Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Recording Studio Basics
Uploaded by
NadiaPriciaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Recording Studio Basics
Uploaded by
NadiaPriciaCopyright:
Available Formats
Nadia Rey April 19, 2011 Audio 1102 Chapter 2: Modern Recording Studio // Recording Studio Basics
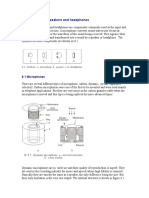
This chapter discusses sound sources in a recording environment and how they are perceived. Transducers convert energy from one form to another. The se transducers come in many forms like our ears or microphones. Microphones are constructed of a diaphragm, which picks up fluctuati ons in air pressure. This is converted into electrical energy. Microphones come in many forms; dynamic, ribbon and condenser. The dynamic microphone is the most common type. This microphone does not require phantom power. The fluctuation from the diaphragm creates an electr ic current which transforms the acoustical energy into electrical energy. This i s known as electromagnetic induction. Ribbon microphones contain a thin piece of metal, which acts as the diaphragm and the transducer. They are less sensitive than the dynamic moving co il microphone. They require more gain from a pre-amp than most other mics. The ribbon is smaller and can be easily damaged, so it should not be used with p hantom power, be hit or dropped. Condenser microphones require phantom power [+48v], do not have coil s or ribbons but are equipped with what is known as a capacitor. When the diaphr agm is moved through acoustical energy it move creating capacitance between the two plates in the capacitor. This movement provides varying electrical energy, w hich produces a pattern similar to a waveform. The continuation of the chapter covers basic audio equipment found i n a recording session or studio, DI boxes, compressors, preAmps,EQs, and recordi ng consoles/mixers. EQ s boost or cut certain frequencies in any sound, compressors find the middle ground between the loudest and softest sound, DI boxes convert line leve l signals into mic level signals (guitars/bass), preamps boost from prosumer to pro level and recording consoles/mixers can come in different forms such as digi tal or analog and are used in a variety of ways to effect an audio signal. The e ffects of gain amplification or attenuation, dynamic processing and equalization .
You might also like
- How Do Microphones WorkDocument6 pagesHow Do Microphones Workprabhjotkaur12No ratings yet
- Pro Engineer School Vol (1) .1Document101 pagesPro Engineer School Vol (1) .1Light HouseNo ratings yet
- Microphone GuideDocument33 pagesMicrophone GuideMarrylyn ArcigaNo ratings yet
- Microphone PDFDocument19 pagesMicrophone PDFChandra Pratap ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Home HTTPD Data Media-Data 6 0300 0714 05 Briefguidetomics PDFDocument32 pagesHome HTTPD Data Media-Data 6 0300 0714 05 Briefguidetomics PDFGeorge NummelinNo ratings yet
- Audio AmplifierDocument4 pagesAudio Amplifierjohn micoNo ratings yet
- Audio TransducerDocument7 pagesAudio Transducernsengimana gilbertNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Microphones : IndexDocument6 pagesDynamic Microphones : IndexJuan Gabriel NiñoNo ratings yet
- #Microphones: A Diaphragm - The Sound Waves Strike The Diaphragm, Causing It To VibrateDocument24 pages#Microphones: A Diaphragm - The Sound Waves Strike The Diaphragm, Causing It To VibrateSebastian VANo ratings yet
- Baseband AudioDocument48 pagesBaseband Audiorahul09990No ratings yet
- Glossary 2Document12 pagesGlossary 2khadidjaNo ratings yet
- Microphone Techniques Live Sound Reinforcement SHURE PDFDocument39 pagesMicrophone Techniques Live Sound Reinforcement SHURE PDFNenad Grujic100% (1)
- 02 Mics & SpeakersDocument5 pages02 Mics & SpeakersAlex SantosNo ratings yet
- Choosing A Microphone: Microphone Types and Uses: Dynamic MicrophonesDocument7 pagesChoosing A Microphone: Microphone Types and Uses: Dynamic Microphonesgeraldstar22No ratings yet
- Microphone Techniques For Live Sound Reinforcement EnglishDocument39 pagesMicrophone Techniques For Live Sound Reinforcement EnglishnuelMan100% (3)
- Microphone WikiDocument20 pagesMicrophone WikiRaymond O. EjercitoNo ratings yet
- Microphone Techniques For Live Sound ReinforcementDocument23 pagesMicrophone Techniques For Live Sound ReinforcementAlexander KohNo ratings yet
- Electro-Acoustical Transducers, Equalisation and Filters: Concept of TransducerDocument13 pagesElectro-Acoustical Transducers, Equalisation and Filters: Concept of TransducerIsmail MusharafNo ratings yet
- Condenser MicrophonesDocument4 pagesCondenser MicrophonesKarthik NarayananNo ratings yet
