0% found this document useful (0 votes)
318 views8 pagesIntroduction To CMOS Design: Dr. Paul D. Franzon
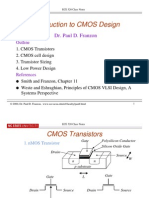
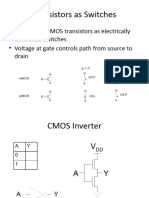
CMOS Transistors 2. CMOS cell design 3. Transistor Sizing References. CMOS circuit speeds can be modeled to a first approximation as RC delays: 1. What does the input of a CMOS gate look like'? Capacitor, C [?] W x L 2. What does the output' during switching look like? Resistor, R [?] L / W 3. Usually hole mobility is half of electron mobility.
Uploaded by
Rohit JagannathCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
318 views8 pagesIntroduction To CMOS Design: Dr. Paul D. Franzon
CMOS Transistors 2. CMOS cell design 3. Transistor Sizing References. CMOS circuit speeds can be modeled to a first approximation as RC delays: 1. What does the input of a CMOS gate look like'? Capacitor, C [?] W x L 2. What does the output' during switching look like? Resistor, R [?] L / W 3. Usually hole mobility is half of electron mobility.
Uploaded by
Rohit JagannathCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd