Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Abstract
Uploaded by
cytech6619Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Abstract
Uploaded by
cytech6619Copyright:
Available Formats
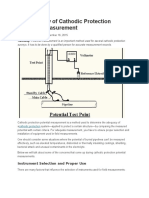
Abstract A definitive criterion for cathodic protection.
The corrosion reaction is defined using the Pourbaix Diagram and includes consideration of the pH, temperature, pressure, nobility of the metal and conductivity of the electrolyte. The passive zone can be established in a laboratory by creating a closed circuit condition in which the voltages can be measured. Natural corrosion cells occurring in simple conditions can be evaluated for the purpose of monitoring the performance of cathodic protection. Metal pipelines are complex networks of conductors submerged in electrolyte of infinitely variable qualities. The present method used to ascertain the effectiveness of cathodic protection has many inherent errors and results in costly and unpredictable corrosion failures. An electrode has been devised to define the exact electrical status of the corrosion reaction at the location of the test. The design allows a closed circuit measurement of the corrosion current that can determine the criterion at which corrosion has been stopped by cathodic protection. This has allowed the development of software that can calculate the condition and corrosion status throughout a network of pipelines using electrical circuit analysis, common in the electronics industry.
1269
You might also like
- Water Level Indicator Circuit Using Bipolar Junction TransistorFrom EverandWater Level Indicator Circuit Using Bipolar Junction TransistorRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (7)
- Digital Testing of HV Circuit BreakerDocument21 pagesDigital Testing of HV Circuit Breakervamshi4all100% (10)
- PDH - e 284Document21 pagesPDH - e 284HassenLNo ratings yet
- Hi Pot Test DetailsDocument7 pagesHi Pot Test Details2003vinay100% (1)
- Cathodic Protection DesignDocument30 pagesCathodic Protection Designmtuanlatoi9704No ratings yet
- CP DesignDocument36 pagesCP DesignhussainNo ratings yet
- FL - Hvac Instrumentation and ControlsDocument30 pagesFL - Hvac Instrumentation and Controlscytech6619No ratings yet
- Cathodic ProtectionDocument40 pagesCathodic Protectionjadav parixeet100% (1)
- The Basics of Cathodic ProtectionDocument17 pagesThe Basics of Cathodic ProtectionfernandoiescNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry Laboratory TextbookDocument130 pagesElectrochemistry Laboratory Textbookalois1917100% (2)
- Recent Developments in IEEE and IEC Standards For Off Line and On Line Partial Discharge Testing of Motor and Generator Stator WindingsDocument6 pagesRecent Developments in IEEE and IEC Standards For Off Line and On Line Partial Discharge Testing of Motor and Generator Stator WindingspanicoscribdNo ratings yet
- Monitoring Methods of Cathodic Protection of Pipelines PDFDocument13 pagesMonitoring Methods of Cathodic Protection of Pipelines PDFMarcos LeiteNo ratings yet
- Partial Discharge As A Quality Assurance Test For Motor Stator WindingsDocument6 pagesPartial Discharge As A Quality Assurance Test For Motor Stator WindingsKUNALJAYNo ratings yet
- A Theoretical Model For Corrosion Assessment in Overhead Line ConductorsDocument6 pagesA Theoretical Model For Corrosion Assessment in Overhead Line Conductorsdeathjester1No ratings yet
- Digital Testing of HV Circuit BreakerDocument24 pagesDigital Testing of HV Circuit Breakerankitsaxena27281% (21)
- Micro Controller Based PotentiostatDocument6 pagesMicro Controller Based PotentiostatMohamad Afif0% (1)
- 2012 11 Full Paper BROESDER Coatings-And-cathodic-disbondmentDocument7 pages2012 11 Full Paper BROESDER Coatings-And-cathodic-disbondmentkakrasana100% (1)
- 12 MGDP I 1150 0 (Instr Utility Air Calculation)Document2 pages12 MGDP I 1150 0 (Instr Utility Air Calculation)cytech6619No ratings yet
- Knowledge Sharing - Corrosion Monitoring in PPTSB - 21st August 2011Document11 pagesKnowledge Sharing - Corrosion Monitoring in PPTSB - 21st August 2011ahmad exsanNo ratings yet
- Ieee Schavenmaker 2000aDocument5 pagesIeee Schavenmaker 2000avallala venkateshNo ratings yet
- EFC-Chapter2 IntroductionElectrochemicalMonitoringDocument27 pagesEFC-Chapter2 IntroductionElectrochemicalMonitoringW BogaertsNo ratings yet
