100% found this document useful (1 vote)
3K views19 pagesBarium Enema
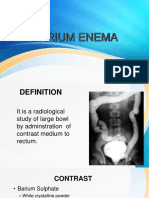
A barium enema is an x-ray exam used to view the large intestine. It involves inserting a catheter into the rectum and slowly infusing barium sulfate suspension and air to coat the bowel walls and distend the intestine for imaging. Multiple images are taken in different positions as the barium travels through the colon to fully visualize it. Potential complications include perforation, obstruction, or water intoxication.
Uploaded by
Hamzeh AlmasriCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (1 vote)
3K views19 pagesBarium Enema
A barium enema is an x-ray exam used to view the large intestine. It involves inserting a catheter into the rectum and slowly infusing barium sulfate suspension and air to coat the bowel walls and distend the intestine for imaging. Multiple images are taken in different positions as the barium travels through the colon to fully visualize it. Potential complications include perforation, obstruction, or water intoxication.
Uploaded by
Hamzeh AlmasriCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 19