Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NCPRA
NCPRA
Uploaded by
Eugine Elizabeth Pilarca PerezCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
NCPRA
NCPRA
Uploaded by
Eugine Elizabeth Pilarca PerezCopyright:
Available Formats
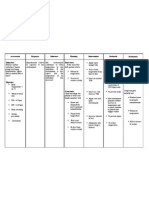
NURSING CARE PLAN Assessment Subjective: lagi na lang akong nakahiga as verbalized by the patient.
Objective Conscious and coherent body weakness restless poor appetite with limited ROM ambulatory c assistance Nursing Diagnosis Activity Intolerance; Level related to difficulty walking secondary to body weakness Analysis Most activity intolerance is related to generalized weakness and debilitation secondary to acute or chronic illness and disease. This is especially apparent in elderly patients with a history of orthopedic, cardiopulmonary, diabetic, or pulmonary- related problems. The aging process itself causes reduction in muscle strength and function, which can impair the ability to maintain activity. Activity intolerance may also be related to factors such as obesity, malnourishment, side effects of medications (e.g., -blockers), or emotional states such as depression Planning Patient will improve mobility participation in the activities of daily living. Interventions - establish rapport - place the client in a comfortable position -take and record vital signs -Determine patient's perception of causes of fatigue or activity intolerance. - Assess patient's level of mobility. Rationale - to facilitate NPI. - to prevent backaches or muscle aches. - to note any significant changes that may be brought about by the disease - These may be temporary or permanent, physical or psychological. Assessment guides treatment. - This aids in defining what patient is capable of, which is necessary before setting realistic goals. - Adequate energy reserves are required for activity. - Difficulties sleeping need to be addressed before activity progression can be achieved. - Depression over inability to perform required activities can further aggravate the Evaluation Patient demonstrated improved mobility participation in activity of daily living in which he is capable of.
- Assess nutritional status. - Monitor patient's sleep pattern and amount of sleep achieved over past few days. - Assess emotional response to change in physical status.
- Encourage
or lack of confidence to exert one's self.
adequate rest periods, especially before meals, other ADLs, and ambulation. - Refrain from performing nonessential procedures. -Assist with ADLs as indicated; however, avoid doing for patient what he or she can do for self.
activity intolerance. - Rest between activities provides time for energy conservation and recovery. - Patients with limited activity tolerance need to prioritize tasks. -Assisting the patient with ADLs allows for conservation of energy. Caregivers need to balance providing assistance with facilitating progressive endurance that will ultimately enhance the patient's activity tolerance and selfesteem. -Exercises maintain muscle strength and joint ROM. -These reduce oxygen consumption, allowing more prolonged activity.
-Encourage active ROM exercises three times daily. -Teach energy conservation techniques.
Assessment
Nursing Diagnosis
Analysis
Planning
Interventions
Rationale
Evaluation
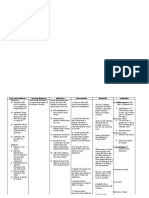
Subjective: ang bagal gumaling ng mga sugat ko As verbalized by the patient
Risk for infection related to high glucose levels, decreased leukocyte function.
Objective: -Flushed appearance -Wound at right foot -Alert and coherent
is a group of metabolic diseases in which a person has high blood sugar, either because the body does not produce enough insulin, or because cells do not respond to the insulin that is produced. This high blood sugar produces the classical symptoms of polyuria (frequent urination), polydipsia (inc reased thirst) and polyphagia (increase d hunger.
After 8 hours of nursing interventions, the patient will identify interventions to prevent or reduce risk of infection
Independent: Observe for signs of infection and inflammation. Promote good handwashing by nurse and patient. Maintain aseptic technique for IV insertion procedure, administration of medications, and providing maintenance and site care. Rotate IV sites as indicated. Provide catheter or perineal care. Teach the female patient to clean from front to back after elimination. Patient may be admitted with infection, which could have precipitated the ketoacidotic state, or may develop a nosocomial infection. Reduces the risk of crosscontamination High glucose in the blood creates an excellent medium for bacterial growth. Minimizes the risk for infection. Peripheral circulation may
After 8 hours of nursing intervention s, the patient was able to identify intervention s to prevent or reduce risk of infection
Provide conscientious skin care, gentl massage bony areas. Keep the skin dry, linens dry and wrinkle free. Place in semi fowlers position. Encourage adequate dietary and fluid intake of 3000 ml per day. Collaborative: Obtain specimen for culture and sensitivities as indicated.
