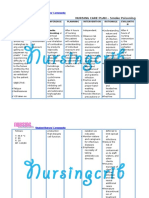
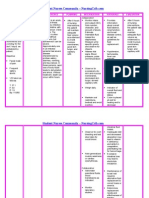
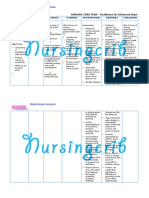
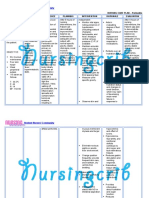
NURSING CARE PLAN
ASSESSMENT DIAGNOSIS INFERENCE PLANNING INTERVENTION RATIONALE EVALUATION
Independent:
Subjective: • Hyperthermia • Typhoid fever is • After 7 days • Monitor patient • Fever pattern • After 7 days
related to a bacterial of nursing temperature may aids in of nursing
“Mainit ang increased disease, caused interventions degree and diagnosing intervention
pakiramdam ko” metabolic by Salmonella , the patient patterns. underlying s, the
as verbalized by rate, illness. typhi. It is will disease. patient was
patient. transmitted demonstrate • Observe for • Chills often able to
through the temperature shaking chills and precede during demonstrate
Objective: ingestion of food within normal profuse high temperature
or drink range and diaphoresis. temperature within
• Flushed skin, contaminated by free from and in presence normal
warmed to the feces or chills. of generalized range and
touch. urine of infected infection. free from
people. • Wash hands with • Reduces cross chills.
• Restlessness. Symptoms anti-bacterial contamination
usually develop soap before and and prevents
• V/S taken as 1–3 weeks after after each care of the spread of
follows: exposure, and activity and infection.
may be mild or encourage proper
T: 38.9 severe. They hygiene.
P: 80 include high • Provide tepid • May help
R: 21 fever, malaise, sponge baths and reduce fever.
Bp: 100/80 headache, avoid the use of Use of ice
constipation or ice water and water and
diarrhea, rose- alcohol. alcohol may
colored spots on cause chills and
the chest, and can elevate
enlarged spleen temperature.
and liver. • Monitor for signs • May reflect
Healthy carrier of deterioration of inappropriate
state may follow condition or antibiotic
acute illness. failure to improve therapy.
Typhoid fever with therapy.
can be treated
with antibiotics.
However,
resistance to
common
antimicrobials is
widespread. Collaborative:
Healthy carriers • Administer anti- • Used to reduce
should be pyretics as fever by its
excluded from prescribed. central action
handling food. on the
hypothalamus.
• Administer anti- • To control the
biotics as spread of
prescribed. infection.
You might also like
- Nursing Care Plan For Myocardial Infarction NCPDocument8 pagesNursing Care Plan For Myocardial Infarction NCPderic87% (15)
- Nursing Care Plan For Pneumonia NCPDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan For Pneumonia NCPderic79% (133)
- Nursing Care Plan For Risk For Aspiration NCPDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan For Risk For Aspiration NCPderic100% (8)
- Nursing Care Plan For Ineffective Infant Feeding Pattern NCPDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan For Ineffective Infant Feeding Pattern NCPderic71% (14)
- Nursing Care Plan For Post Trauma NCPDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan For Post Trauma NCPderic82% (11)
- Nursing Care Plan For Readiness For Enhanced Spiritual Well Being NCPDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan For Readiness For Enhanced Spiritual Well Being NCPderic83% (6)
- Nursing Care Plan For Liver Cirrhosis NCPDocument14 pagesNursing Care Plan For Liver Cirrhosis NCPderic92% (12)
- Nursing Care Plan For Rabies NCPDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan For Rabies NCPderic100% (9)
- Nursing Care Plan For Peptic Ulcer NCPDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Peptic Ulcer NCPderic85% (46)
- Nursing Care Plan For Insomnia NCPDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Insomnia NCPderic83% (24)
- Nursing Care Plan For AmputationDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan For Amputationderic81% (26)
- Nursing Care Plan For Seizure NCPDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Seizure NCPderic88% (40)
- Nursing Care Plan For Insufficient Breastmilk NCPDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Insufficient Breastmilk NCPderic100% (17)
- Anatomy and Physiology of Typhoid FeverDocument5 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Typhoid FeverCharise Ligores67% (6)
- Nursing Care Plan For AIDS/HIVDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan For AIDS/HIVderic81% (16)
