Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Iv - Pathophysiology: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating Factor
Uploaded by
Jatevenzche Lao0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views1 pageObesity, poor nutrition, pre-existing conditions, and placental defects can precipitate preeclampsia by impairing placental implantation and endothelial function, increasing platelet activation and reducing blood flow. This causes placental ischemia and injury, releasing factors that cause widespread maternal syndrome of hypertension, increased vascular resistance, and organ damage like kidney impairment from decreased filtration and increased reabsorption.
Original Description:
Original Title
2
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentObesity, poor nutrition, pre-existing conditions, and placental defects can precipitate preeclampsia by impairing placental implantation and endothelial function, increasing platelet activation and reducing blood flow. This causes placental ischemia and injury, releasing factors that cause widespread maternal syndrome of hypertension, increased vascular resistance, and organ damage like kidney impairment from decreased filtration and increased reabsorption.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views1 pageIv - Pathophysiology: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating Factor
Uploaded by
Jatevenzche LaoObesity, poor nutrition, pre-existing conditions, and placental defects can precipitate preeclampsia by impairing placental implantation and endothelial function, increasing platelet activation and reducing blood flow. This causes placental ischemia and injury, releasing factors that cause widespread maternal syndrome of hypertension, increased vascular resistance, and organ damage like kidney impairment from decreased filtration and increased reabsorption.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
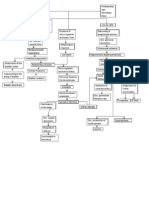
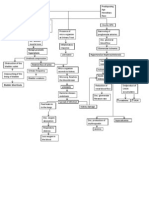
IV.
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
Precipitating factor: Obesity Poor maternal nutrition Pre-existing hypertension Renal disease Defective placental implantation Endovascular trophoblastic cells invade the maternal spiral arteries Release of placental factor Fibrin, platelets and lipophages aggregates
Predisposing factors: Age-39 years old Hereditary -HPN
Replacement of endothelium, destruction of medical musculoelastic tissue, and fibrinoid change in the vessel wall
Increased platelet activation
Acute atherosis partially or completely blocking the arterioles
Increased thrombosane Placental infraction vasospasm Fetal distress Endothelial dysfunction Fetal death
Placental ischemia
Hypertension
vasoconstiction
Increase d BP=160/ 110mm Hg
Reduced perfusion of affected organs
kidney
Decrease GFR
Increase permeability of the glomerular membrane
Increase reabsorption in tubules
Decrease urine output Increase uric acid Increase creatine
proteinuria
Increase sodium retention + H2O
LEGEND: - Process - Signs & symptoms - Medication - Pathophysiological pathways
edema
You might also like
- Renal Chart 2Document21 pagesRenal Chart 2fortheloveofmedicineNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology On Liver CirrhosisDocument38 pagesPathophysiology On Liver Cirrhosisတမန္ေတာ္ တမန္ေတာ္100% (30)
- Liver Cirrhosis: Review HepatologyDocument71 pagesLiver Cirrhosis: Review HepatologyAstri Arri FebriantiNo ratings yet
- Chronic Renal FailureDocument3 pagesChronic Renal FailureIvana Yasmin Bulandres100% (2)
- Liver Cirrhosis: Precipitating Factors: Predisposing FactorDocument22 pagesLiver Cirrhosis: Precipitating Factors: Predisposing FactorJorie RocoNo ratings yet
- Portal HypertensionDocument65 pagesPortal HypertensionVenu MadhavNo ratings yet
- Acute Kidney InjuryDocument60 pagesAcute Kidney InjuryAbegail Fermanejo-GeneraoNo ratings yet
- Pathology Polycystic Kidney DiseaseDocument4 pagesPathology Polycystic Kidney DiseaseOnyedika EgbujoNo ratings yet
- Chronic Liver DiseaseDocument30 pagesChronic Liver Diseaseprajwal86% (7)
- Pathophysiology: Precipitating FactorDocument6 pagesPathophysiology: Precipitating FactorMark Anthony YabresNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsDocument3 pagesPathophysiology: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsMizchelle Angeles VilladorNo ratings yet
- Liver Cirrohsis (Lecture)Document87 pagesLiver Cirrohsis (Lecture)Rina Sundari Dels100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of DMDocument5 pagesPathophysiology of DMRgn Mckl100% (3)
- Pathophysiology of Liver Cancer 2Document3 pagesPathophysiology of Liver Cancer 2Charis Paroginog92% (12)
- Preeclampsia PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesPreeclampsia PathophysiologyIrene Zuñiga100% (4)
