Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Promethazine HCL
Promethazine HCL
Uploaded by
Anna Marie Ong ArseñaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Promethazine HCL
Promethazine HCL
Uploaded by
Anna Marie Ong ArseñaCopyright:
Available Formats
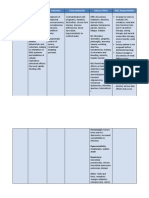
Drug Data Generic Name Promethazine HCl Trade Name Phenergan Minimum Dose 25 mg 1 tab q 4-6, Maximum Dose
50 mg 1 tab q 4 Contents Promethazine HCl Availability and color - Tablets: 12.5, 25, 50 mg - Syrup: 6.25, 25 mg/5mL - Suppositories: 12.5, 25, 50 mg - Injection: 25, 50 mg/mL Routes of administration Oral Intramuscular Intravenous
Classification Pharmacologic Class Phenothiazine Therapeutic Class Antiemetic, Antihistamine, Sedative, Hypnotic Pregnancy Risk Factor C
Mechanism of Action Selectively blocks the H1 receptors, diminishing the effects of histamine on cells of the upper respiratory tract and eyes and decreasing the sneezing, mucus production, itching and tearing that accompany allergic reactions in sensitized people exposed to antigens; blocks cholinergic receptors in the vomiting centre that are believed to mediate the nausea and vomiting caused by gastric irritation, by input from the vestibular apparatus, and by input from the chemoreceptor trigger zone; depresses the RAS, including the parts of the brain involved with wakefulness. Pharmacokinetics A: Well absorbed (Oral, IM); peak plasma concentrations after 2-3 hr. D: Widely distributed: Brain, crosses the placenta, enters breast milk. Protein-binding: 76-93%. M: Extensive hepatic 1st-pass metabolism; converted to promethazine sulfoxide, Ndesmethylpromethazine. E: Via urine and bile (as metabolites) Drug Half Life 9-16 hr
Indication General Indications - Prevention and treatment of nausea and vomiting associated with labyrinthitis - Prevention of motion sickness - Short-term management of insomnia - Symptomatic relief of perennial and seasonal allergic rhinitis, allergic conjunctivitis, uncomplicated urticaria and angioedema - Amelioration of allergic reactions to blood or plasma - Dermatographism, adjunctive therapy in anaphylactic reactions - Preoperative, postoperative, or obstetric sedation - Adjunct to analgesics to control postoperative pain - Adjunctive IV therapy with reduced amounts of meperidine or other opioid analgesics in special surgical conditions
Source: http://mims.com.ph/
Contraindications
Concentrations - Hypersensitivity to antihistamines or phenothiazines - Comatose patients - Severe CNS depression - Bone marrow depression - Vomiting of unknown cause - Concomitant therapy with MAOIs - Lactation Precaution - Lower respiratory tract disorders - Glaucoma - Prosthatic hypertrophy - CV disease, hypertension - Breast cancer - Thyrotoxicosis - Children - Child with history of sleep apnea - A family history of SIDS - Reyes syndrome - Elderly - Pregnancy Drug interaction Drug to drug - Additive anticholinergic effects with anticholinergic drugs - Increased frequency and severity of neuromuscular excitation and hypotension with methohexital, thiamylal, Phenobarbital anesthetic, thiopental - Enhanced CNS depression with alcohol Drug to food - none reported
Source: Karch, Amy: 2009 Lippincotts Nursing Drug Guide, pp. 999-1000
Adverse Reaction CNS: Dizziness, drowsiness, poor coordination, confusion, restlessness, excitation, seizures, tremors, headache, blurred vision, diplopia, vertigo, tinnitus CV: Hypotension, palpitations, bradycardia, tachycardia, extrasystoles Dermatologic: Urticaria, rash, photosensitivity, chills GI: Epigastric distress, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation GU: Urinary frequency, dysuria, urinary retention, decreased libido, impotence Hematologic: Hemolytic anemia, hypoplastic anemia, thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, agranulocytosis, pancytopenia Local: Thickening of bronchial secretions, chest tightness, dry mouth, nose and throat; respiratory depression, suppression of cough reflex, potential of aspiration Other: Tingling, heaviness and wetness of hands
Source: Karch, Amy: 2009 Lippincotts Nursing Drug Guide, p. 1000
Nursing Responsibilities
Before - Observe 15 rights in drug administration. - Assess for hypersensitivity and other contraindications. - Reduce dosage for patients with hepatic impairment. - Reduce dosage of barbiturates given concurrently with promethazine by at least a half. - Arrange for dosage reduction of opioid analgesics given concomitantly by onefourth to one-half. During - Do not give tablets or rectal suppositories to children younger than 2 yr. - Give IM injections deep into muscle. - Do not administer subcutaneously, tissue necrosis may occur. - Do not administer intrarterially; arteriospasm and gangrene of the limb may result. - Instruct to take drug exactly as prescribed. After - Instruct to avoid alcohol. - Instruct to avoid driving or engaging in other dangerous activities of dizziness, drowsiness or vision changes occur. - Educate about avoiding prolonged exposure to the sun, or using of sunscreen or covering garments. - Maintain fluid intake, use precautions against heatstroke in hot weather. - Report sore throat, fever, unusual bleeding or bruising, rash, fever, weakness, tremors, impaired vision, dark urine, pale stools, yellowing of the skin or eyes.
