Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Quality Management
Uploaded by
abcdconCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Quality Management
Uploaded by
abcdconCopyright:
Available Formats
QUALITY MANAGEMENT
Prof. Kaushik Paul
Associate Professor
Operations Area
E-Mail: kaushik.paul@igsm.in
Phone: 43559308
2
Total Quality Management Defined
Quality Specifications and Costs
Six Sigma Quality and Tools
External Benchmarking
ISO 9000
Service Quality Measurement
OBJECTIVES
3
TOTAL QUALITY MANAGEMENT (TQM)
Total quality management is defined as managing the entire organization
so that it excels on all dimensions of products and services that are
important to the customer
4
QUALITY SPECIFICATIONS
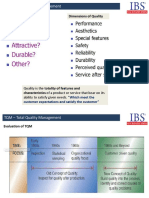
Design quality: Inherent value of the product in the marketplace
Dimensions include: Performance, Features, Reliability,
Durability, Serviceability, Response, Aesthetics, and
Reputation.
Conformance quality: Degree to which the product or service
design specifications are met
5
COSTS OF QUALITY
External Failure
Costs
Appraisal Costs
Prevention Costs
Internal Failure
Costs
Costs of
Quality
6
SIX SIGMA QUALITY
A philosophy and set of methods companies use to eliminate defects in
their products and processes
Seeks to reduce variation in the processes that lead to product defects
The name, six sigma refers to the variation that exists within plus or
minus six standard deviations of the process outputs
o 6
7
SIX SIGMA QUALITY (CONTINUED)
Six Sigma allows managers to readily describe process performance
using a common metric: Defects Per Million Opportunities (DPMO)
1, 000, 000 x
units of No. x
unit
per error for
ies opportunit
of Number
defects of Number
(
(
(
= DPMO
8
SIX SIGMA QUALITY (CONTINUED)
Example of Defects Per Million Opportunities
(DPMO) calculation. Suppose we observe 200
letters delivered incorrectly to the wrong
addresses in a small city during a single day
when a total of 200,000 letters were delivered.
What is the DPMO in this situation?
| |
000 , 1 = = 1, 000, 000 x
200, 000 x 1
200
DPMO
So, for every one
million letters
delivered this
citys postal
managers can
expect to have
1,000 letters
incorrectly sent to
the wrong
address.
Cost of Quality: What might that DPMO mean in terms of over-time
employment to correct the errors?
9
SIX SIGMA QUALITY: DMAIC CYCLE
Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control (DMAIC)
Developed by General Electric as a means of focusing effort on quality
using a methodological approach
Overall focus of the methodology is to understand and achieve what the
customer wants
DMAIC consists of five steps.
10
ANALYTICAL TOOLS FOR SIX SIGMA AND
CONTINUOUS IMPROVEMENT: CONTROL CHARTS
Can be used to monitor ongoing production process quality
and quality conformance to stated standards of quality
970
980
990
1000
1010
1020
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
LCL
UCL
11
OTHER SIX SIGMA TOOLS
Opportunity Flow Diagram used to graphically show those activities
that add value from those that are performed (and maybe could be
reduced or removed) that do not add value to the finished product
Failure Mode and Effect Analysis (FMEA) is a structured approach to
identify, estimate, prioritize, and evaluate risk of possible failures at
each stage in the process
Design of Experiments (DOE) a statistical test to determine cause-and-
effect relationships between process variables and output
12
SIX SIGMA ROLES AND RESPONSIBILITIES
1. Executive leaders must champion the process of improvement
2. Corporation-wide training in Six Sigma concepts and tools
3. Setting stretch objectives for improvement
4. Continuous reinforcement and rewards
13
THE SHINGO SYSTEM: FAIL-SAFE DESIGN
Shingos argument:
SQC methods do not prevent defects
Defects arise when people make errors
Defects can be prevented by providing workers with feedback on
errors
Poka -Yoke includes:
Checklists
Special tooling that prevents workers from making errors
14
ISO 9000
Series of standards agreed upon by the International Organization for
Standardization (ISO)
Adopted in 1987
More than 100 countries
A prerequisite for global competition?
ISO 9000 directs you to "document what you do and then do as you
documented"
15
THREE FORMS OF ISO CERTIFICATION
1. First party: A firm audits itself against ISO 9000 standards
2. Second party: A customer audits its supplier
3. Third party: A "qualified" national or international standards or
certifying agency serves as auditor
16
EXTERNAL BENCHMARKING STEPS
1. Identify those processes needing improvement
2. Identify a firm that is the world leader in performing the process
3. Contact the managers of that company and make a personal visit to
interview managers and workers
4. Analyze data
17
SERVICE QUALITY MEASUREMENT:SERVQUAL
A perceived service quality questionnaire survey methodology
Examines Dimensions of Service Quality including: Reliability,
Responsiveness, Assurance, Empathy, and Tangibles (e.g.,
appearance of physical facilities, equipment, etc.)
New version of this methodology is called e-Service Quality dealing
service on the Internet
Dimensions of Service Quality on the e-Service methodology include:
Reliability, Responsiveness, Access, Flexibility, Ease of Navigation,
Efficiency, Assurance/Trust, Security/Privacy, Price Knowledge, Site
Aesthetics, and Customization/Personalization
Reference: Operations Management for Competitive Advantage
By Chase, Jacobs & Aquilano, 10e
HOPE YOU ENJOYED THE CLASS. QUESTIONS PLEASE
THANK YOU
You might also like
- Entrepreneurship by Hisrich, Shepherd, Peters Chapter 1 MCQs and QuestionsDocument6 pagesEntrepreneurship by Hisrich, Shepherd, Peters Chapter 1 MCQs and QuestionsTooba100% (5)
- Project Report On Installation of Unit For Fabrication of Shuttering/scaffolding MaterialDocument8 pagesProject Report On Installation of Unit For Fabrication of Shuttering/scaffolding MaterialEIRI Board of Consultants and Publishers0% (2)
- Six Sigma Green BeltDocument63 pagesSix Sigma Green Beltsanjayerp5076100% (12)
- Intro S.PDDocument11 pagesIntro S.PDNitin BelleNo ratings yet
- Quality and Performance Excellence 8E Chapter 3Document33 pagesQuality and Performance Excellence 8E Chapter 3Aisah ReemNo ratings yet
- CMMI V2.0 OverviewDocument28 pagesCMMI V2.0 OverviewTomTom100% (3)
- Chapter 2 (A) Total Quality Management PDFDocument44 pagesChapter 2 (A) Total Quality Management PDFSarah AqirahNo ratings yet
- Case Study On Aditya Birla GroupDocument34 pagesCase Study On Aditya Birla GroupChetan Aravandekar0% (1)
- Ryan M Scharetg TMobile BillDocument3 pagesRyan M Scharetg TMobile BillJonathan Seagull LivingstonNo ratings yet
- Week 8 - Ch12 Six Sigma QualityDocument36 pagesWeek 8 - Ch12 Six Sigma QualityFlorenciano Johanes PongohNo ratings yet
- Total Quality Management: Anusuya Charan Ashma Katiyar Kritika Gupta Rajesh Yadav Sakshi Mohan Shaweta Goyal Vikash JoshiDocument29 pagesTotal Quality Management: Anusuya Charan Ashma Katiyar Kritika Gupta Rajesh Yadav Sakshi Mohan Shaweta Goyal Vikash JoshisudarshitaNo ratings yet
- 6 - Sigma InternetDocument24 pages6 - Sigma InternetRicarditisNo ratings yet
- Principles of Six SigmaDocument24 pagesPrinciples of Six SigmaAnoop KumarNo ratings yet
- Principles of Six SigmaDocument24 pagesPrinciples of Six Sigmarama jenaNo ratings yet
- Plan Software Quality With Testing /TITLEDocument17 pagesPlan Software Quality With Testing /TITLESelamawit AmanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 9 - Six SigmaDocument10 pagesLesson 9 - Six SigmaLovesel MalabuyocNo ratings yet
- CH V - Quality ManagmentDocument50 pagesCH V - Quality ManagmentSanjay ThakurNo ratings yet
- UNIT IV TQMDocument49 pagesUNIT IV TQMmohanravi1986No ratings yet
- Cme347 Lean Manufacturing Question Bank in PDFDocument18 pagesCme347 Lean Manufacturing Question Bank in PDFTHIRUMALAI0% (1)
- Ops Exam 3 ReviewDocument7 pagesOps Exam 3 ReviewEmily SNo ratings yet
- Six Sigma Quality: Chapter TwelveDocument25 pagesSix Sigma Quality: Chapter TwelveTopan ArdiansyahNo ratings yet
- Alok ChutiyaDocument19 pagesAlok Chutiyaanurag trivediNo ratings yet
- Manajemen Operasi Week 2 PrsentasiDocument46 pagesManajemen Operasi Week 2 PrsentasiCICI SITI BARKAHNo ratings yet
- Six Sigma Quality and Continuous Improvement ToolsDocument30 pagesSix Sigma Quality and Continuous Improvement ToolsJem ChuaNo ratings yet
- Total Quality Management: .... That When You Harbor Bitterness, Happiness Will Dock ElsewhereDocument37 pagesTotal Quality Management: .... That When You Harbor Bitterness, Happiness Will Dock Elsewherewin_kcNo ratings yet
- Chap08 ProjectqualitymanagementDocument30 pagesChap08 Projectqualitymanagementiliya maisarahNo ratings yet
- IX Igma - : AbstractDocument10 pagesIX Igma - : AbstractViswanath TurlapatiNo ratings yet
- Quality ManagementDocument69 pagesQuality ManagementVibhaJaiswalNo ratings yet
- Define Measure Analyze: Lean Six Sigma TrainingDocument209 pagesDefine Measure Analyze: Lean Six Sigma TrainingaavijayNo ratings yet
- Managing Quality: Operations Management R. Dan Reid & Nada R. SandersDocument24 pagesManaging Quality: Operations Management R. Dan Reid & Nada R. SandersFaisal KhanNo ratings yet
- QUALITY MANAGEMENT GUIDEDocument30 pagesQUALITY MANAGEMENT GUIDEAlamin KhanNo ratings yet
- TQM FinalDocument23 pagesTQM FinalSantosh BurudNo ratings yet
- Chap007 ADocument49 pagesChap007 AMvelo PhungulaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Quality: Tunga, Omari 0713579016Document38 pagesIntroduction To Quality: Tunga, Omari 0713579016ummuayman jumaNo ratings yet
- TQM5Document16 pagesTQM5Rio Aristo BirawaNo ratings yet
- Software Quality Metrics and ModelsDocument37 pagesSoftware Quality Metrics and ModelsShusySasucheNo ratings yet
- Module-II Bu Pom NotesDocument35 pagesModule-II Bu Pom NotesKazia Shamoon AhmedNo ratings yet
- Six Sigma Group 5Document47 pagesSix Sigma Group 5Angeline Boado de OcampoNo ratings yet
- Final HandoutDocument3 pagesFinal HandoutCrisanta EstebanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document28 pagesChapter 6SALIM HUSAYN AMBEEYAH ALOUKILINo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - QualityDocument81 pagesChapter 5 - QualityThư Trần Nguyễn AnhNo ratings yet
- Second ClassDocument48 pagesSecond ClassMartinus Golden SiteketaNo ratings yet
- Vishnu Chaudhary (164261) - Six SigmaDocument17 pagesVishnu Chaudhary (164261) - Six Sigmavishnu chaudharyNo ratings yet
- OM M9 TQM HandoutDocument64 pagesOM M9 TQM HandoutChandan SainiNo ratings yet
- Software Quality Assurance Methods and StandardsDocument26 pagesSoftware Quality Assurance Methods and StandardsIHDJsjnNo ratings yet
- Designing Quality Products, Processes and ServicesDocument47 pagesDesigning Quality Products, Processes and ServicesKoushik gangipelly100% (1)
- Session 14 - Quality ManagementDocument17 pagesSession 14 - Quality ManagementNeha SardanaNo ratings yet
- Managing Quality and Boosting ProductivityDocument30 pagesManaging Quality and Boosting ProductivityadnanNo ratings yet
- Six Sigma Quality Improvement ProgramDocument10 pagesSix Sigma Quality Improvement Programraviteja556No ratings yet
- Lec 3 TQMDocument24 pagesLec 3 TQMWaleed AhmedNo ratings yet
- Operations & Productions Management: Bahria UniversityDocument16 pagesOperations & Productions Management: Bahria UniversityFareed khan ZKNo ratings yet
- Quality and ReliabilityDocument32 pagesQuality and ReliabilitymaheshNo ratings yet
- TQM - Total Quality Management: What Is Quality ? Dimensions of QualityDocument23 pagesTQM - Total Quality Management: What Is Quality ? Dimensions of QualityabhiNo ratings yet
- Six Sigma Quality: Chapter TwelveDocument25 pagesSix Sigma Quality: Chapter TwelveSabila SyarafinaNo ratings yet
- SQA Pressmanv1Document84 pagesSQA Pressmanv1Cindy Septian Ayu SaputriNo ratings yet
- CH 9 StevensonDocument53 pagesCH 9 StevensonPetersonNo ratings yet
- Mba Six SigmaDocument19 pagesMba Six SigmaMandhara KsNo ratings yet
- What Is TQM?Document43 pagesWhat Is TQM?nimra100% (1)
- Six sigma overviewDocument39 pagesSix sigma overviewRaveendra RaoNo ratings yet
- Workflows: How to Design, Improve and Automate High Performance Processes.From EverandWorkflows: How to Design, Improve and Automate High Performance Processes.No ratings yet
- Marketing ResearchDocument26 pagesMarketing ResearchAshish ChatrathNo ratings yet
- Investment Mgt.Document9 pagesInvestment Mgt.Ashish ChatrathNo ratings yet
- Final Report of Summer TrainingDocument110 pagesFinal Report of Summer TrainingAshish ChatrathNo ratings yet
- Airte PRJL (MOS I, GRP II)Document64 pagesAirte PRJL (MOS I, GRP II)Ashish Chatrath100% (8)
- How To Calculate Total IncomeDocument16 pagesHow To Calculate Total IncomeAshish ChatrathNo ratings yet
- The Saga of Globalization of Indian Brand: IM Project OnDocument14 pagesThe Saga of Globalization of Indian Brand: IM Project OnAshish Chatrath100% (2)
- Camels Model of IDBIDocument15 pagesCamels Model of IDBIAshish ChatrathNo ratings yet
- How Budget Is PreparedDocument13 pagesHow Budget Is Preparedambesh SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Tata Motors' Acquisation of JLRDocument14 pagesTata Motors' Acquisation of JLRAshish Chatrath100% (2)
- Ashish Chatrath Final DissertationDocument63 pagesAshish Chatrath Final DissertationAshish ChatrathNo ratings yet
- BCG Asignment On ITCDocument13 pagesBCG Asignment On ITCAshish Chatrath100% (6)
- Harley Davidson: Presented By: Ashish ChatarathDocument23 pagesHarley Davidson: Presented By: Ashish ChatarathAshish Chatrath100% (2)
- Strategic Capacity PlanningDocument27 pagesStrategic Capacity PlanningAshish Chatrath78% (9)
- Supply Chain ManagementDocument15 pagesSupply Chain ManagementAshish Chatrath100% (16)
- Lean ProductionDocument31 pagesLean ProductionAshish Chatrath100% (2)
- Operations Strategy and CompetitivenessDocument21 pagesOperations Strategy and CompetitivenessAshish Chatrath100% (1)
- Product Design and Process Selection - ServicesDocument15 pagesProduct Design and Process Selection - ServicesAshish Chatrath100% (1)
- Introduction To Operations ManagementDocument22 pagesIntroduction To Operations ManagementAshish Chatrath100% (8)
- Inventory ControlDocument31 pagesInventory ControlAshish Chatrath100% (1)
- Facility LocationDocument13 pagesFacility LocationAshish ChatrathNo ratings yet
- Demand ManagementDocument39 pagesDemand ManagementAshish Chatrath100% (1)
- Facility LayoutDocument36 pagesFacility LayoutAshish Chatrath100% (4)
- Decision Theory FinalDocument42 pagesDecision Theory FinalAshish Chatrath100% (2)
- Venkatesh ResumeDocument6 pagesVenkatesh ResumeSantosh Reddy Chennuru100% (1)
- Audit BoyntonDocument27 pagesAudit BoyntonMasdarR.MochJetrezzNo ratings yet
- Greek Labour LawDocument3 pagesGreek Labour LawSerban MihaelaNo ratings yet
- Business Risk (D)Document5 pagesBusiness Risk (D)Tchao AdrienNo ratings yet
- Cape, Jessielyn Vea C. PCBET-01-301P AC9/ THURSAY/ 9:00AM-12:00PMDocument5 pagesCape, Jessielyn Vea C. PCBET-01-301P AC9/ THURSAY/ 9:00AM-12:00PMhan jisungNo ratings yet
- Primavera Oil Gas Solutions Brief 2203049Document6 pagesPrimavera Oil Gas Solutions Brief 2203049sujitmenonNo ratings yet
- Barilla-SpA CaseStudy Short Reaction PaperDocument3 pagesBarilla-SpA CaseStudy Short Reaction Papersvk320No ratings yet
- Finance Class 04 - New With TestDocument23 pagesFinance Class 04 - New With TestMM Fakhrul IslamNo ratings yet
- Denali Investors Partner Letter - 2014 Q2Document6 pagesDenali Investors Partner Letter - 2014 Q2ValueInvestingGuy100% (1)
- Motores PDFDocument196 pagesMotores PDFDanilo CherresNo ratings yet
- Impact of Shelf Life On Fast Moving Consumer GoodsDocument50 pagesImpact of Shelf Life On Fast Moving Consumer GoodsPragati SinghNo ratings yet
- Finals Activity No .2 Completing THE Accounting Cycle: Palad, Nica C. Mr. Alfred BautistaDocument6 pagesFinals Activity No .2 Completing THE Accounting Cycle: Palad, Nica C. Mr. Alfred BautistaMica Mae CorreaNo ratings yet
- SACCO Budgeting and Business Planning ManualDocument54 pagesSACCO Budgeting and Business Planning ManualFred IlomoNo ratings yet
- Travel Procedure Module #3Document9 pagesTravel Procedure Module #3Salvatore VieiraNo ratings yet
- Project To Expand Puerto Rico - Vieques - Culebra Maritime Service OK'd For Federal Funding - News Is My BusinessDocument2 pagesProject To Expand Puerto Rico - Vieques - Culebra Maritime Service OK'd For Federal Funding - News Is My BusinessCORALationsNo ratings yet
- Blank Hundred ChartDocument3 pagesBlank Hundred ChartMenkent Santisteban BarcelonNo ratings yet
- ThelerougecandycompanyDocument4 pagesThelerougecandycompanyAreeba.SulemanNo ratings yet
- Account Payable Tables in R12Document8 pagesAccount Payable Tables in R12anchauhanNo ratings yet
- IAS34Document2 pagesIAS34Mohammad Faisal SaleemNo ratings yet
- ACI LimitedDocument2 pagesACI LimitedAshique IqbalNo ratings yet
- Find stock prices for delisted companies in DatastreamDocument3 pagesFind stock prices for delisted companies in Datastreamprofjblaze2No ratings yet
- Resa Law24Document3 pagesResa Law24NaSheengNo ratings yet
- Contract Close-OutDocument3 pagesContract Close-OutParents' Coalition of Montgomery County, MarylandNo ratings yet
- Economic Espionage: A Framework For A Workable Solution: Mark E.A. DanielsonDocument46 pagesEconomic Espionage: A Framework For A Workable Solution: Mark E.A. DanielsonmiligramNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Managing System Project PDFDocument44 pagesChapter 3 - Managing System Project PDFJoshua Ocampo SenetaNo ratings yet
- US Economics Digest: The 2014 FOMC: A New Cast of CharactersDocument10 pagesUS Economics Digest: The 2014 FOMC: A New Cast of CharactersGlenn ViklundNo ratings yet