Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Wound Sepsis and Infections
Uploaded by
mimovodaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Wound Sepsis and Infections
Uploaded by
mimovodaCopyright:
Available Formats
Wound sepsis and infections
:Definition
It is a subtype of surgical infection that occurs following the breakdown of local &
.systemic host defenses
(Pathology: (4 stages
contamination .1
inflammation .2
Suppuration .3
Healing .4
Pathogenesis
Wound infection usually stated during or after operation with bacteria
.(from the patient (autogenous) or due to contamination (exogenous
:The risk of infection increased by
Rough surgical manipulation with devitalization of tissues & leaving a .1
.large dead space with haematoma formation
.Long time tissue exposure .2
patient defensive mechanisms due to….DM, chemotherapy,↓ .3
…corticosteroids, RF
:Clinical Picture
:Symptoms
(History of recent operation (within 10 days
General : FAHM
.Local: pain, swelling
:Signs
.Wound is swollen, indurated → abscess burst to form sinus discharging pus
:Prophylaxis of wound infection
:Good aseptic precautions .1
Skin preparation, sterilization, care of operative theaters. avoid -
.excessive dressing
:Proper surgical techniques .2
Gentle handling of tissue, haemostasis, avoid excessive cauterization, -
avoid excessive unnecessary sutures and dead spaces and put a drain if it is
.needed
:Support body defenses .3
.Good nutrition, blood transfusion if indicated -
:Prophylactic antibiotics .4
? When? How -
:Treatment of wound infection
.Suitable antibiotics: usually broad spectrum for aerobic or anaerobic .1
.Removal of foreign bodies, stitches or pack .2
.Evacuation of haematoma .3
4. Care of wound. If wound infection occurred early drainage of .4
.infection
PRINCIPLES OF ANTIBIOTIC PROPHYLAXIS
SURGICAL PROPHYLAXIS
Definition:The administration of an antibiotic prior to a surgical
.procedure to prevent postoperative infection
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (120)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Law On Common Carriers: Laws Regulating Transportation CompaniesDocument3 pagesLaw On Common Carriers: Laws Regulating Transportation CompaniesLenoel Nayrb Urquia Cosmiano100% (1)
- An Objective of Dress Code PolicyDocument4 pagesAn Objective of Dress Code PolicySiddhraj Singh KushwahaNo ratings yet
- Literary Terms Practice Worksheet 3Document11 pagesLiterary Terms Practice Worksheet 3Jiezl Abellano AfinidadNo ratings yet
- Thera Bank - ProjectDocument34 pagesThera Bank - Projectbhumika singh100% (4)
- IV Fluids ChartDocument1 pageIV Fluids Chartzahidtaniv71% (7)
- Emotions Influence Color Preference PDFDocument48 pagesEmotions Influence Color Preference PDFfllorinvNo ratings yet
- M40 Mix DesignDocument2 pagesM40 Mix DesignHajarath Prasad Abburu100% (1)
- Click Here For Download: (PDF) HerDocument2 pagesClick Here For Download: (PDF) HerJerahm Flancia0% (1)
- MahayanaDocument26 pagesMahayanaAleza Menorca100% (1)
- G.R. No. 201354 September 21, 2016Document11 pagesG.R. No. 201354 September 21, 2016Winston YutaNo ratings yet
- Christiane Nord - Text Analysis in Translation (1991) PDFDocument280 pagesChristiane Nord - Text Analysis in Translation (1991) PDFDiana Polgar100% (2)
- FP010CALL Trabajo CO Ardila Jaime Molina PiñeyroDocument12 pagesFP010CALL Trabajo CO Ardila Jaime Molina PiñeyroRomina Paola PiñeyroNo ratings yet
- Amc Test Feb 2011Document8 pagesAmc Test Feb 2011mimovodaNo ratings yet