- Chapter # 16: Loud Speakers, Headphones and EarpieceDocument12 pagesChapter # 16: Loud Speakers, Headphones and EarpieceMuhammad ArshadNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetism in Audio SystemsDocument15 pagesElectromagnetism in Audio SystemsSam JrNo ratings yet
- Audio Equipments Final PDFDocument83 pagesAudio Equipments Final PDFparamveer singhNo ratings yet
- Microphones, Speakers and HeadphonesDocument8 pagesMicrophones, Speakers and Headphonestanujchopra1No ratings yet
- Microphone Loudspeaker 1Document4 pagesMicrophone Loudspeaker 1bmoNo ratings yet
- MicrophonesDocument6 pagesMicrophonesMartin LewisNo ratings yet
- Audio Video System: Microphones & Loud SpeakersDocument15 pagesAudio Video System: Microphones & Loud SpeakersSATHISHKUMAR RNo ratings yet
- Microphones and Loudspeakers SummaryDocument12 pagesMicrophones and Loudspeakers Summarylester0% (1)
- AEC 207 Week 1Document11 pagesAEC 207 Week 1Ekemini SundayNo ratings yet
- Broadcast Engineering and AcousticsDocument33 pagesBroadcast Engineering and AcousticsAudie AmonNo ratings yet
- Microphones: The DynamicDocument14 pagesMicrophones: The DynamicDodo KlimkoNo ratings yet
- First Patent On Foil Electret Microphone by G. M. Sessler Et Al. (Pages 1 To 3)Document2 pagesFirst Patent On Foil Electret Microphone by G. M. Sessler Et Al. (Pages 1 To 3)ShinedinNo ratings yet
- Consumer Electronics PDFDocument22 pagesConsumer Electronics PDFXYZNo ratings yet
- Ce Model - 1 Ans KeyDocument16 pagesCe Model - 1 Ans KeyThiagu RajivNo ratings yet
- Microphone Research PaperDocument9 pagesMicrophone Research PaperBen AyersNo ratings yet
- Module 2 SOUND RECORDING AND REPRODUCTIONDocument92 pagesModule 2 SOUND RECORDING AND REPRODUCTIONRenz Dela Cruz ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Presentation On A Loudspeaker: Prepared byDocument20 pagesPresentation On A Loudspeaker: Prepared byrishipatel17No ratings yet
- Condenser Microphone: Capacitor Microphone or Electrostatic Microphone. Here, The Diaphragm Acts As One Plate of ADocument12 pagesCondenser Microphone: Capacitor Microphone or Electrostatic Microphone. Here, The Diaphragm Acts As One Plate of ADeepak MahtoNo ratings yet
- How Amplifiers Work1 by NafeesDocument5 pagesHow Amplifiers Work1 by NafeesnafeesNo ratings yet
- Microphones: I. How They WorkDocument12 pagesMicrophones: I. How They WorkAndrey SurkovNo ratings yet
- QUARTER 2 Lesson 2 (SCIENCE 10)Document4 pagesQUARTER 2 Lesson 2 (SCIENCE 10)Chermaine VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Live Sound Survival Guide WebDocument40 pagesLive Sound Survival Guide Webandrew_ai3100% (7)
- Barroso, Niko Angelo M. Broadcast Engineering: Current LoudspeakerDocument3 pagesBarroso, Niko Angelo M. Broadcast Engineering: Current LoudspeakerAchilles AldaveNo ratings yet
- Microphones and Its TypesDocument17 pagesMicrophones and Its TypesManushree MaityNo ratings yet
- Modify A Cheap LDC Condenser Microphone - 7 Steps (With Pictures) - InstructablesDocument1 pageModify A Cheap LDC Condenser Microphone - 7 Steps (With Pictures) - Instructablespepe sanchezNo ratings yet
- ASUCD Entertainment Council Rough Guide To Live Sound (Old Version)Document4 pagesASUCD Entertainment Council Rough Guide To Live Sound (Old Version)Tim KerbavazNo ratings yet
- Audiography Notes PDFDocument8 pagesAudiography Notes PDFKhatiwada Anoop100% (1)
- Speaker & Amplifier: Ayush Saini-CH12B1005 Harmanpreet Singh-CS12B1017 Udhav Sethi-ES12B1022Document10 pagesSpeaker & Amplifier: Ayush Saini-CH12B1005 Harmanpreet Singh-CS12B1017 Udhav Sethi-ES12B1022qwertyNo ratings yet
- Microphones Ssi AutosavedDocument3 pagesMicrophones Ssi Autosavedapi-355552263No ratings yet
- Consumer Electronics NotesDocument21 pagesConsumer Electronics NotesBhadresh Renuka88% (8)
- Chapter5 Sound-Reproduction ReducedDocument35 pagesChapter5 Sound-Reproduction Reducedmohamed zainNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument4 pagesReportHrishikesh KakatyNo ratings yet
- Audio Engg & Acoustic Lab ManualDocument44 pagesAudio Engg & Acoustic Lab ManualSabari Muthu RamanNo ratings yet
- AltoPro LiveSound Guide FinalDocument18 pagesAltoPro LiveSound Guide FinalBrandy ThomasNo ratings yet
- Project ProposalDocument5 pagesProject ProposalSarmast Bilawal Khuhro0% (1)
- So,You Want To Be An Audio Engineer: A Complete Beginners Guide For Selecting Audio GearFrom EverandSo,You Want To Be An Audio Engineer: A Complete Beginners Guide For Selecting Audio GearRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Amateur Radio Electronics on Your MobileFrom EverandAmateur Radio Electronics on Your MobileRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)