Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Athan
Athan
Uploaded by
Athan OducayenOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Athan
Athan
Uploaded by
Athan OducayenCopyright:
Available Formats
Jonathan Mark Oducayen 12B
Grp 9 1-27-11
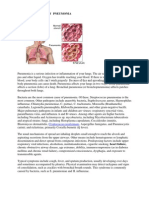
Bronchopneumonia
Bronchopneumonia or bronchial pneumonia or "Bronchogenic pneumonia" (not to be
confused with lobar pneumonia) is the acute inflammation of the walls of the bronchioles. It is a type of
pneumonia characterized by multiple foci of isolated, acute consolidation, affecting one or more
pulmonary lobules.
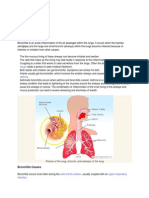
Causes of Bronchopneumonia
Bronchopneumonia is closely associated with hospital-acquired pneumonia. In a
person suffering from bronchopneumonia, bacteria invade the lungs, which results to an
inflammatory immune response. This reaction of the lungs leads to the filling of the alveolar
sacs with exudates. As a result, consolidation takes place: a condition wherein the air space
in the lungs is replaced with fluids.
Symptoms of Bronchopneumonia in Children
Cough with yellow or green mucus
High grade fever
Pain in the chest
Breathlessness
Loss of appetite
Sick looking child
Treatment of Bronchopneumonia in Babies
Antibiotics prescribed by your doctor should be taken regularly as advised. This is the
first line of treatment in bronchopneumonia.
Along with the above treatment additionally proper food supplementation, hydration
by giving adequate water, vegetable juices made up of carrot, and spinach can be
given.
Pneumococcal vactionation is advised in children.
You might also like
- A Simple Guide to Dilated Bronchi, Mucus Blockage (Bronchiectasis), Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Dilated Bronchi, Mucus Blockage (Bronchiectasis), Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide To Different Pneumonias, Diagnosis, Treatment In Medical PracticeFrom EverandA Simple Guide To Different Pneumonias, Diagnosis, Treatment In Medical PracticeNo ratings yet
- Medical Mnemonic Sketches : Pulmonary DiseasesFrom EverandMedical Mnemonic Sketches : Pulmonary DiseasesNo ratings yet
- PneumoniaDocument68 pagesPneumoniaJelmalyn Basali100% (1)
- Bronchiectasis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandBronchiectasis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Bronchitis Vs BronchiolitisDocument52 pagesBronchitis Vs BronchiolitisUngku Hajar Nur AthirahNo ratings yet
- Bronchopneumonia Lesson PlanDocument16 pagesBronchopneumonia Lesson Planlijalem taye100% (1)
- Bronchial ObstructionDocument137 pagesBronchial ObstructionGrajdianu Natalia100% (1)
- Bronchiectasis NishaDocument44 pagesBronchiectasis NishaKaarthigan RamaiahNo ratings yet
- Bronchopneumonia Lesson PlanDocument16 pagesBronchopneumonia Lesson PlanUday Kumar88% (17)
- Broncho PneumoniaDocument5 pagesBroncho PneumoniamarkkkkkkkheeessNo ratings yet
- Bronchopneumonia TreatmentDocument2 pagesBronchopneumonia TreatmentJam RapaconNo ratings yet
- Bronkopneumonia Pada Pasien PediatrikDocument5 pagesBronkopneumonia Pada Pasien PediatrikCecilia Evangelista NiluhNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis Banding I. BronkopneumoniaDocument20 pagesDiagnosis Banding I. BronkopneumoniaHijriah SyafitriNo ratings yet
- Ast 2Document17 pagesAst 2AbuAbdullah KhanNo ratings yet
- Asthm 2Document34 pagesAsthm 2AbuAbdullah KhanNo ratings yet
- Bronko PneumoniaDocument33 pagesBronko PneumoniaNurul Hidayati SyarahNo ratings yet
- Bronchopneumonia: Presented By: Dian HadinataDocument24 pagesBronchopneumonia: Presented By: Dian HadinataRickyNo ratings yet
- Schematic Diagram OF BronchopneumoniaDocument11 pagesSchematic Diagram OF BronchopneumoniaanGel1115No ratings yet
- BronchopneumoniaDocument11 pagesBronchopneumoniaDesiree GuerraNo ratings yet
- DifferentialsDocument7 pagesDifferentialsStewart Garneth Reston RancesNo ratings yet
- Introduction BronchoPneumoniaDocument2 pagesIntroduction BronchoPneumoniaJanna FavilaNo ratings yet
- PneumoniaDocument34 pagesPneumoniaAbduraman NazifNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument85 pagesRespiratory SystemJames MoralesNo ratings yet
