Professional Documents
Culture Documents
GIT - Esophagus
GIT - Esophagus
Uploaded by
sebarikattaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
GIT - Esophagus
GIT - Esophagus
Uploaded by
sebarikattaCopyright:
Available Formats
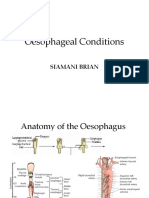
Esophagus
o o
Nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium musculature Skeletal mm. striated : upper 1/3 Smooth mm. lower 1/3 Mix of smooth and stiated in middle. o Embryology Develops from foregut by week 10 Upper esophagus : from branchial arches 4,5, and 6. o Blood supply Branches of inferior thyroid aa. upper Branches of aorta middle and lower Branch of gastric aa. lower and middle posteriorly o Nerve supply Symphathetic =sympathetic trunk Parasympathetic = vagus Motor = vagus Esophageal disorders o Dysphagia Difficulty swallowing Selective Solids worst than liquid Schatzkis ring o Intermittent and non progressive disphagia Usually in lower part of esophagus Peptic stricutures o Progressive w/ chronic heart burn Esophageal cancers o Progressive dysphagia o Age >50 YOA Non selective Both solids and liquids Achalasia o Progressive, chronic o Lower esophageal sphincter (LES) fails to relax Loss of Myenteric plexus Dialated esophagus on barium swallow Bird beak appearance nd 2 due to Chagas disease
Gastrointestinal tract GIT
Cardiomyopathy + Megacolon o Increased risk of esophageal carcinoma o Scleroderma: CREST syndrome E: esophageal dysmotility due to pressure proximal to LES. o Clinically Dysphagia solid + liquid Regurgitation of food at night Weight loss o Tx Injection of botulinum toxin endoscopy Pneumatic dilatation of LES w/ a balloon Surgery: Modified Hellers myotomy Diffuse esophageal spasm o Intermittent comes and goes Scleroderma o Chronic heart burn o CREST syndrome
Odynophagia Sharp substernal pain on swallowing Usually severe erosive disease Mostly due to infection o Candidiasis, Herpes virus nd 2 to corrosive injury o Caustic ingestion poison, acid, bleach, etc. o Pill induced Heart burn Substernal burning pain radiating to neck Acid reflux to esophagus Highly specific to GERD Dx tools Esophagoscopy Barium esophagraphy Esophageal manometry Esophageal pH recording Esophagitis Etiology Infectious o Candida, CMV, Herpes virus, HIV, varicella Corrosive esophagitis o 2nd to caustic substance ingestion Pill induced o Alendronate, Doxycycline, ASA, iron sulfate, Quinidine Clinical symptoms
Dx
Heart burn, Odynophagia
Clinically monitoring the progress w/ antiviral and antifungal agents Endoscopy for resistant cases only Pill induced: prevent by taking pills w/ water in upright position after a meal Barrets Esophagus Premalignant condition Metaplasia Squamous epithelium replaced by columnar epithelium Sequel to chronic reflux d/o Sx Dysphagia Reflux sx: heart burn, regurgitation Dx Edoscopically diagnosed o Circumferential or tongue like orange colored gastric mucosa running up into distal tubular esophagus o 3 types of mucosa Gastric cardiac Gastric fundic Intestinal metaplasia risk of carcinoma w/ this type o If unnoticed / not tx can lead to Stricture and bleeding Adenocarcinoma - rare Tx Proton pump inhibitors Surgery o Endoscopic surveillance w/ biopsy every 2-3 yrs o Endoscopic ablation o Endoscopic mucosal resection high grade dysplasias o Resection of segment w/ metaplasia GastroEsophageal Reflux Disorder GERD Risk factors Incompetent LES Hiatal hernia Irritable effect of refluxate Abnormal esophageal clearance Delayed gastric emptying Sx Heart burn by recumbency, meals, bending Tx Mild GERD: lifestyle changes, Antaacids, H2 receptor blockers Moderate GERD: H2 receptor blockers, Proton pump inhibitors, promotility drugs
