Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mi Patho Ponr
Uploaded by
Fritz Regis W. TumaponCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mi Patho Ponr
Uploaded by
Fritz Regis W. TumaponCopyright:
Available Formats
Platelet adhesion & aggregation and fibrin deposition
Precipitating Factors Preexisting conditions: Diabetes mellitus
Predisposing Factors Treatment: Lifestyle: Rest & modification Age: >45 years (61 y/o) Gender: MALE Family lifestyle history of CHD
Formation of atherosclerotic plaque in the Hypertension coronary artery Lifestyle: High-fat diet Blood volume circulated into the myocardial tissue will be decreased, causing ischemia Smoking Sedentary lifestyle
Signs & Symptoms: Chest pain that usually happens during work but relieved by rest Dx test: Coronary angiography ECG
Pharmacologic: Nitroglycerin Antiplatelets Antilipedemics Beta blockers Surgical: CABG PTCA Good prognosis Etiology: Atherosclerosis Plaque continues to form Thrombosis/embolism Coronary stenosis/spasm Complete occlusion of the coronary artery Platelet aggregation If treated
If NOT treated cholesterol Low HDL X-ray
O2 deprivation of myocardial tissueslevels ofin shifting from Increased results LDL cholesterol aerobic to anaerobic metabolism
Accumulation of free acid and Macrophages releaselacticradicals that decrease in LDL oxidize cellular pH
Acidosis causes the myocardium to become Exposure of to lysosomal effects within the vulnerable subendothelial tissue to blood components to conduction disorders cell, and leads& endothelial cell loss
67
If ischemia is longer than 45 minutes, irreversible myocardial cell damage & necrosis occurs
Signs & Symptoms:
Pharmacologic management: Thrombolytic therapy within 3 hours of onset to restore vessel patency & minimize necrosis Nitroglycerin to relieve chest pain Morphine to relieve pain Aspirin for platelet inhibition IV heparin to promote patency in affected artery Lidocaine, epinephrine combat dysrhythmias Medical-surgical management: PTCA CABG Stent insertion to
As myocardial cells necrose, intracellular enzymes will be released
Atypical chest pain unrelieved by rest & nitroglycerin Nausea & dizziness Shortness of breath/difficulty of breathing Unexplained anxiety, weakness or fatigue
ACUTE MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION
If treated
Palpitations, diaphoresis or paleness
Fair prognosis
Infarcted area may compromise ventricular contractile function
Dx test: Coronary angiography ECG Radionuclide imaging
Decreased cardiac output
Cardiac enzyme tests (Troponin I, CK-MB, LDH, Myoglobin, AST)
Blood that should be pumped into the systemic circulation back up into the left atrium and into the lungs
Signs & Symptoms: Dyspnea, orthopnea Fatigue Crackles, cough hemoptysis non-productive
Shifting of intravascular fluid into the interstitium of the lung & pulmonary edema occurs
LEFT-SIDED HEART FAILURE
68 If treated
A
If NOT treated
B
If NOT treated
B Signs & symptoms: Fever Bacteria will colonize in the fluid Alveoli will be inflamed
Pharmacologic management: O2 administration Loop diuretics Intravenous nitrates (glycerol nitrate) Digoxin ACE inhibitors Beta-blockers Morphine Lifestyle modification
Crackles; non-productive cough Dx tests: Sputum AFB Pharmacological management: Antipyretics Mucolytics O2 administration Antibacterial therapy
Lung consolidation
Alveolar collapse
Low O2 saturation & decreased tissue perfusion
Poor prognosis Fair prognosis DEATH
69
70
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Afib NCPDocument3 pagesAfib NCPGen RodriguezNo ratings yet
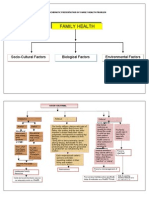