Source: Karch, Amy: 2009 Lippincotts Nursing Drug Guide, p. 999
Source: http://mims.com.ph/, Karch, Amy: 2009 Lippincotts Nursing Drug Guide, p. 999
Source: http://mims.com.ph/, Karch, Amy: 2009 Lippincotts Nursing Drug Guide, pp. 999-1000
Source: Karch, Amy: 2009 Lippincotts Nursing Drug Guide, pp. 1000-1001
You might also like
- Contract of Lease (Motor Vehicle)Document3 pagesContract of Lease (Motor Vehicle)Ivanne Hisoler71% (7)
- Threat Analysis CollateralDocument232 pagesThreat Analysis CollateralCedric LecanteNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis and Nursing Interventions For Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverDocument2 pagesNursing Diagnosis and Nursing Interventions For Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverThirdy Aquino82% (28)
- Basc-2 Presentation - All SlidesDocument59 pagesBasc-2 Presentation - All Slidesapi-290174387100% (1)
- HydrocortisoneDocument2 pagesHydrocortisoneIvanne Hisoler100% (15)
- Drug Study On DiazepamDocument1 pageDrug Study On DiazepamMaya Acosta BiruarNo ratings yet
- Naloxone and Benzylpenicillin DRUG STUDYDocument3 pagesNaloxone and Benzylpenicillin DRUG STUDYNasrah N. Musa100% (3)
- Ofloxacin Drug StudyDocument2 pagesOfloxacin Drug StudyCheezy Bread100% (1)
- Daily Assignment PlanDocument2 pagesDaily Assignment PlanIvanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- HydralazineDocument1 pageHydralazineIvanne Hisoler75% (8)
- World Food Safety Guidelines 2010Document91 pagesWorld Food Safety Guidelines 2010Len Villamoya SimpasNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal NursingDocument8 pagesGastrointestinal Nursingohsnapitslei90% (10)
- Drug Classification Action of Drug Indication and Contraindication Side Effect Nursing ConsiderationDocument2 pagesDrug Classification Action of Drug Indication and Contraindication Side Effect Nursing ConsiderationDanica Kate GalleonNo ratings yet
- PromethazineDocument3 pagesPromethazineGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- DroperidolDocument1 pageDroperidolIvanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- Ritalin LA: Initial, 20 MG PO qAM May Adjust Dose in Weekly 10-mg Incremen TS, Not To Exceed 60 Mg/day (Patients Requiring A Lower InitialDocument2 pagesRitalin LA: Initial, 20 MG PO qAM May Adjust Dose in Weekly 10-mg Incremen TS, Not To Exceed 60 Mg/day (Patients Requiring A Lower InitialKwin SaludaresNo ratings yet
- Clomid Drug StudyDocument3 pagesClomid Drug StudySheen Ivashkov-BelikovNo ratings yet
- ChlorphenamineDocument1 pageChlorphenaminereinaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study PethidineDocument2 pagesDrug Study Pethidinerica sebabillonesNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Amphotericin B, Meropenem, Furosemide, Ciprofloxacin, Pentoxifylline, Pip-Tazo, Midazolam, VecuroniumDocument12 pagesDrug Study Amphotericin B, Meropenem, Furosemide, Ciprofloxacin, Pentoxifylline, Pip-Tazo, Midazolam, Vecuroniumpaupaulala100% (4)
- Drug Study - MidazolamDocument8 pagesDrug Study - MidazolamKian HerreraNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - HydrocodoneDocument2 pagesDrug Study - HydrocodoneTarquin Tomada86% (7)
- Generic Name:: Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indications Contraindi-Cation Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument1 pageGeneric Name:: Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indications Contraindi-Cation Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesmaemalabonNo ratings yet