Severe GERD: unresponsive to PPIs, surgical w/ Nissans fundoplication Diffuse esophageal spasm DES Esophageal dysmotility syndrome of smooth mm. Spontaneous non peristaltic contractions Sx Dysphagia Non cardiac chest pain Manometery (ambulatory) Simultaneous un coordinated esophageal contactions o CORK SCREW on barium swallow Tx Calcium channel blockers Nitrates Mallory-Weiss Syndrome Nonpenetrating mucosal tear at GastroEsophageal junction Sx Induced by: retching, lifting heavy objects, vomiting in Hx Strong predisposition to alcohol Sudden hemetemesis NO MELENA Tx Fluid resuscitation + blood transfusion Endoscopic hemostatic therapy Angiographic arterial embolization Esophageal webs Thin, diaphragm like membranes of mucosa Congenital, Graft vs. host disease Pemphigus vulgaris, pemphigoid Plummer-Vinson Syndrome w/ iron deficiency anemia Esophageal rings Smooth circumferential thin structures Common in distal esophagus Seen in GERD, Haital hernia Sx: Dysphagia Dx: barium esophagogram Tx: Bougie dilatation Zenkers diverticulum Mucosal protrusion through pharyngoesophageal junction b/w cricopharyngeus + inferior cricopharyngeus mm. due to loss of elasticity of upper esophageal sphincter Sx: dysphagia + regurgiatation of food
Complication: Halistosis bad breath Bronchiectasis, pneumonia, Lung abscess* Tx: diverticulotomy, esophago myotomy Esophageal carcinoma Epidemilogy Age: 50-70 YOA M>F - 3:1 Squamous cell carcinoma common in Blacks Adenocarcinoma common in Whites Common site: distal 1/3 of esophagus Risk factors Squamous cell carcinoma o Alcohol, tobacco o Caustic induced esophageal strictures o Achalasia Adenocarcinoma o Barretts esophagus Sx Progressive dysphagia Malaise, weakness, weight loss Hoarseness of voice* Chest pain Cervical + Supraclavicula lymphadenopathy** Organ infiltration with metastasis Evaluation Non specific changes Anemia Abnormal liver function tests 2ndary metastasis Dx CXR: widened mediastinum -- 2nd adenopathy Barium swallow: polypoid or infiltrative or ulcerative lesion Endoscopy w/ biopsy = definite Dx** Tx Extensive local spread or metastasis = Palliative care Radiation, Laser (yag) Stents placement Photodynamic therapy Surgery o For stage 1 and stage 2A -- esophagectomy Chemotherapy + radiotherapy o Cisplatinum, Flurouracil
You might also like
- Overview of Lower GastroIntestinal Bleeding 1.1Document42 pagesOverview of Lower GastroIntestinal Bleeding 1.1Raja Ain100% (1)
- Gastrointestinal PathologyDocument14 pagesGastrointestinal PathologyRahul ShuklaNo ratings yet
- OB Power Point Presentation 002Document57 pagesOB Power Point Presentation 002RitamariaNo ratings yet
- Freudian Theory: Psychoanalytical Theory Psychosexual TheoryDocument25 pagesFreudian Theory: Psychoanalytical Theory Psychosexual TheoryAmelita KulalladNo ratings yet
- Esophagous Stomach Small Intestine PathologyDocument58 pagesEsophagous Stomach Small Intestine PathologytahaNo ratings yet
