Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Drug Study Amoxicillin
Drug Study Amoxicillin
Uploaded by
Mitch Elle InfanteOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Drug Study Amoxicillin
Drug Study Amoxicillin
Uploaded by
Mitch Elle InfanteCopyright:
Available Formats
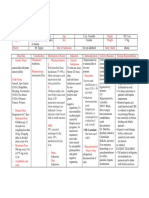
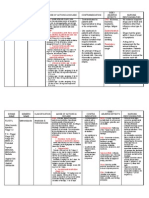
Name of Patient Diagnosis Doctor Drug Data Generic Name
Anding, Jessica Donaire R/O conjunctivitis secondary to trauma Dr. Tipgos Classification Therapeutic: Antibiotic Pharmacologic aminopenicillins
Age Sex Date of Admission Indication General Indications To treat ear, nose, throat, GU tract, skin, and soft-tissue infections caused by susceptible grampositive and gramnegative organisms, To treat tonsillitis or pharyngitis caused by Streptococcus pyogenes, To treat lower respiratory tract infec tions caused by susceptible gram-positive and gramnegative organisms,
5 yrs. 5 months Female Not yet admitted Contraindications Hypersensitivity to amoxicillin or its components Precaution Severe renal insufficiency ( dose if CCr <30 mL/min) Infectious mononucleosis, acute lymphocytic leukemia, or cytomegaloviru s infection ( risk of rash) OB: Lactation: Has been used safely Drug interaction -drug to drug allopurinol: Increased risk of rash
Height Weight Body Build
105.5 cm 17 kg sthenic
amoxicillin trihydrate (amoxycillin) Trade Name Amoxil, Apo-Amoxi (CAN), DisperMox, Moxatag, Novamoxin (CAN), Nu-Amoxi (CAN), Polymox, Trimox, Wymox Patients Dose Suspension for 7 days Minimum Dose Children age 12 wk and over weighing less than 20 kg. 20 mg/kg daily in divided doses every 8 hr Maximum Dose 500 mg every 8 hr or 875 mg every 12 hr Availability and color
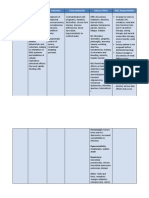
Mechanism of Action Pharmacokinetics A Well absorbed from duodenum (7590%). More resistant to acid inactivation than other penicillins D Diffuses readily into most body tissues and fluids. CSF penetration increased when meninges are inflamed. Crosses placenta; enters breast milk in small amounts M&E 70% excreted unchanged in the urine; 30% metabolized by the liver Onset Unknown Peak Unknown
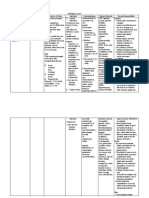
Adverse Reaction Nursing Responsibilities CNS: Agitation, Before anxiety, behavior Patients with changes, mononucleosis confusion, shouldnt dizziness, receive amoxicillin insomnia, because this class of reversible drugs may cause an hyperactivity, erythematous rash. seizures Use drug cautiously in CV: patients with hepatic Hypersensitivity impairment. vasculitis Monitor hepatic and EENT: Black, renal function and CBC, hairy tongue; as ordered, in patients mucocutaneous on prolonged therapy. candididasis; use cautiously in breasttooth feeding and elderly discoloration patients. GI: Diarrhea, Expect to start therapy diarrhea related to before culture and Clostridium sensitivity test results difficile, elevated are known. liver enzymes, as ordered. hemorrhag- ic or PATIENT TEACHING pseudomembrano Tell patient to refrigerate us colitis, reconstituted susjaundice, hepatic pension and to shake dysfunction, well before each use.
CAPSULES, CHEWABLE TABLETS, ORAL SUSPENSION, PEDIATRIC DROPS, POWDER OR TABLETS FOR ORAL SUSPENSION, TABLETS Routes of administration P.O.
Duration\ 68 hr Drug Half Life Neonates: 3.7 hr; Infants and Children: 12 hr; Adults: 0.7 1.4 hr
Treatment of Skin and skin structure infections Patients Actual Indication
Treatment of Skin and skin structure infections
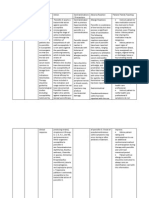
chloramphenicol, erythromycins, sulfon- amides, tetracyclines: Reduced bactericidal effect of amoxicillin methotrexate: Increased risk of methotrex- ate toxicity oral contraceptives with estrogen: Possibly 76 amphetamine sulfate reduced effectiveness of contraceptive probenecid: Increased amoxicillin effects
nausea, vomiting When amoxicillin GU: Crystalluria, suspension is prescribed vaginal mycosis for a child, instruct HEME: parents to place it Agranulocytosis, directly on childs anemia (including tongue to swallow. If hemolytic this doesnt work, tell anemia), parents to mix dose of eosinophilia, suspension with formula granulo- cytosis, or cold drink (milk, fruit leukopenia, juice, ginger ale, water) thrombocytopenia and have child drink it , immediately. thrombocytopenic Instruct patient using purpura DisperMox tablets to SKIN: Erythema place one tablet and multiforme, about 2 teaspoonfuls of erythematous water in a glass, drink maculopapular entire mix ture, add rash, generalized more water to the glass, exanthe- matous and drink again to pustulosis, ensure delivery of full Stevens-Johnson dose. syn- drome, toxic During epidermal Be aware that chewable necrolysis, tablets and tablets for urticaria Other: oral suspension contain Allergic reaction, phenylalanine. anaphylaxis, Tell patient to chew or serum crush chewable tablets sicknesslike and not to swallow them reaction (such as whole. arthralgia, Dont confuse arthritis, fever, amoxicillin tablets with myalgia, rash, and amoxicillin tablets for
urticaria)
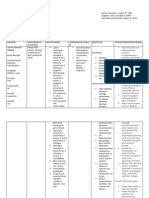
oral suspension (DisperMox). Theyre not interchangeable. If allergic reaction occurs, stop amoxicillin immediately and provide emergency care as indicated and ordered. Monitor patient for superinfection. If it occurs, expect to discontinue drug and provide treatment After Teach patient to report adverse reactions notify prescriber if infection worsens or doesnt improve after 72 hours. To prevent infection from recurring, urge patient to take amoxicillin for full length of time prescribed, even if he feels better. Urge patient to tell prescriber about diarrhea thats severe or lasts longer than 3 days. Remind patient that watery or bloody
stools can occur 2 or more months after antibiotic therapy and may be serious, requiring prompt treatment. Monitor patient closely for diarrhea, which may indicate pseudomembranous colitis Expect treatment that lasts at least 10 days for hemolytic streptococci infections. Source: Deglin, Vallerand, Sanoski, D aviss Drug Guide for Nurses F.A. Davis Company. 2010 Source: Deglin, Vallerand, Sanos ki, Daviss Drug Guide for Nurses F.A. Davis Company. 2010 Source: http://www.drugguide .com/ddo/ub/view/Da vis-DrugGuide/51047/3/amoxi cillin?q=amoxicillin Source: Deglin, Vallerand, Sanos ki, Daviss Drug Guide for Nurses F.A. Davis Company. 2010 Source: Deglin, Vallerand, Sanosk i, Daviss Drug Guide for Nurses F.A. Davis Company. 2010 Source: http://www.drugg uide.com/ddo/ub/ view/Davis-DrugGuide/51047/4/a moxicillin?q=amo xicillin Source: Deglin, Vallerand, Sanoski, Davis s Drug Guide for Nurses F.A. Davis Company. 2010
You might also like
- Methotrexate Drug StudyDocument1 pageMethotrexate Drug StudyAlexa Lexington Rae Zagado0% (1)
- Vaginal Discharge + PruritisDocument56 pagesVaginal Discharge + PruritisEkoApriandhiNo ratings yet
- Addiction Trajectories Edited by Eugene Raikhel and William GarriottDocument42 pagesAddiction Trajectories Edited by Eugene Raikhel and William GarriottDuke University Press50% (2)
- Hair Tissue Mineral AnalysisDocument7 pagesHair Tissue Mineral AnalysisShaiabbNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY - AmoxicillinDocument7 pagesDRUG STUDY - AmoxicillinFaye Gatchalian100% (1)
- Radiology of MSKDocument54 pagesRadiology of MSKgabriellafelisaNo ratings yet
- Betamethasone (Drug Study)Document4 pagesBetamethasone (Drug Study)Franz.thenurse6888100% (1)
- Pharmacologic: Systemic Administration AssessmentDocument3 pagesPharmacologic: Systemic Administration Assessmentitsmeaya100% (1)
- Drug Study - Cefazolin DoxycyclineDocument2 pagesDrug Study - Cefazolin DoxycyclineDan Dan Soi T50% (2)
- Valeria Grishko Animal Guides in LifeDocument6 pagesValeria Grishko Animal Guides in LifeVerónicaMonyo100% (1)
- Protocols by Resham Malhotra PDFDocument7 pagesProtocols by Resham Malhotra PDFScience NerdNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY AmoxicillinDocument1 pageDRUG STUDY Amoxicillinjulesubayubay542886% (14)
- Drug Study Amoxicillin PDFDocument4 pagesDrug Study Amoxicillin PDFMc SantosNo ratings yet
- TerramycinDocument1 pageTerramycinJulie May50% (2)
- FluphenazineDocument3 pagesFluphenazineKaren T. CeletariaNo ratings yet
- Montelukast SodiumDocument2 pagesMontelukast Sodiumyhanna17No ratings yet
- Methotrexate )Document2 pagesMethotrexate )Angela Tenorio100% (2)
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyAko Si Vern ÖNo ratings yet
- PHENYLEPHRINEDocument3 pagesPHENYLEPHRINERoger Jr PumarenNo ratings yet
- Rifampicin Drug StudyDocument3 pagesRifampicin Drug StudyMaila Joy Pring Fuentes67% (3)
- Fluticasone Drug StudyDocument3 pagesFluticasone Drug StudyArabelle GONo ratings yet
- Drug Study OrthoDocument17 pagesDrug Study OrthoMc Crister SilangNo ratings yet
- Cefaclor, Salbutamol, Paracetamol and NCPDocument13 pagesCefaclor, Salbutamol, Paracetamol and NCPAriane Rose Saria CedronNo ratings yet
- GBS Source 1Document4 pagesGBS Source 1PJHG50% (2)
- BiperidenDocument3 pagesBiperidenKaren T. Celetaria100% (1)
- Paracetamol Drug StudyDocument1 pageParacetamol Drug StudyMaricor Toring85% (13)
- TerbutalineDocument1 pageTerbutalineRyan Paul Balot0% (1)
- ErythromycinDocument1 pageErythromycinKenneth Robert Abrantes0% (1)
- Drug Study of Magnesium SulfateDocument2 pagesDrug Study of Magnesium SulfateEm Hernandez Arana83% (6)
- Ofloxacin Drug StudyDocument2 pagesOfloxacin Drug StudyCheezy Bread100% (1)
- Radiology Skills ChecklistDocument4 pagesRadiology Skills ChecklistnorthweststaffingNo ratings yet
- Lasers in PeriodonticsDocument61 pagesLasers in PeriodonticsDrRanjeet Kumar ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Aminophylline Drug StudyDocument1 pageAminophylline Drug StudyEmman Balido67% (3)
- Mefenamic AcidDocument1 pageMefenamic AcidChiara Tenorio Ü100% (2)
- NCP-Risk For Fluid Volume DeficitDocument3 pagesNCP-Risk For Fluid Volume DeficitJai Go100% (1)
- DRUG STUDY (Amoxicilin)Document2 pagesDRUG STUDY (Amoxicilin)Gerly LagutingNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Amphotericin B, Meropenem, Furosemide, Ciprofloxacin, Pentoxifylline, Pip-Tazo, Midazolam, VecuroniumDocument12 pagesDrug Study Amphotericin B, Meropenem, Furosemide, Ciprofloxacin, Pentoxifylline, Pip-Tazo, Midazolam, Vecuroniumpaupaulala100% (4)
- MontelukastDocument2 pagesMontelukastGrace del RosarioNo ratings yet
- A Review On LozengesDocument9 pagesA Review On LozengesShakrie AbdullahNo ratings yet
- CA PretestDocument6 pagesCA PretestEdalyn Capili0% (3)
- DRUG STUDY - AmoxicillinDocument2 pagesDRUG STUDY - AmoxicillinFlorenz Gatchalian60% (5)
- Brompheniramine Maleate (Drug Study)Document2 pagesBrompheniramine Maleate (Drug Study)Franz.thenurse6888No ratings yet
- CephalexinDocument3 pagesCephalexinCiera YoungNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Tamiflu, FlagylDocument2 pagesDrug Study - Tamiflu, Flagylmark_gain100% (1)
- Drug Study CaseDocument7 pagesDrug Study CaseKevin Sam AguirreNo ratings yet
- Montelukast SodiumDocument2 pagesMontelukast Sodiumapi-3797941100% (2)
- Drug Classification Action of Drug Indication and Contraindication Side Effect Nursing ConsiderationDocument2 pagesDrug Classification Action of Drug Indication and Contraindication Side Effect Nursing ConsiderationDanica Kate GalleonNo ratings yet
- Ritalin LA: Initial, 20 MG PO qAM May Adjust Dose in Weekly 10-mg Incremen TS, Not To Exceed 60 Mg/day (Patients Requiring A Lower InitialDocument2 pagesRitalin LA: Initial, 20 MG PO qAM May Adjust Dose in Weekly 10-mg Incremen TS, Not To Exceed 60 Mg/day (Patients Requiring A Lower InitialKwin SaludaresNo ratings yet
- Drug Study CefuroximeDocument1 pageDrug Study CefuroximeKarmell Maliwanag100% (2)
- Drug Study Dose, Route and Frequency Mechanism of Action Indications Contra-Indications Side Effects Adverse Effects Nursing ConsiderationDocument8 pagesDrug Study Dose, Route and Frequency Mechanism of Action Indications Contra-Indications Side Effects Adverse Effects Nursing Considerationsneb1392No ratings yet
- ErythromycinDocument2 pagesErythromycinKathleen PalomariaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study MetronidazoleDocument2 pagesDrug Study MetronidazoleJha NetNo ratings yet
- DRUG ORDER Generic Name: - Ampicillin Brand Name: - AmpicinDocument1 pageDRUG ORDER Generic Name: - Ampicillin Brand Name: - AmpicinRadicalRay100% (3)
- Amoxicillin Drug StudyDocument1 pageAmoxicillin Drug StudyAngela CancinoNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY Amoxicillin PDFDocument2 pagesDRUG STUDY Amoxicillin PDFMc SantosNo ratings yet
- ZonisamideDocument2 pagesZonisamideRo-anne AkuNo ratings yet
- PiroxicamDocument2 pagesPiroxicamVirginia Aira Lara MarquezNo ratings yet
- Drug Study AmpicillinDocument6 pagesDrug Study AmpicillinDgjj Compuiter100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug Studym100% (1)
- Cephalexin: Adjust-A-Dose (For All Indications)Document3 pagesCephalexin: Adjust-A-Dose (For All Indications)HannaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyJuliana LegarteNo ratings yet
- Meds SummaryDocument22 pagesMeds SummaryChamCham AquinoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyDick Morgan FerrerNo ratings yet
- DrugmedsDocument52 pagesDrugmedsshirleyNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyCheriz LukbanNo ratings yet
- Health ArticlesDocument5 pagesHealth Articlesprashant_shivdas_1No ratings yet
- PP ObatDocument7 pagesPP ObatSaifan AbdurrohmanNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyFloramae Celine BosqueNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: Albuterol Brand Name: Salbutamol, Proventil, Ventolin, Accuneb, Airet, Novo-SalbutamolDocument26 pagesGeneric Name: Albuterol Brand Name: Salbutamol, Proventil, Ventolin, Accuneb, Airet, Novo-SalbutamolAnna Joy Antone100% (1)
- Drugs Study, Nursing, PreoperativeDocument9 pagesDrugs Study, Nursing, PreoperativeKevin Sam AguirreNo ratings yet
- Amoxicillin and Clavulanate PotassiumDocument6 pagesAmoxicillin and Clavulanate PotassiumPascalis AyukNo ratings yet
- AugmentinDocument6 pagesAugmentinAirene SibleNo ratings yet
- Ranicef Tablets Cefdinir Tablets 300MG FidsonDocument13 pagesRanicef Tablets Cefdinir Tablets 300MG FidsonWright JohnNo ratings yet
- Case PresentationDocument29 pagesCase PresentationLeezhaj VargasNo ratings yet
- Cebu Normal University - College of Nursing Drug Study: AbsorptionDocument2 pagesCebu Normal University - College of Nursing Drug Study: AbsorptionKaren T. CeletariaNo ratings yet
- Cebu Normal University: Progress ReportDocument4 pagesCebu Normal University: Progress ReportKaren T. CeletariaNo ratings yet
- Assignment Dia NoDocument4 pagesAssignment Dia NoKaren T. CeletariaNo ratings yet
- Progress ReportDocument4 pagesProgress ReportKaren T. CeletariaNo ratings yet
- Activity 2Document7 pagesActivity 2Karen T. CeletariaNo ratings yet
- Substance Misuse Disorders: Dr. Ravi PaulDocument19 pagesSubstance Misuse Disorders: Dr. Ravi PaulRavi PaulNo ratings yet
- English-Booklet Dentistry PDFDocument35 pagesEnglish-Booklet Dentistry PDFFarah Ridzuan100% (1)
- Anosognosia FSDocument2 pagesAnosognosia FSraquel perezNo ratings yet
- Assignment Task 1: Grace Levens 215061064Document9 pagesAssignment Task 1: Grace Levens 215061064Grace LevensNo ratings yet
- Van Niel Carolyn ResumeCA 2010Document3 pagesVan Niel Carolyn ResumeCA 2010Javier EvansNo ratings yet
- A Clinician's Guide To Cost-Effectiveness Analysis: Annals of Internal Medicine. 1990 113:147-154Document8 pagesA Clinician's Guide To Cost-Effectiveness Analysis: Annals of Internal Medicine. 1990 113:147-154dsjervisNo ratings yet
- W1Document100 pagesW1rajanityagi23100% (1)
- Surgery Written Assignment2016Document2 pagesSurgery Written Assignment2016Tyler EmmendorferNo ratings yet
- 802.034 Datasheet Phyaction CL v1.5 en LRDocument4 pages802.034 Datasheet Phyaction CL v1.5 en LRSofie BeckersNo ratings yet
- Psych Meds Booster Nov 2022 PnleDocument11 pagesPsych Meds Booster Nov 2022 PnleDarwin DerracoNo ratings yet
- Nurse Practitioner 2Document11 pagesNurse Practitioner 2api-285531147No ratings yet
- Nystatin DrugstudyDocument2 pagesNystatin DrugstudyfLOR_ZIANE_MAENo ratings yet
- A New Surgical Treatment of Keloid Keloid Core ExcisionDocument7 pagesA New Surgical Treatment of Keloid Keloid Core Excisiongalih widodoNo ratings yet
- LovelandrdhDocument1 pageLovelandrdhapi-278465954No ratings yet
- No Change in Serum Metal Ions Levels After Primary Total Hip R - 2022 - ArthroplDocument4 pagesNo Change in Serum Metal Ions Levels After Primary Total Hip R - 2022 - ArthroplSanty OktavianiNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 PPT Psychiatry Lecture NotesDocument16 pagesUnit 7 PPT Psychiatry Lecture NotesDENNIS N. MUÑOZNo ratings yet
- GDC Training Standards in Implant DentistryDocument9 pagesGDC Training Standards in Implant Dentistrylg_1234No ratings yet
- Pex 399Document7 pagesPex 399Di RaNo ratings yet