- 2014 - Modeling and Control of Impressed Current Cathodic Protection (ICCP) SystemDocument9 pages2014 - Modeling and Control of Impressed Current Cathodic Protection (ICCP) SystemademargcjuniorNo ratings yet
- An Overview of Cathodic Protection Potential MeasurementDocument7 pagesAn Overview of Cathodic Protection Potential MeasurementAlzaki AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Inspection For Corrosion: 8.1 Cathodic Protection Potential MeasurementsDocument3 pagesInspection For Corrosion: 8.1 Cathodic Protection Potential MeasurementsGetapo RaminNo ratings yet
- Digital Testing of Voltage CircuitDocument23 pagesDigital Testing of Voltage CircuitpraneethNo ratings yet
- Research Article The Influence of Blood Glucose Meter Resistance Variation On The Performance of A Biosensor With A Gold-Coated Circuit BoardDocument9 pagesResearch Article The Influence of Blood Glucose Meter Resistance Variation On The Performance of A Biosensor With A Gold-Coated Circuit Boardglucose glucoseNo ratings yet
- MatCorr56 (6) (2005)Document9 pagesMatCorr56 (6) (2005)Pako RosasNo ratings yet
- L PR MonitoringDocument8 pagesL PR MonitoringLikhith NalluriNo ratings yet
- Capacitance-Voltage Profiling and The Character Is at Ion of III-V Semiconductors Using Electrolyte BarriersDocument22 pagesCapacitance-Voltage Profiling and The Character Is at Ion of III-V Semiconductors Using Electrolyte BarriersAkhil MehrotraNo ratings yet
- Corrosion Science: L.Y. Xu, X. Su, Y.F. ChengDocument6 pagesCorrosion Science: L.Y. Xu, X. Su, Y.F. ChengArif PasaditaNo ratings yet
- Literature Review On Electrical ResistivityDocument5 pagesLiterature Review On Electrical Resistivityc5q1thnj100% (1)
- Corrater Probe Selection GuideDocument4 pagesCorrater Probe Selection GuideLWYenNo ratings yet
- 10 1002@1522-268320021023@203520@@aid-Elps35203 0 Co2-G PDFDocument8 pages10 1002@1522-268320021023@203520@@aid-Elps35203 0 Co2-G PDFBảo AnhNo ratings yet
- Electronic Rust ProtectionDocument2 pagesElectronic Rust ProtectionWisdom BasseyNo ratings yet
- PD Measurements On HV JointsDocument4 pagesPD Measurements On HV Jointsจีรศักดิ์ คงบุรีNo ratings yet
- Reference Electrodes For Monitoring of Cathodic Protection On Buried Pipelines R11 Approved November 2018Document32 pagesReference Electrodes For Monitoring of Cathodic Protection On Buried Pipelines R11 Approved November 2018Miie EmiieNo ratings yet
- Cor Cop N India 2004Document10 pagesCor Cop N India 2004abhi_luvme03No ratings yet
- Stojkovic 2013Document6 pagesStojkovic 2013Marko StojkovicNo ratings yet
- External Corrosion Direct Assessment: (ECDA)Document7 pagesExternal Corrosion Direct Assessment: (ECDA)amghardjillali_44923No ratings yet
- TMP 47 A7Document13 pagesTMP 47 A7FrontiersNo ratings yet
- Monitoring of Concrete Permeability, Carbonation and Corrosion Rates in The Concrete of The Containers of El Cabril (Spain) DisposalDocument8 pagesMonitoring of Concrete Permeability, Carbonation and Corrosion Rates in The Concrete of The Containers of El Cabril (Spain) Disposalmihaela_filip_8No ratings yet
- Grassini 2016Document16 pagesGrassini 2016Mohamed BenchikhNo ratings yet
- Study of Impressed Current Cathodic Protection (ICCP) On The Steel Pipeline Under DC Stray Current InterferenceDocument17 pagesStudy of Impressed Current Cathodic Protection (ICCP) On The Steel Pipeline Under DC Stray Current InterferenceMahir DžafićNo ratings yet
- HVE PresentationDocument41 pagesHVE PresentationJaswant RathoreNo ratings yet
- Pengujian Konduktivitas Listrik - 1Document4 pagesPengujian Konduktivitas Listrik - 1AviceniaMarinaIrianiNo ratings yet
- A Method For Determining Arc Breakdownin Low-Voltage Electrical NetworksDocument15 pagesA Method For Determining Arc Breakdownin Low-Voltage Electrical NetworksdaaanuNo ratings yet
- Loop TestingDocument2 pagesLoop TestingVelitinelNo ratings yet
- Çok Önemli̇ KaynakDocument6 pagesÇok Önemli̇ KaynakYesim YilmazNo ratings yet
- How Cathodic Protection WorksDocument4 pagesHow Cathodic Protection WorksluongttluongNo ratings yet
- Partial Discharge: o o o o o o o o o oDocument4 pagesPartial Discharge: o o o o o o o o o oNavdeep KaurNo ratings yet
- Safety: Practical 2P7 - CorrosionDocument20 pagesSafety: Practical 2P7 - CorrosionAbdul MalikNo ratings yet
- Ultra ConductorsDocument19 pagesUltra ConductorsAnu Kp100% (3)