- Haq Dan Bati1Document9 pagesHaq Dan Bati1Naomi Pradita YuwanaNo ratings yet
- Bronchiectasis: Getnet Alemu, MD Huchs Feb 3, 2012Document38 pagesBronchiectasis: Getnet Alemu, MD Huchs Feb 3, 2012yosefNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia 9Document9 pagesPneumonia 9Samba SukanyaNo ratings yet
- Bronchiolitis - Dr. IonescuDocument30 pagesBronchiolitis - Dr. IonescuArleen MatincaNo ratings yet
- Bronchopneumonia Treatment - Symptoms, Causes of Broncho PneumoniaDocument5 pagesBronchopneumonia Treatment - Symptoms, Causes of Broncho Pneumoniajaizel_mhine14No ratings yet
- "Bronchitis": Respiratory DisorderDocument40 pages"Bronchitis": Respiratory Disorderaswin379No ratings yet
- BronchitisDocument40 pagesBronchitisJAMES NYIRENDANo ratings yet
- MSNDocument16 pagesMSNVikram bhai prajapatiNo ratings yet
- Walang Pamagat Na DokumentoDocument3 pagesWalang Pamagat Na Dokumentobenedict cruz DevianaNo ratings yet
- Pathology: A. ChestDocument10 pagesPathology: A. ChestCielo DeguzmanNo ratings yet
- NCP For Bronchopneumonia With 7 Nursing DiagnosisDocument4 pagesNCP For Bronchopneumonia With 7 Nursing DiagnosisBeng AlontoNo ratings yet
- LP Pneumonia Keperawatan Anak. Salinan Salinan - Id.en SalinanDocument13 pagesLP Pneumonia Keperawatan Anak. Salinan Salinan - Id.en SalinanMuhammad ZainuddinNo ratings yet
- Bronchiectasis: DR Budi Enoch SPPDDocument21 pagesBronchiectasis: DR Budi Enoch SPPDVito CuyNo ratings yet
- Bronchiectasis ConrodDocument32 pagesBronchiectasis ConrodM karthiNo ratings yet
- 3th Semester Pediatric Pa Tho Physiology Broncho Lit IsDocument1 page3th Semester Pediatric Pa Tho Physiology Broncho Lit IsSussan GoldsworthyNo ratings yet
- Why It Happens?: BronchiectasisDocument2 pagesWhy It Happens?: BronchiectasisRejoy ObinaNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument6 pagesIntroductionRea Paulline Paguio FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Addis Ababa University: Collage of Health Science Pediatrics and Neonatology On PneumoniaDocument21 pagesAddis Ababa University: Collage of Health Science Pediatrics and Neonatology On PneumoniaCheru DugaseNo ratings yet
- PneumoniaDocument3 pagesPneumoniaKami KhanNo ratings yet
- Trabajo de Ingles ComplainsDocument2 pagesTrabajo de Ingles ComplainsHoffmann Pardo CadizNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Inference Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Inference Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationAyen Fajardo-HernalNo ratings yet
- Wae'l Hayajneh: PneumoniaDocument14 pagesWae'l Hayajneh: PneumoniaRashed ShatnawiNo ratings yet
- Introduction Acute BronchitisDocument19 pagesIntroduction Acute BronchitisFarida EbrahimNo ratings yet
- Textbook of Respiratory Disease in Dogs and Cats Bacterial Pneumonia in Dogs and CatsDocument10 pagesTextbook of Respiratory Disease in Dogs and Cats Bacterial Pneumonia in Dogs and CatsDiego CushicóndorNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia-Handout Part 1Document7 pagesPneumonia-Handout Part 1Kristine RamosNo ratings yet
- The Best Way To Make Your Dreams Come True Is To: Wake Up..Document28 pagesThe Best Way To Make Your Dreams Come True Is To: Wake Up..Chandan Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Bud Hi Raja 2013Document5 pagesBud Hi Raja 2013lalaNo ratings yet
- Symptoms of Bronchopneumonia in Adults and Children: PneumoniaDocument10 pagesSymptoms of Bronchopneumonia in Adults and Children: PneumoniajessyNo ratings yet
- Pa Tho Physiology of PneumoniaDocument6 pagesPa Tho Physiology of PneumoniaPaula YoungNo ratings yet
- Non Tuberculous Infections (Updated)Document54 pagesNon Tuberculous Infections (Updated)ZijieNo ratings yet
- Symptoms of Bronchopneumonia in Adults and Children: PneumoniaDocument10 pagesSymptoms of Bronchopneumonia in Adults and Children: PneumoniajessyNo ratings yet
- BronchitisDocument3 pagesBronchitiscorsaruNo ratings yet
- Pcap Didactics ChanDocument61 pagesPcap Didactics ChanValerie Anne BebitaNo ratings yet
- 长沙医学院 国际教育学院 Pathology (病理学)Document57 pages长沙医学院 国际教育学院 Pathology (病理学)Ichsan FajriNo ratings yet
- PBL of PneumoniaDocument9 pagesPBL of PneumoniaRobelNo ratings yet