be impaired, placing patient at increased risk for skin irritation or breakdown and infection. Facilitates lung expansion and reduces risk of aspiration. Decrease susceptibility to infection. Identifies organisms so that most appropriate drug therapy can be instituted
You might also like
- Nlam FinalsDocument18 pagesNlam FinalsJae Kline Garcia100% (1)
- Coronary Artery Disease Care PlanDocument2 pagesCoronary Artery Disease Care PlanDanelle Harrison, RN100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan: Risk For Disuse SyndromeDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Risk For Disuse SyndromeRozsy FakhrurNo ratings yet
- Healthcare - Nursing Care Plan - Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument4 pagesHealthcare - Nursing Care Plan - Decreased Cardiac OutputBenjamin CañalitaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Pulmonary EbolismDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan: Pulmonary EbolismneuronurseNo ratings yet
- San Francisco St. Butuan City 8600, Region XIII Caraga, PhilippinesDocument3 pagesSan Francisco St. Butuan City 8600, Region XIII Caraga, Philippineskuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- Body Weakness NCPDocument1 pageBody Weakness NCPtwicetrashNo ratings yet
- Asessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument1 pageAsessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationChelsea Mae Bagalay GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding NCPDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan For Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding NCPLatrell Gelacio100% (1)
- Actual NCPDocument2 pagesActual NCPbaki0146No ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care PlanAlvin DagumbalNo ratings yet
- NCP 1Document1 pageNCP 1hsiriaNo ratings yet
- NCP HypertensionDocument1 pageNCP HypertensionCharisse VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Discharge Plan CapDocument3 pagesDischarge Plan Capalexander abasNo ratings yet
- Date and Time Objectives Learning Contents Strategies Target Population Resources Evaluation OutcomeDocument8 pagesDate and Time Objectives Learning Contents Strategies Target Population Resources Evaluation OutcometrizzlecNo ratings yet
- Physical Assessment On GERD PatientDocument8 pagesPhysical Assessment On GERD PatientRobert Medina100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan: Date/ Time Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Evaluatio NDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Date/ Time Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Evaluatio NnananaNo ratings yet
- NCP and DStudyDocument8 pagesNCP and DStudyJessica Rosan Hewald ManapatNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Subjective Data " GoalDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Subjective Data " GoalJay VillasotoNo ratings yet
- NCP Risk For InfectionDocument6 pagesNCP Risk For InfectionCazze SunioNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For LYING inDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan For LYING inKarissa CiprianoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesNursing Care Planjnx_anonymousNo ratings yet
- Chn-Herbal MedicineDocument5 pagesChn-Herbal MedicineBSN 1-N CASTRO, RicciNo ratings yet
- 1ST RotDocument2 pages1ST RotDummy AccountNo ratings yet
- Sudaria Ivy G. AnswerKeysDocument25 pagesSudaria Ivy G. AnswerKeysDeinielle Magdangal RomeroNo ratings yet
- BSN 3e Duropan Ncp-Knowledge DeficitDocument12 pagesBSN 3e Duropan Ncp-Knowledge DeficitJane DuropanNo ratings yet
- NCP Fluid Vol Excess AgnDocument3 pagesNCP Fluid Vol Excess AgnArbie JacintoNo ratings yet
- "Hindi Ko Kayo Masyadong Marinig Sa Kanang Tenga Ko, Pwede Bang Sa Kaliwang Side Ko Kayo Magsalita?" As Verbalized by The PatientDocument2 pages"Hindi Ko Kayo Masyadong Marinig Sa Kanang Tenga Ko, Pwede Bang Sa Kaliwang Side Ko Kayo Magsalita?" As Verbalized by The PatientMussaib Mushtaq100% (1)
- Body Weakness NCPDocument1 pageBody Weakness NCPArnold Christian QuilonNo ratings yet
- NCP ErDocument4 pagesNCP ErljarseniornNo ratings yet
- Gout N C P BY BHERU LALDocument1 pageGout N C P BY BHERU LALBheru LalNo ratings yet
- N1007 Week Two - Nurse Care Plan - Diabetes - James ScalesDocument1 pageN1007 Week Two - Nurse Care Plan - Diabetes - James Scalesjumpshooter88100% (1)
- NCP HyperthermiaDocument1 pageNCP HyperthermiaPastor James PacadaljenNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument1 pageNCPJachel Kathleen LaguioNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationCarolAnneRagpalaGaudiaNo ratings yet
- CP Intestinal Obstruction Nursing Care PlanDocument7 pagesCP Intestinal Obstruction Nursing Care PlanShiella Heart MalanaNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Peripheral Tissue Perfusion Related To Vasoconstriction Secondary To High Glucose Level.Document6 pagesIneffective Peripheral Tissue Perfusion Related To Vasoconstriction Secondary To High Glucose Level.SAROL, RYAN CHRISTIAN B.No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan - Fatigue (Antepartum)Document3 pagesNursing Care Plan - Fatigue (Antepartum)kaimimiyaNo ratings yet
- SDL 1Document2 pagesSDL 1Duchess Juliane Jose MirambelNo ratings yet
- Aaa Gastrectomy NCP FinalDocument13 pagesAaa Gastrectomy NCP Finallexzaf100% (1)
- Patty NCP HyperthermiaDocument4 pagesPatty NCP HyperthermiaPatricia Jean FaeldoneaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan UlcerDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Ulcerxrampley2100% (2)
- Concept MapDocument1 pageConcept MapNicole Ivy GorimoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument6 pagesNursing Care PlanFrances CalaraNo ratings yet
- NCP DMDocument2 pagesNCP DMAna Ramos LopezNo ratings yet
- Gi-Rle - NCP For Deficient Fluid VolumeDocument2 pagesGi-Rle - NCP For Deficient Fluid VolumeEvangeline Villa de Gracia100% (1)
- TAHBSO ReportDocument4 pagesTAHBSO ReportsachiiMeNo ratings yet
- Hypertension Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesHypertension Nursing Care PlanCj LowryNo ratings yet
- NCM 117 Final Exam MamelDocument16 pagesNCM 117 Final Exam MamelJade CentinoNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPMichael John F. NatividadNo ratings yet
- Short Term: Independent: Independent: Short TermDocument2 pagesShort Term: Independent: Independent: Short TermAndre ImperialNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis A N C P BY BHERU LALDocument2 pagesHepatitis A N C P BY BHERU LALBheru LalNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan BalnkDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan BalnkKateLayaogNo ratings yet
- NCP 2Document2 pagesNCP 2hsiria100% (1)
- NCPDocument6 pagesNCPNik Rose ElNo ratings yet
- Muscle Weakness - Restlessness - Decreased Skin Turgor: CollaborativeDocument5 pagesMuscle Weakness - Restlessness - Decreased Skin Turgor: CollaborativebeshyNo ratings yet
- Assesment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssesment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationSienaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective: "Maglisod Man Kog Short Term: Independent: - Establish RapportDocument3 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective: "Maglisod Man Kog Short Term: Independent: - Establish RapportSergi Lee OrateNo ratings yet
- Activity Intolerance NCPDocument2 pagesActivity Intolerance NCPAdriano Odysseus Jon O.No ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument6 pagesNursing Care PlanperezNo ratings yet
- Large Bowel ObstructionDocument8 pagesLarge Bowel Obstructionstara123No ratings yet
- Article DMDocument1 pageArticle DMstara123No ratings yet
- Small Bowel ObstructionDocument8 pagesSmall Bowel Obstructionstara123No ratings yet
- ArticlesDocument3 pagesArticlesstara123No ratings yet
- PhenylketonuriaDocument2 pagesPhenylketonuriastara123No ratings yet
- COURSE in WARD Presentation (Hemophilia)Document16 pagesCOURSE in WARD Presentation (Hemophilia)stara123100% (1)
- Pharygitis AND TonsillitisDocument29 pagesPharygitis AND Tonsillitisstara123No ratings yet
- Polycystic Kidney Disease: Tara Angela Pandac n314Document11 pagesPolycystic Kidney Disease: Tara Angela Pandac n314stara123No ratings yet