- An Overview of Cathodic Protection Potential MeasurementDocument7 pagesAn Overview of Cathodic Protection Potential MeasurementKhanh DTNo ratings yet
- Current Sensors Using Magnetic MaterialsDocument7 pagesCurrent Sensors Using Magnetic MaterialsSuttisak SuriyachanhomNo ratings yet
- FEE Manual Sem2Document60 pagesFEE Manual Sem2ghadgeom25No ratings yet
- Development of An Electronic Instrument For Eddy Current TestingDocument9 pagesDevelopment of An Electronic Instrument For Eddy Current TestingsafaaNo ratings yet
- Development of Electrochemical Micro Machining For Air-Lubricated Hydrodynamic BearingsDocument6 pagesDevelopment of Electrochemical Micro Machining For Air-Lubricated Hydrodynamic BearingsMark LambertNo ratings yet
- Effect of Measurement and Instrumentation Errors On Potential ReadingsDocument10 pagesEffect of Measurement and Instrumentation Errors On Potential Readingssohrab25No ratings yet
- Ultra ConductorsDocument19 pagesUltra ConductorsI79E1A0 4i6No ratings yet
- Rowland 2008ADocument9 pagesRowland 2008ASavvas KatemliadisNo ratings yet
- Clamp ConnectorsDocument3 pagesClamp Connectorscytech6619No ratings yet
- Non-Insulated Terminals & Sleeves: For Safety UseDocument1 pageNon-Insulated Terminals & Sleeves: For Safety Usecytech6619No ratings yet
- Hydrastep WorkingDocument166 pagesHydrastep WorkingAyan ChattarajNo ratings yet
- Sensepoint XCD: Flammable, Toxic and Oxygen Gas Detector For Industrial ApplicationsDocument8 pagesSensepoint XCD: Flammable, Toxic and Oxygen Gas Detector For Industrial Applicationscytech6619No ratings yet
- Hydrastep & Hydratect Water/steam Monitoring Systems: Solartron Mobrey LTD B246801Document7 pagesHydrastep & Hydratect Water/steam Monitoring Systems: Solartron Mobrey LTD B246801cytech6619No ratings yet
- Hydrastep and Hydratect Water/Steam Monitoring SystemsDocument12 pagesHydrastep and Hydratect Water/Steam Monitoring Systemscytech6619No ratings yet
- A08 eDocument3 pagesA08 ecytech6619No ratings yet
- Hydrastep and Hydratect Water/Steam Monitoring SystemsDocument12 pagesHydrastep and Hydratect Water/Steam Monitoring Systemscytech6619No ratings yet
- Equal AnglesDocument2 pagesEqual Anglescytech6619No ratings yet
- Flat BarsDocument3 pagesFlat Barscytech6619No ratings yet
- 2851 - MS Electrical WorksDocument16 pages2851 - MS Electrical WorksleoconsolacionNo ratings yet
- Checkered PlatesDocument1 pageCheckered PlatesRamilArtatesNo ratings yet
- DELL PowerEdge R710 Technical GuideBookDocument63 pagesDELL PowerEdge R710 Technical GuideBooksimon_sparks_1No ratings yet
- Deformed BarsDocument1 pageDeformed Barscytech6619No ratings yet
- Channels: Tis / Jis Standards (TIS 1227: 1996 / JIS G3192: 1990)Document2 pagesChannels: Tis / Jis Standards (TIS 1227: 1996 / JIS G3192: 1990)cytech6619No ratings yet
- Carbon Steel PipeDocument2 pagesCarbon Steel PipemadooNo ratings yet
- Earthtags LocknutsDocument1 pageEarthtags Locknutscytech6619No ratings yet
- Checkered PlateDocument1 pageCheckered Platecytech6619No ratings yet
- 4post and 2post Rails For Dell Poweredge: Installation Instructions Kit P/N: 2Ubrk-R7Document8 pages4post and 2post Rails For Dell Poweredge: Installation Instructions Kit P/N: 2Ubrk-R7cytech6619No ratings yet
- 4post and 2post Rails For Dell Poweredge: Installation Instructions Kit P/N: 2Ubrk-R7Document8 pages4post and 2post Rails For Dell Poweredge: Installation Instructions Kit P/N: 2Ubrk-R7cytech6619No ratings yet
- Sliding Rail Kit For Dell Servers: Installation Instructions P/N: 2URAIL-R7 P/N: 2UARM-R7 (Optional)Document4 pagesSliding Rail Kit For Dell Servers: Installation Instructions P/N: 2URAIL-R7 P/N: 2UARM-R7 (Optional)cytech6619No ratings yet
- Rack Guide v20Document37 pagesRack Guide v20cytech6619No ratings yet
- 475 477Document1 page475 477cytech6619No ratings yet
- 487 489Document1 page487 489cytech6619No ratings yet
- Insulated Adaptors ShroudsDocument1 pageInsulated Adaptors Shroudscytech6619No ratings yet
- Accessories: Nylon & Red Fibre Washers Serrated WasherDocument1 pageAccessories: Nylon & Red Fibre Washers Serrated Washercytech6619No ratings yet
- Assembly Instructions For Stopping Plug: 475/477 Exd I & Exd IIDocument1 pageAssembly Instructions For Stopping Plug: 475/477 Exd I & Exd IIcytech6619No ratings yet
- Thin Wall Section of Enclosure: Earth TagDocument1 pageThin Wall Section of Enclosure: Earth Tagcytech6619No ratings yet