- A Renegade Psychiatrist's StoryDocument36 pagesA Renegade Psychiatrist's StorymimovodaNo ratings yet
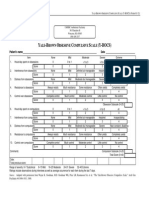
- YBOCRatingScale PDFDocument1 pageYBOCRatingScale PDFPriska ValiniaNo ratings yet
- (Psychology, Self-Help) Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) DiagnosisDocument2 pages(Psychology, Self-Help) Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) DiagnosisVeio MacieiraNo ratings yet
- Recall June11Document7 pagesRecall June11mimovodaNo ratings yet
- YBOCRatingScale PDFDocument1 pageYBOCRatingScale PDFPriska ValiniaNo ratings yet
- HalloDocument1 pageHallomimovodaNo ratings yet
- 130 Nov 12Document1 page130 Nov 12mimovodaNo ratings yet
- HalloDocument1 pageHallomimovodaNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument1 pageIntroductionmimovodaNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument1 pageIntroductionmimovodaNo ratings yet
- Ts 6Document1 pageTs 6mimovodaNo ratings yet
- PC 150Document1 pagePC 150mimovodaNo ratings yet
- BDDocument1 pageBDmimovodaNo ratings yet
- BDDocument1 pageBDmimovodaNo ratings yet
- You AreDocument1 pageYou AremimovodaNo ratings yet
- HELLOODocument1 pageHELLOOmimovodaNo ratings yet
- HELLOODocument1 pageHELLOOmimovodaNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal Surgery: IntestineDocument3 pagesGastrointestinal Surgery: IntestinemimovodaNo ratings yet
- List of Naruto Char.Document40 pagesList of Naruto Char.Keziah MecarteNo ratings yet
- 2013 03 01 Maurizio Di Noia PresentationDocument80 pages2013 03 01 Maurizio Di Noia PresentationRene KotzeNo ratings yet
- DBS AR 2019 Final Final PDFDocument371 pagesDBS AR 2019 Final Final PDFDevi Nurusr100% (1)
- Causing v. ComelecDocument13 pagesCausing v. ComelecChristian Edward CoronadoNo ratings yet
- Task 1 Methods in Teaching LiteratureDocument2 pagesTask 1 Methods in Teaching LiteratureJaepiNo ratings yet
- CPN Project TopicsDocument1 pageCPN Project TopicsvirginNo ratings yet
- Noorul Islam Centre For Higher Education Noorul Islam University, Kumaracoil M.E. Biomedical Instrumentation Curriculum & Syllabus Semester IDocument26 pagesNoorul Islam Centre For Higher Education Noorul Islam University, Kumaracoil M.E. Biomedical Instrumentation Curriculum & Syllabus Semester Iisaac RNo ratings yet
- Ready For First TB Unit3Document10 pagesReady For First TB Unit3Maka KartvelishviliNo ratings yet
- 5568 AssignmentDocument12 pages5568 AssignmentAtif AliNo ratings yet
- File 000011Document25 pagesFile 000011Jf LarongNo ratings yet
- Ra 9048 Implementing RulesDocument9 pagesRa 9048 Implementing RulesToffeeNo ratings yet
- Marriage and Divorce Conflicts in The International PerspectiveDocument33 pagesMarriage and Divorce Conflicts in The International PerspectiveAnjani kumarNo ratings yet
- HF CharactersDocument5 pagesHF CharactersAudri DebnathNo ratings yet
- Failure of Composite Materials PDFDocument2 pagesFailure of Composite Materials PDFPatrickNo ratings yet
- Portel's Value Chain AnalysisDocument3 pagesPortel's Value Chain AnalysisNivedNo ratings yet
- Kuo SzuYu 2014 PHD ThesisDocument261 pagesKuo SzuYu 2014 PHD ThesiskatandeNo ratings yet
- Course Content: SAP Fiori Implementation (SAPX03)Document3 pagesCourse Content: SAP Fiori Implementation (SAPX03)Jathin Varma KanumuriNo ratings yet
- Fraud Best PracticeDocument35 pagesFraud Best PracticeIkhwanNo ratings yet
- How Death Came To The CityDocument3 pagesHow Death Came To The City789863No ratings yet