- Nursing Care Plan For Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding NCPDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan For Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding NCPderic79% (14)
- Nursing Care Plan For Multiple Sclerosis NCPDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Multiple Sclerosis NCPderic88% (17)
- NCP HypothermiaDocument2 pagesNCP HypothermiaJohn Paolo Ocampo100% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan For HemodialysisDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Hemodialysisderic80% (20)
- Nursing Care Plan For Readiness For Enhanced Sleep NCPDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan For Readiness For Enhanced Sleep NCPderic100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan For Risk For Compromised Human Dignity NCPDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan For Risk For Compromised Human Dignity NCPderic100% (2)
- Nueva Ecija University of Science And: O V A ADocument2 pagesNueva Ecija University of Science And: O V A ABeverly DatuNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Chronic PancreatitisDocument8 pagesNursing Care Plan: Chronic PancreatitisAnne B. Buenvenida100% (2)
- Typhoid NCPDocument10 pagesTyphoid NCPArchana SahuNo ratings yet
- Typhoid FeverDocument1 pageTyphoid FeverGenila Marie Oberes Bait-itNo ratings yet
- Case Study On Typhoid FeverDocument33 pagesCase Study On Typhoid Feverjarelle bondoc93% (14)
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Nursing Objective Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Nursing Objective Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationRhoanne Handang100% (4)
- Case Study TBDocument9 pagesCase Study TBCheche_Guinto_8235100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan For TonsillitisDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan For TonsillitisEden Cruz50% (6)
- Assessment Needs Nursing Diagnos IS Goal/Obj Ective Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument10 pagesAssessment Needs Nursing Diagnos IS Goal/Obj Ective Intervention Rationale EvaluationApol Pen67% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan FeverDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan Feverderic96% (69)
- NURSING CARE PLAN Chicken PoxDocument2 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN Chicken Poxderic87% (62)
- Nursing Care Plan For Carbon Monoxide PoisoningDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan For Carbon Monoxide Poisoningderic73% (11)
- Nursing Care Plan For Smoke Poisoning NCPDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Smoke Poisoning NCPderic100% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan For Rape Trauma Syndrome NCPDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan For Rape Trauma Syndrome NCPderic100% (4)
- Nursing Care Plan For Interrupted Breastfeeding NCPDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan For Interrupted Breastfeeding NCPderic88% (8)
- Nursing Care Plan For Disturbed Sleep Pattern NCPDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan For Disturbed Sleep Pattern NCPderic67% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan For Neonatal Sepsis NCPDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan For Neonatal Sepsis NCPderic67% (9)
- Nursing Diagnosis HyperthermiaDocument2 pagesNursing Diagnosis HyperthermiaErl Driz100% (1)
- Sample Nursing Care Plan For Typhoid Fever (Risk)Document2 pagesSample Nursing Care Plan For Typhoid Fever (Risk)Rhae Raynog100% (11)
- Nursing Care Plan For Typhoid FeverDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan For Typhoid FeverRoderick Agbuya63% (8)
- Typhoid Fever NCPDocument46 pagesTyphoid Fever NCPLyra Lustre RN67% (3)
- NCP TyphoidDocument4 pagesNCP TyphoidFate ZephyrNo ratings yet
- NCP HyperthermiaDocument3 pagesNCP HyperthermiaMarla NavarroNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationJamie Haravata0% (1)
- Case Study On Typhoid FeverDocument20 pagesCase Study On Typhoid FeverChukwuka Henry25% (4)
- NURSING CARE PLAN - CholeraDocument2 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN - Choleraderic87% (30)
- NURSING CARE PLAN - Hepatitis ADocument2 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN - Hepatitis Aderic74% (19)
- NCP Dengue Fever-MalariaDocument2 pagesNCP Dengue Fever-Malariachristian quiaoit25% (4)
- NCP HydrocephalusDocument6 pagesNCP HydrocephalusgopscharanNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument4 pagesNCPmimingdot33No ratings yet
- NCP FeverDocument2 pagesNCP FeverMary Joyce LimoicoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan On FeverDocument15 pagesNursing Care Plan On Feverkamini ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- NCP - LeprosyDocument3 pagesNCP - LeprosyKevin DareNo ratings yet
- NCP FeverDocument1 pageNCP FeverLuis Romnic Vinuya100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan TB MeningitisDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan TB Meningitisderic74% (19)
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- NCP DiarrheaDocument2 pagesNCP DiarrheaElisha Faith Sevilla Espineli0% (1)
- Medication ThalassemiaDocument3 pagesMedication ThalassemiaDivya ToppoNo ratings yet
- Section P - Group 1 E.C.S. - Pediatric Ward Mr. Ralph P. Pilapil, R.N. Clinical InstructorDocument62 pagesSection P - Group 1 E.C.S. - Pediatric Ward Mr. Ralph P. Pilapil, R.N. Clinical InstructorClaudine N SantillanNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Neonatal SepsisDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Neonatal Sepsisderic100% (20)
- NCP 1Document2 pagesNCP 1Rica AgostoNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective DataDocument2 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective DataJordz PlaciNo ratings yet
- Nursingcrib Com NURSING CARE PLAN Chicken Pox PDFDocument2 pagesNursingcrib Com NURSING CARE PLAN Chicken Pox PDFAkeroNo ratings yet
- Com +Nursing+Care+Plan+Chicken+PoxDocument2 pagesCom +Nursing+Care+Plan+Chicken+PoxDahl Obañana Erojo100% (1)
- Cues Nursing Diagnos IS Analysis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument7 pagesCues Nursing Diagnos IS Analysis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationLoriejae Marie DesulocNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Objectives Intervention Rationale Evaluation IndependentDocument6 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Objectives Intervention Rationale Evaluation IndependentKasandra Dawn Moquia Beriso100% (1)
- Chicken Pox N C P BY BHERU LALDocument2 pagesChicken Pox N C P BY BHERU LALBheru Lal100% (1)
- نسخة نسخة Note 11 Feb 2023 2Document4 pagesنسخة نسخة Note 11 Feb 2023 2Elaf.No ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlansDocument16 pagesNursing Care PlansJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- NCP Leptospirosis - NewDocument5 pagesNCP Leptospirosis - Newglaiza_requintoNo ratings yet
- CHN RleDocument3 pagesCHN RleCarissa Mae Tapec EstradaNo ratings yet
- NCP LeptospirosisDocument6 pagesNCP LeptospirosisJean Marie DavidNo ratings yet
- Pedia Ward Chapter 4dDocument4 pagesPedia Ward Chapter 4dJohn Edward EscoteNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Sweating Temperature Rigors Nausea Vomiting Diarrhoea Lethargy MalaiseDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan: Sweating Temperature Rigors Nausea Vomiting Diarrhoea Lethargy Malaise06eltianNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationAngelica Charisse BuliganNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Analysis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Analysis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationChristian ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- Drug Study of Acute PyelonephritisDocument6 pagesDrug Study of Acute PyelonephritisGhra CiousNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPJonna Mae TurquezaNo ratings yet
- NCP 3Document2 pagesNCP 3FitzLucario QueNo ratings yet
- Typhoid FeverDocument11 pagesTyphoid FeverjhenvitoNo ratings yet
- Bedside Clinic 2007Document10 pagesBedside Clinic 2007api-3718174No ratings yet
- Capitol University College of NursingDocument7 pagesCapitol University College of NursingJesus Carlo Adalla QuirapNo ratings yet
- NCP - Chicken PoxDocument4 pagesNCP - Chicken Poxhanna_lim0% (1)
- Case StudyDocument4 pagesCase StudyNygie HaudarNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For GlaucomaDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan For Glaucomaderic79% (28)
- Nursing Care Plan For Readiness For Enhanced Hope NCPDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan For Readiness For Enhanced Hope NCPderic100% (6)
- Nursing Care Plan For Pedia TB Meningitis NCPDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Pedia TB Meningitis NCPderic100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For Peritonitis NCPDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Peritonitis NCPderic86% (7)