- Family Health: Socio-Cultural Factors Biological Factors Environmental FactorsDocument16 pagesFamily Health: Socio-Cultural Factors Biological Factors Environmental FactorsFritz Regis W. TumaponNo ratings yet
- Chest Tube ThoracostomyDocument1 pageChest Tube ThoracostomyFritz Regis W. TumaponNo ratings yet
- ER DRUGS AT A GLANCEDocument3 pagesER DRUGS AT A GLANCEmyleneacar100% (3)
- Table of ContentDocument2 pagesTable of ContentFritz Regis W. TumaponNo ratings yet
- BCU Edit Tomat PDFDocument16 pagesBCU Edit Tomat PDFmuhammad adamNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Tamponade: An Educational Review: Massimo Imazio and Gaetano Maria de FerrariDocument9 pagesCardiac Tamponade: An Educational Review: Massimo Imazio and Gaetano Maria de FerrariAngela OrozcoNo ratings yet
- Cardiac TamponadeDocument2 pagesCardiac TamponadechoobiNo ratings yet
- Lapsus + CHF CAD AbcDocument41 pagesLapsus + CHF CAD AbcMiftah Farid AsmaunNo ratings yet
- Clubbing Amd Myo InfracDocument7 pagesClubbing Amd Myo InfracokaciaNo ratings yet
- Manage Cardiac Output in Hyperthyroid PatientDocument3 pagesManage Cardiac Output in Hyperthyroid PatientPrincess QuirinaNo ratings yet
- BPS Board Certified Cardiology Syllabus For Entrance ExamDocument5 pagesBPS Board Certified Cardiology Syllabus For Entrance ExamGHAPRC RUDRAPURNo ratings yet
- Physio Control Lifepak 12 Operating Instructions 2Document187 pagesPhysio Control Lifepak 12 Operating Instructions 2A. A.G.No ratings yet
- Vijayalakshmi 2008Document7 pagesVijayalakshmi 2008Rakesh DashNo ratings yet
- Echocardiography Curriculum ToolDocument11 pagesEchocardiography Curriculum ToolJoseph BarkerNo ratings yet
- iFR Vs FFR For Guiding Coronary Revascularization - DEFINE-FLAIR (2 Year Results)Document32 pagesiFR Vs FFR For Guiding Coronary Revascularization - DEFINE-FLAIR (2 Year Results)rainmed USNo ratings yet
- Morgan 2012Document5 pagesMorgan 2012aixacamila3No ratings yet
- EHealth and COVIDDocument10 pagesEHealth and COVIDWalter ReyesNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan AnswerDocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan Answercoosa liquorsNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of Antiarrhythmic Drugs - RecordedDocument33 pagesPharmacology of Antiarrhythmic Drugs - RecordedSarah SabtiNo ratings yet
- Acute Coronary SyndromeDocument24 pagesAcute Coronary SyndromeMuhammad Alauddin Sarwar100% (8)
- Differences BTW ACS, Stable AnginaDocument7 pagesDifferences BTW ACS, Stable AnginaCarmenhNo ratings yet
- Tetralogy of Fallot: Cyanotic Congenital Heart DiseaseDocument31 pagesTetralogy of Fallot: Cyanotic Congenital Heart DiseaseJabir EspinaNo ratings yet
- Valvular Heart Diseases & CardiomyopathiesDocument73 pagesValvular Heart Diseases & CardiomyopathiesDammaqsaa W BiyyanaaNo ratings yet
- Cardiac DiseasesDocument8 pagesCardiac DiseasesTJ NgNo ratings yet
- Prometric McqsDocument30 pagesPrometric Mcqsjishan8250% (2)
- Ic Guía Esc 2021-99-128Document30 pagesIc Guía Esc 2021-99-128aassNo ratings yet
- 2023 Food Revolution Summit Docuseries ProgramDocument28 pages2023 Food Revolution Summit Docuseries Programelijoja06No ratings yet
- Cardiology 2012 MrcppassDocument127 pagesCardiology 2012 MrcppassRaouf Ra'fat SolimanNo ratings yet
- Acute Coronary SyndromeDocument19 pagesAcute Coronary SyndromeSherree HayesNo ratings yet
- IIA - Altered Tissue PerfusionDocument14 pagesIIA - Altered Tissue PerfusionDharylle CariñoNo ratings yet
- Hartrevalidatie PRL Eng KNGFDocument52 pagesHartrevalidatie PRL Eng KNGFsilkofosNo ratings yet
- Case Reports AbstractsDocument7 pagesCase Reports AbstractsNovie AstiniNo ratings yet
- ECG ErrorsDocument5 pagesECG ErrorsmikeNo ratings yet