- Phenergan (Promethazine)Document1 pagePhenergan (Promethazine)E100% (1)
- Phenytoin and Protamine SulfateDocument2 pagesPhenytoin and Protamine SulfateTintin Ponciano100% (1)
- Labetalol Hydro ChlorideDocument3 pagesLabetalol Hydro Chlorideapi-3797941100% (1)
- Drug Study: Labetalol Hydro ChlorideDocument6 pagesDrug Study: Labetalol Hydro ChlorideMark ToxNo ratings yet
- TRIAZOLAMDocument4 pagesTRIAZOLAMEzequiel RosalesNo ratings yet
- Librium ChlordiazepoxideDocument2 pagesLibrium ChlordiazepoxideENo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug Studyjazmine_caritos100% (2)
- Mechanism of Action Indication and Rationale Contraindication Common Side Effects Nursing Consideration While Taking The DrugsDocument1 pageMechanism of Action Indication and Rationale Contraindication Common Side Effects Nursing Consideration While Taking The DrugsPeter Emmil GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Drug Study of Magnesium SulfateDocument2 pagesDrug Study of Magnesium SulfateEm Hernandez Arana83% (6)
- Bleomycin Drug StudyDocument1 pageBleomycin Drug StudykyawNo ratings yet
- PhenobarbitalDocument1 pagePhenobarbitalSherwin LauronNo ratings yet
- Drug Study For AntaminDocument1 pageDrug Study For AntaminJILLIAN MARIE BARREDO100% (1)
- AmilorideDocument1 pageAmilorideRox San100% (1)
- DRUG STUDY Amoxicillin PDFDocument2 pagesDRUG STUDY Amoxicillin PDFMc SantosNo ratings yet
- DigoxinDocument1 pageDigoxinIvanne Hisoler100% (3)
- College of Health Sciences: Urdaneta City UniversityDocument2 pagesCollege of Health Sciences: Urdaneta City UniversityDan Dan Manaois100% (1)
- Drug Study-MethyldopaDocument4 pagesDrug Study-MethyldopaJinnijinniNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY (Diphenhydramine)Document2 pagesDRUG STUDY (Diphenhydramine)Avianna Calliope0% (1)
- Drug Study - AlfuzosinDocument1 pageDrug Study - AlfuzosinKian HerreraNo ratings yet
- Drug Study NubainDocument2 pagesDrug Study NubainLuige Avila100% (11)
- Generic Name (Brand Name) Methergine (Methylergonovine Maleate)Document3 pagesGeneric Name (Brand Name) Methergine (Methylergonovine Maleate)jennix_030883% (6)
- Drug Routes Side Effects Co4Ntraindications Nursing Responsibility Brand Name: Inhalation: CoughDocument2 pagesDrug Routes Side Effects Co4Ntraindications Nursing Responsibility Brand Name: Inhalation: CoughChristianne Janella PagadorNo ratings yet
- DisulfiramDocument1 pageDisulfiramIvanne Hisoler100% (1)
- A Drug Study On AlendronateDocument12 pagesA Drug Study On AlendronateTrio San LuisNo ratings yet
- Drug Action Indication Side Effect Adverse Effect Nursing ConsiderationsDocument1 pageDrug Action Indication Side Effect Adverse Effect Nursing ConsiderationsRo-anne AkuNo ratings yet
- XylocaineDocument1 pageXylocaineRozanne BanzaliNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indication/Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Responsibilities: GenericDocument2 pagesDrug Name Mechanism of Action Indication/Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Responsibilities: GenericArian May MarcosNo ratings yet
- Midazolam Drug Study SaclotDocument1 pageMidazolam Drug Study SaclotMaybelle Cababat SaclotNo ratings yet
- Case Study - DrugsDocument4 pagesCase Study - DrugsYza DizaNo ratings yet