- MED Diseases of The EsophagusDocument4 pagesMED Diseases of The EsophagusJulie Anne AciertoNo ratings yet
- Test 2 NotesDocument38 pagesTest 2 Notesbjpalmer100% (2)
- DysphagiaDocument35 pagesDysphagiaBashar KhalilNo ratings yet
- Esophageal and Stomach Pathology-May+2019Document71 pagesEsophageal and Stomach Pathology-May+2019Karami Brutus0% (1)
- Surgery EORDocument76 pagesSurgery EORAndrew BowmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 - Gastrointestinal TractDocument29 pagesChapter 17 - Gastrointestinal TractAgnieszka WisniewskaNo ratings yet
- Wa0001Document41 pagesWa0001Riya ShindeNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal System: Symptomatology of TheDocument85 pagesGastrointestinal System: Symptomatology of TheAbdelrahman MokhtarNo ratings yet
- Dysphagia: Dr. Sameeah A. Rashid MBCHB, DMRD, Fibms College of Medicine, Hawler Medical UniversityDocument35 pagesDysphagia: Dr. Sameeah A. Rashid MBCHB, DMRD, Fibms College of Medicine, Hawler Medical UniversityDarawan MirzaNo ratings yet
- Oesophagus StomachDocument28 pagesOesophagus Stomachwanja91No ratings yet
- GI Sympt Mokhtar (2015)Document85 pagesGI Sympt Mokhtar (2015)Abdelrahman MokhtarNo ratings yet
- Materi Kep. Kritis Acute GI BleedingDocument35 pagesMateri Kep. Kritis Acute GI Bleedingharsani auroraNo ratings yet
- Surgical Disease of The Esophagus: Mahteme Bekele, MD Assistant Professor of SurgeryDocument72 pagesSurgical Disease of The Esophagus: Mahteme Bekele, MD Assistant Professor of SurgeryBiniamNo ratings yet
- Acute Gi Bleeding: Rohman AzzamDocument34 pagesAcute Gi Bleeding: Rohman AzzamgebyarayuNo ratings yet
- De VIRGILIO-10Document36 pagesDe VIRGILIO-10Dr-Mohammad Ali-Fayiz Al TamimiNo ratings yet
- Esophageal DisordersDocument37 pagesEsophageal DisordersDanielle FosterNo ratings yet
- GIT Fully DoneDocument14 pagesGIT Fully DoneTirtha Taposh100% (1)
- Esophageal ConditionsDocument43 pagesEsophageal ConditionsMICHAEL SAKALANo ratings yet
- Dysphagia: Ian Paul Titus DM FRCSDocument59 pagesDysphagia: Ian Paul Titus DM FRCSGiovanni HenryNo ratings yet
- EsophagusDocument26 pagesEsophagusamadoorahmedNo ratings yet
- GastroenterologySlides2020 Copy TG6Document33 pagesGastroenterologySlides2020 Copy TG6yasmeen.houshiehNo ratings yet
- Dysphagia: DR (Prof.) A B Singh Unit Department of General Surgery Patna Medical College & HospitalDocument48 pagesDysphagia: DR (Prof.) A B Singh Unit Department of General Surgery Patna Medical College & HospitalAswin Rajasekaran100% (1)
- Management of Gastroesophagea L Reflux in ElderlyDocument40 pagesManagement of Gastroesophagea L Reflux in ElderlyPrimarini RiatiNo ratings yet
- DYSPHAGIADocument35 pagesDYSPHAGIAChristopher Yeoh100% (2)
- Barret's & Tumors of Esophagus, SR, April 20Document52 pagesBarret's & Tumors of Esophagus, SR, April 20Tehreem NadeemNo ratings yet
- 07a. Non Neoplastic Disease of OesophagusDocument35 pages07a. Non Neoplastic Disease of Oesophagus21701101016 - Juliana Ayu NugrahaNo ratings yet
- Diseases of Esophagus & Dysphagia: Dr. Vishal SharmaDocument146 pagesDiseases of Esophagus & Dysphagia: Dr. Vishal SharmaMohamed KamaraNo ratings yet
- Surgical Diseases of The EsophagusDocument35 pagesSurgical Diseases of The Esophagusmogesie1995No ratings yet