- Cirrhosis of LiverDocument106 pagesCirrhosis of LiveraahadNo ratings yet
- Presented By: Medicine Unit 1Document95 pagesPresented By: Medicine Unit 1Abdullah Muceddidi100% (1)
- Fitz Abdominal Paces NotesDocument19 pagesFitz Abdominal Paces NotesDrShamshad Khan100% (1)
- Pathophysiology EclampsiaDocument5 pagesPathophysiology EclampsiaChristine Karen Ang SuarezNo ratings yet
- Liver CirrohosisDocument157 pagesLiver CirrohosisSeema SachdevaNo ratings yet
- Practical Hemostasis and ThrombosisFrom EverandPractical Hemostasis and ThrombosisNigel S. KeyNo ratings yet
- Renal Concept MapDocument8 pagesRenal Concept MapRob DavilaNo ratings yet
- Preeclampsia PathoDocument1 pagePreeclampsia Pathoapi-316030498No ratings yet
- Complications of Cirrhosis MbbsDocument16 pagesComplications of Cirrhosis MbbsNadun MethwadaneNo ratings yet
- Renal Concept MapDocument8 pagesRenal Concept MapDavis KallanNo ratings yet
- Portal Hypertension: Dr. Shwetang SolankiDocument25 pagesPortal Hypertension: Dr. Shwetang SolankiShwetang SolankiNo ratings yet
- Chronic Renal FailureDocument54 pagesChronic Renal Failuresanjivdas100% (3)
- Pediatric Renal & Genitourinary DisordersDocument72 pagesPediatric Renal & Genitourinary DisordersMarie Angelique Cruz CrestaniNo ratings yet
- Renal - Pathophysiology 2020 PDFDocument89 pagesRenal - Pathophysiology 2020 PDFHardian HardianNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology Acute Pyelonephriti1Document2 pagesPathophysiology Acute Pyelonephriti1Stephanie Joy EscalaNo ratings yet
- Predisposing Factors Age Diet Dehydration Precipitating Factors Family or Personal History Digestive Diseases and SurgeryDocument2 pagesPredisposing Factors Age Diet Dehydration Precipitating Factors Family or Personal History Digestive Diseases and SurgeryChloé Jane HilarioNo ratings yet
- 74 Acute Renal Failure UpdatedDocument48 pages74 Acute Renal Failure UpdatedaweleNo ratings yet
- An Approach To Bleeding DisordersDocument30 pagesAn Approach To Bleeding DisordersSiddique BhattiNo ratings yet
- Complications of CirrhosisDocument2 pagesComplications of CirrhosisDanielle DiorioNo ratings yet
- CastroDocument17 pagesCastrongoto88No ratings yet
- RenalDocument150 pagesRenalHoe TeohNo ratings yet
- Hepatic Cirrhosis (肝硬化): Yu BaopingDocument62 pagesHepatic Cirrhosis (肝硬化): Yu BaopingKurbulNo ratings yet
- Dis LiverDocument40 pagesDis LiverPrem MorhanNo ratings yet
- 4 Ps NotesDocument33 pages4 Ps NotesErika Bea PaculanangNo ratings yet
- Pathophysio PreeclampsiaDocument2 pagesPathophysio PreeclampsiaMarlowe Czar Catalan SoriñoNo ratings yet
- Bimbingan Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument15 pagesBimbingan Chronic Kidney DiseaseMuhammad Haris FirdausNo ratings yet
- Medsurg ReviewDocument34 pagesMedsurg ReviewestberryNo ratings yet
- Kidney, Bladder and Prostate Pathology For Allied Health SciencesDocument38 pagesKidney, Bladder and Prostate Pathology For Allied Health SciencesMichael BrownNo ratings yet
- 2 Renal Buzzword ChartDocument6 pages2 Renal Buzzword ChartTyler KingNo ratings yet
- Approach To Kidney DiseaseDocument28 pagesApproach To Kidney Diseasejohn ray gonzalesNo ratings yet
- Illustrative Cases+ Some HelpDocument12 pagesIllustrative Cases+ Some HelpWande AyodeleNo ratings yet
- Jaundice: Common Bile Duct Hindrance To Bile Flow Manifests With Jaundice, Fever, PainDocument7 pagesJaundice: Common Bile Duct Hindrance To Bile Flow Manifests With Jaundice, Fever, PainRemelou Garchitorena AlfelorNo ratings yet
- Renal Concept MapDocument8 pagesRenal Concept MapXtine CajiNo ratings yet
- Askep HepaticDocument52 pagesAskep HepaticNia AnjarNo ratings yet
- Patho Liver Cirrhosis PathoDocument1 pagePatho Liver Cirrhosis Pathochelle_asenjoNo ratings yet
- PembahasanDocument1,129 pagesPembahasanatc100% (1)
- Acute Renal Failure DiagramDocument3 pagesAcute Renal Failure DiagramMichelle BarojaNo ratings yet
- Cirrhosis: DR AkhondeiDocument111 pagesCirrhosis: DR AkhondeiMuvenn KannanNo ratings yet
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Hypertensive NephroschelorosisDocument2 pagesBenign Prostatic Hyperplasia Hypertensive NephroschelorosisRiin IrasustaNo ratings yet
- Fulminant Hepatic Failure in ChildrenDocument60 pagesFulminant Hepatic Failure in ChildrendhaylecNo ratings yet
- Hematuria in ChildrenDocument27 pagesHematuria in ChildrenKousik AmancharlaNo ratings yet
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Hypertensive NephroschelorosisDocument2 pagesBenign Prostatic Hyperplasia Hypertensive NephroschelorosisRiin IrasustaNo ratings yet
- Necrotizing Enterocolitis: Janice Nicklay Catalan M.DDocument27 pagesNecrotizing Enterocolitis: Janice Nicklay Catalan M.DrianurjanahNo ratings yet