- LidocaineDocument2 pagesLidocaineAhprelle Quiring Rodiel100% (1)
- Clonidine Hydrochloride (Drug Study)Document2 pagesClonidine Hydrochloride (Drug Study)Franz.thenurse688875% (4)
- Methotrexate )Document2 pagesMethotrexate )Angela Tenorio100% (2)
- Atropine Sulfate (Drug Study)Document3 pagesAtropine Sulfate (Drug Study)Franz.thenurse6888100% (1)
- Benzonatate (Drug Study)Document1 pageBenzonatate (Drug Study)Franz.thenurse6888No ratings yet
- Ativan (Lorazepam) Drug StudyDocument3 pagesAtivan (Lorazepam) Drug StudyCHERISE CORDOVA100% (2)
- Drug Study Atropine SulfateDocument1 pageDrug Study Atropine Sulfateirhizzp75% (8)
- Generic Name: Ordered: Indications: Contraindications BeforeDocument3 pagesGeneric Name: Ordered: Indications: Contraindications BeforeChenime Añana0% (1)
- DiazepamDocument1 pageDiazepamIvanne Hisoler71% (7)
- Pharmacologic: Onset: Peak: CnsDocument7 pagesPharmacologic: Onset: Peak: CnsCharissa Magistrado De LeonNo ratings yet
- AcetazolamideDocument3 pagesAcetazolamideGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Valproic Acid Drug StudyDocument4 pagesValproic Acid Drug StudyJeyser T. Gamutia100% (1)
- HydralazineDocument2 pagesHydralazineShermayne Mallapre HernandezNo ratings yet
- Antidepressants, Antihistamines, General Anesthetics, MAO Inhibitors, OpioidsDocument3 pagesAntidepressants, Antihistamines, General Anesthetics, MAO Inhibitors, Opioidskaycelyn jimenezNo ratings yet
- Drug 2Document4 pagesDrug 2Abie Jewel Joy RoqueNo ratings yet
- Psychotropic Drug Study in Psychiatry As A Nursing SpecialtyDocument4 pagesPsychotropic Drug Study in Psychiatry As A Nursing SpecialtyRoland YusteNo ratings yet
- For MaDocument9 pagesFor MaKathrina TumbagaNo ratings yet
- Republic vs. Castellvi DigestDocument1 pageRepublic vs. Castellvi DigestIvanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- Lumantas MD v. CalapizDocument2 pagesLumantas MD v. CalapizIvanne Hisoler100% (1)
- Land Titles Cases (6.21.14)Document31 pagesLand Titles Cases (6.21.14)Ivanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- Case Digest (QC v. Ericta)Document1 pageCase Digest (QC v. Ericta)Ivanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- Eminent Domain Case DigestsDocument18 pagesEminent Domain Case DigestsIvanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- Persons - Midterms NotesDocument23 pagesPersons - Midterms NotesEvina Michaela LupangoNo ratings yet
- MetoclopramideDocument1 pageMetoclopramideIvanne Hisoler89% (28)
- Terbutaline SulfateDocument1 pageTerbutaline SulfateIvanne Hisoler100% (2)
- Penicillin G BenzathineDocument1 pagePenicillin G BenzathineIvanne Hisoler100% (7)
- OxytocinDocument1 pageOxytocinIvanne Hisoler100% (7)
- MethadoneDocument2 pagesMethadoneIvanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- MethotrexateDocument2 pagesMethotrexateIvanne Hisoler83% (6)
- FurosemideDocument2 pagesFurosemideIvanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- DroperidolDocument1 pageDroperidolIvanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- Magnesium SulfateDocument1 pageMagnesium SulfateIvanne Hisoler67% (3)
- Dopamine HCLDocument1 pageDopamine HCLIvanne Hisoler100% (3)
- DiazepamDocument1 pageDiazepamIvanne Hisoler71% (7)
- DisulfiramDocument1 pageDisulfiramIvanne Hisoler100% (1)
- AmpicillinDocument1 pageAmpicillinIvanne Hisoler100% (1)
- DigoxinDocument1 pageDigoxinIvanne Hisoler100% (3)
- DactinomycinDocument1 pageDactinomycinIvanne Hisoler0% (2)
- Brain Aging OriginalDocument21 pagesBrain Aging Originaldocrubes50No ratings yet
- Parcare Assessment MaxillofacialDocument22 pagesParcare Assessment Maxillofacialqta omerNo ratings yet
- Ob Post TestDocument11 pagesOb Post TestAlexNo ratings yet
- Harrys Cosmetology Chapter 26 30Document110 pagesHarrys Cosmetology Chapter 26 30NidhiNo ratings yet
- Far Eastern Fox LoreDocument34 pagesFar Eastern Fox Loreardeegee100% (1)
- Obstetrics Test Blue PrintDocument8 pagesObstetrics Test Blue Printjose carlo araojoNo ratings yet
- Effect of Anxiety To Academic Performance of Students in Selected Grade 10 Students in Sta. Monica National High School School Year 2018-2019Document16 pagesEffect of Anxiety To Academic Performance of Students in Selected Grade 10 Students in Sta. Monica National High School School Year 2018-2019Ivan Mhel Salamat100% (3)
- HematopoiesisDocument35 pagesHematopoiesistika Purnama SariNo ratings yet
- The Human Body Systems: (Zoology Lecture)Document46 pagesThe Human Body Systems: (Zoology Lecture)शंकराय नमोNo ratings yet
- The Health Consequences of Human TraffickingDocument36 pagesThe Health Consequences of Human TraffickingWardiati YusufNo ratings yet
- DPP - Excretory Productes & Their Elimination PDFDocument7 pagesDPP - Excretory Productes & Their Elimination PDFKisna guptaNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal DevelopmentDocument40 pagesMusculoskeletal DevelopmentMajd HusseinNo ratings yet
- MTI - EME Prog. - Statutory Provisions - 08082019Document134 pagesMTI - EME Prog. - Statutory Provisions - 08082019omganesaNo ratings yet
- Diabetis-Metabolic DisordersDocument358 pagesDiabetis-Metabolic DisordersHampson MalekanoNo ratings yet
- Pedo Long AnswerDocument116 pagesPedo Long AnswersamikshaNo ratings yet
- Tibetan Buddhist Perspective On HealingDocument12 pagesTibetan Buddhist Perspective On Healingtpspace100% (2)
- Is 14543. 2004 Packaged Drinking Water SpecificationsDocument35 pagesIs 14543. 2004 Packaged Drinking Water SpecificationsRahmathNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology IIIDocument2 pagesPharmacology IIITejasNo ratings yet
- Problem Set Patterns of InheritanceDocument5 pagesProblem Set Patterns of InheritanceKarl RochaNo ratings yet
- Sarin Sirimongkolsakul - Interview Someone in Person About How Theyre Handling The QuarantineDocument1 pageSarin Sirimongkolsakul - Interview Someone in Person About How Theyre Handling The Quarantineapi-463449417No ratings yet
- Basic Life Support: DR - Dr. Zafrullah Khany Jasa, Span - KnaDocument47 pagesBasic Life Support: DR - Dr. Zafrullah Khany Jasa, Span - KnaHamba AllahNo ratings yet
- (Download pdf) Levin And Oneals The Diabetic Foot Diabetic Foot Levin Oneals 7Th Edition Version full chapter pdf docxDocument53 pages(Download pdf) Levin And Oneals The Diabetic Foot Diabetic Foot Levin Oneals 7Th Edition Version full chapter pdf docxmagnankuunyo55100% (5)
- Au Di Major Case Study HistoplasmosisDocument18 pagesAu Di Major Case Study Histoplasmosisapi-301816885No ratings yet
- Picea Abies Norway Spruce: Fact Sheet ST-448Document4 pagesPicea Abies Norway Spruce: Fact Sheet ST-448tdrnkNo ratings yet
- Parasitology Lec ReviewerDocument10 pagesParasitology Lec ReviewerPatricia Ann JoseNo ratings yet