- Pancreatitis & Pseudocyst in ChildrenDocument56 pagesPancreatitis & Pseudocyst in ChildrendrkiranmNo ratings yet
- Acute GI BleedingDocument35 pagesAcute GI BleedingGalih GimastiarNo ratings yet
- Esophageal Motility Disorders: DR / Hytham NafadyDocument31 pagesEsophageal Motility Disorders: DR / Hytham NafadyRabie MeramNo ratings yet
- About The Diseases. Gallbladder & Biliary Tract DisordersDocument10 pagesAbout The Diseases. Gallbladder & Biliary Tract DisordersJeenah HannahNo ratings yet
- DYSPHAGIA FINALgDocument48 pagesDYSPHAGIA FINALgSurbhi BhartiNo ratings yet
- PathologyDocument28 pagesPathologyninja-2001No ratings yet
- Radiologi Kasus DigestifDocument110 pagesRadiologi Kasus DigestifarifgteguhNo ratings yet
- Abdominallecture 2015Document103 pagesAbdominallecture 2015Abdelrahman MokhtarNo ratings yet
- Pead 3 - Abdominal Pain and VommitingDocument22 pagesPead 3 - Abdominal Pain and Vommitingbbyes100% (1)
- Dysphagia: Dr. Sangeeta Aggarwal Assistant Professor, E.N.T Deptt GMCH, PatialaDocument29 pagesDysphagia: Dr. Sangeeta Aggarwal Assistant Professor, E.N.T Deptt GMCH, PatialaVishalNo ratings yet
- Small Bowel Obstruction: By: Dr. Yasser El Basatiny Prof. of Laparoscopic SurgeryDocument41 pagesSmall Bowel Obstruction: By: Dr. Yasser El Basatiny Prof. of Laparoscopic SurgerydenekeNo ratings yet
- Ascites New and ManagementDocument29 pagesAscites New and ManagementANENA RHODANo ratings yet
- Bowel ObstructionDocument48 pagesBowel ObstructionPatrick John100% (1)
- Yosephine Case 5aDocument31 pagesYosephine Case 5aRanto B. TampubolonNo ratings yet
- Gallbladder and Pancrease PathologyDocument4 pagesGallbladder and Pancrease Pathologyjohn smithNo ratings yet
- Clinical Approach To Patient With Gastrointestinal DiseaseDocument5 pagesClinical Approach To Patient With Gastrointestinal DiseasePriyanka SamalNo ratings yet
- Inflammatory DisordersDocument18 pagesInflammatory Disordersfebie pachecoNo ratings yet
- MED2 5.02 Oncologic Emergencies - Dr. F. AdefuinDocument5 pagesMED2 5.02 Oncologic Emergencies - Dr. F. AdefuinAra DiocosNo ratings yet
- Esophagus: Diseases of The EsophagusDocument60 pagesEsophagus: Diseases of The EsophagusSalma NajjarNo ratings yet
- GI Quiz 1 NotesDocument8 pagesGI Quiz 1 NotesSara JosephNo ratings yet
- Acute Gastroenteritis: DR Tjatur Winarsanto SPPDDocument34 pagesAcute Gastroenteritis: DR Tjatur Winarsanto SPPDMayiz Renata LimerseNo ratings yet
- GI ReviewDocument44 pagesGI Reviews129682No ratings yet
- Diseases of OesophagusDocument46 pagesDiseases of OesophagusBrother GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Emergency Medicine: Acute AbdomenDocument33 pagesEmergency Medicine: Acute AbdomenPrashant MishraNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal O The Esophagus O The Stomach O The Small Intestine O The Large Intestine The Liver The Gallbladder The Pancreas Diabetes The KidneyDocument53 pagesGastrointestinal O The Esophagus O The Stomach O The Small Intestine O The Large Intestine The Liver The Gallbladder The Pancreas Diabetes The KidneymickeyNo ratings yet
- Carcinoma StomachDocument54 pagesCarcinoma StomachDn Ezrinah Dn EshamNo ratings yet
- Morport 12 Des 17Document31 pagesMorport 12 Des 17Cindhy Karania Metta SilavattoNo ratings yet
- Helminth 3Document2 pagesHelminth 3Farlogy100% (6)
- Hypo Phosphate MiaDocument7 pagesHypo Phosphate MiaChristian Manuel Chiara ChiletNo ratings yet
- Blountdisease 180424165537Document35 pagesBlountdisease 180424165537Agung TobingNo ratings yet
- Syntonic Phototherapy PMLS Aug 2010 PDFDocument5 pagesSyntonic Phototherapy PMLS Aug 2010 PDFmarco avilaNo ratings yet
- Hypercalcemic Crisis: A Case Study: Loren A. Crown, M.D. Andra Kofahl, EMT-P Robert B. Smith, M.DDocument4 pagesHypercalcemic Crisis: A Case Study: Loren A. Crown, M.D. Andra Kofahl, EMT-P Robert B. Smith, M.DRo KohnNo ratings yet
- Oxygen PresentationDocument26 pagesOxygen PresentationPennyStevana100% (1)
- Drug Discovery Research in Pharmacognosy - Vallisuta O & Olimat SM (Editors) PDFDocument254 pagesDrug Discovery Research in Pharmacognosy - Vallisuta O & Olimat SM (Editors) PDFShailaja SharmaNo ratings yet
- Coronary Artery Disease-Willerson 2015-Pg 228-254Document27 pagesCoronary Artery Disease-Willerson 2015-Pg 228-254Muthu KumarNo ratings yet
- Principles of AmputationDocument72 pagesPrinciples of Amputationptannenbaum100% (6)
- E5 T5.4 - Blood TransfusionDocument45 pagesE5 T5.4 - Blood TransfusionIndah KomalasariNo ratings yet
- Anesthetic Drugs PharmacologyDocument33 pagesAnesthetic Drugs PharmacologynasyariesNo ratings yet
- Intracanal Medicaments and IrrigantsDocument85 pagesIntracanal Medicaments and IrrigantsAmit Abbey100% (1)
- Hipertensi EmergencyDocument31 pagesHipertensi Emergencysar tikaNo ratings yet
- Post Extraction AbstractDocument8 pagesPost Extraction AbstractThangam VeluNo ratings yet
- Journals Abbreviations A-ZDocument477 pagesJournals Abbreviations A-ZHitesh VermaNo ratings yet
- Journal Reading: Oleh DR Frensi Ayu PrimantariDocument23 pagesJournal Reading: Oleh DR Frensi Ayu PrimantariFrensi Ayu PrimantariNo ratings yet
- Table 2. Seven NANDA-I, NIC, and NOC Linkages in Psychosocial DimensionDocument5 pagesTable 2. Seven NANDA-I, NIC, and NOC Linkages in Psychosocial Dimensionabdurahmanlove1234No ratings yet
- Schema TherapyDocument4 pagesSchema Therapybhattiali6203100% (1)
- Clinical ReasoningDocument18 pagesClinical ReasoningAna IlmanianNo ratings yet
- Unit 1, Part 4 Clin. PKDocument11 pagesUnit 1, Part 4 Clin. PKshammaNo ratings yet
- Application Technique Traction PDFDocument25 pagesApplication Technique Traction PDFAZOZ 19No ratings yet
- Anestezia Epidurala Si SpinalaDocument5 pagesAnestezia Epidurala Si SpinalaRangu Liliana MarianaNo ratings yet
- A. Ward Round IPS Example FINALDocument5 pagesA. Ward Round IPS Example FINALEzra Ledya Sevtiana SinagaNo ratings yet
- Multipath Model PDFDocument10 pagesMultipath Model PDFAbhishek KumarNo ratings yet
- Clinical Pearls CardiologyDocument6 pagesClinical Pearls CardiologyMaritza24No ratings yet
- DivorceDocument21 pagesDivorcepatundeNo ratings yet
- Biomech of Head Gear-Ortho / Orthodontic Courses by Indian Dental AcademyDocument57 pagesBiomech of Head Gear-Ortho / Orthodontic Courses by Indian Dental Academyindian dental academy100% (2)
- Herpes Simplex Virus 1 (HSV1)Document9 pagesHerpes Simplex Virus 1 (HSV1)helmiNo ratings yet
- Hodgkin's Lymphoma, Previously Known As Hodgkin's Disease, Is A Type ofDocument9 pagesHodgkin's Lymphoma, Previously Known As Hodgkin's Disease, Is A Type ofMarilou PadillaNo ratings yet