- Nursing Care Plan For Overflow Urinary Incontinence NCPDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Overflow Urinary Incontinence NCPderic71% (7)
- Unknown Author - AutoantibodypdfDocument7 pagesUnknown Author - AutoantibodypdfBhupi AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Activity:: Physical Fitness Aims For Holistic Development. Complete The Diagram Below On What IsDocument2 pagesActivity:: Physical Fitness Aims For Holistic Development. Complete The Diagram Below On What IsJackie Lou SantosNo ratings yet
- Contemporary Issue of Teenage PregnancyDocument6 pagesContemporary Issue of Teenage Pregnancyventigas tentigoNo ratings yet
- Haemophilus SPPDocument109 pagesHaemophilus SPPJamie CañebaNo ratings yet
- Balanopostitis and Penyle Edema Atypical Manifestation of Primary SipilisDocument2 pagesBalanopostitis and Penyle Edema Atypical Manifestation of Primary SipilisTeja LaksanaNo ratings yet
- Events 1 60 Recommended Articles of Events of Significance by AcetheCLATDocument392 pagesEvents 1 60 Recommended Articles of Events of Significance by AcetheCLATTejash TapadiyaNo ratings yet
- 31 - OMS Diarrhée Et Pneumonie PDFDocument54 pages31 - OMS Diarrhée Et Pneumonie PDFsasNo ratings yet
- Clinical Research CoordinatorDocument1 pageClinical Research Coordinatorapi-77731042No ratings yet
- PFCCS Instructor Director Consultant CriteriaDocument3 pagesPFCCS Instructor Director Consultant CriteriaImam RahmadiNo ratings yet
- VilleroyBoch SpaDocument22 pagesVilleroyBoch Spachu_proNo ratings yet
- BNF For Children (BNFC) 2018-2019 (Year 2018-2019) : Advance Book InformationDocument1 pageBNF For Children (BNFC) 2018-2019 (Year 2018-2019) : Advance Book InformationKhaing Moh Moh ZinNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Activity 2 - HIS Lab - Primary Health Care WorkerDocument2 pagesLaboratory Activity 2 - HIS Lab - Primary Health Care WorkerCaissa Andrea Beatrice BaylenNo ratings yet
- Assignment (PE)Document3 pagesAssignment (PE)Jonna VillegasNo ratings yet
- Yin2007 - SAAMDocument6 pagesYin2007 - SAAMericapinceratoNo ratings yet
- Multistate Comment Letter To DHS Re Public Charge Ground of InadmissibilityDocument24 pagesMultistate Comment Letter To DHS Re Public Charge Ground of InadmissibilityWXMINo ratings yet
- Introduction To Patient - S Medical Chart (2012) PDFDocument29 pagesIntroduction To Patient - S Medical Chart (2012) PDFFrancinetteNo ratings yet
- Sales and Inventory System For Furniture ShopDocument118 pagesSales and Inventory System For Furniture ShopHenry SugueNo ratings yet
- Nalco Varidos FSK: Cigweld Pty LTDDocument10 pagesNalco Varidos FSK: Cigweld Pty LTDPouria KazemzadehNo ratings yet
- Unit 8 Nutritional Consideration in The Prevention and Management of Type II Diabetes Mellitus, Educational PlatformDocument15 pagesUnit 8 Nutritional Consideration in The Prevention and Management of Type II Diabetes Mellitus, Educational Platformzia ullahNo ratings yet
- HYPERTENSION AhaDocument9 pagesHYPERTENSION AhaDesam Desi Amroni KNo ratings yet
- SHS PE MODULE 1 - RemovedDocument21 pagesSHS PE MODULE 1 - RemovedXypher NNo ratings yet
- Emenuhan Kebutuhan Nutrisi Balita Yang Dirawat Inap Di Rumah SakitDocument7 pagesEmenuhan Kebutuhan Nutrisi Balita Yang Dirawat Inap Di Rumah SakitAnnisa Nur Majidah100% (1)
- Week 7. 2 CHN-FNCPDocument51 pagesWeek 7. 2 CHN-FNCPPatrick Jumao-asNo ratings yet
- Primark Chemical Commitment Meeting - Dhaka - Sep - 2016Document31 pagesPrimark Chemical Commitment Meeting - Dhaka - Sep - 2016Dyeing DyeingNo ratings yet
- Arm and Foot BathDocument10 pagesArm and Foot BathDr Siddharth SP YadavNo ratings yet
- On PovertyDocument86 pagesOn PovertyampofogodwinNo ratings yet
- Get The Nutrition FactsDocument2 pagesGet The Nutrition FactsHayudini, Ashrina J.No ratings yet
- Diabetes Case StudyDocument7 pagesDiabetes Case Studyapi-242589113No ratings yet
- Wolaita Sodo University, College of Health Sciences and Medicine, Department of Clinical Anatomy, Sodo, EthiopiaDocument16 pagesWolaita Sodo University, College of Health Sciences and Medicine, Department of Clinical Anatomy, Sodo, Ethiopiaamanmalako50No ratings yet
- Drug Addiction:a Curable Mental Disorder?Document7 pagesDrug Addiction:a Curable Mental Disorder?shanun shari sakuntiNo ratings yet