Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Amoxicillin
Uploaded by
Anthony BrookOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Amoxicillin
Uploaded by
Anthony BrookCopyright:
Available Formats
Name Description
Amoxicillin
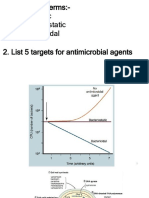
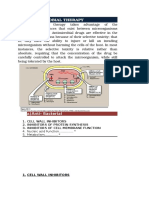
A broad-spectrum semisynthetic antibiotic similar to ampicillin except that its resistance to gastric acid permits higher serum levels with oral administration. Amoxicillin is commonly prescribed with clauvanic acid (a beta lactamase inhibitor) as it is susceptible to beta-lacatamase degradation. Anti-Bacterial Agents Penicillins For the treatment of infections of the ear, nose, and throat, the genitourinary tract,
Categories Indication
the skin and skin structure, and the lower respiratory tract due to susceptible (only b-lactamase-negative) strains of Streptococcus spp. (a- and b-hemolytic strains only), S. pneumoniae, Staphylococcus spp., H. influenzae, E. coli, P. mirabilis, or E. faecalis. Also for the treatment of acute, uncomplicated gonorrhea (ano-genital Pharmacology and urethral infections) due to N. gonorrhoeae (males and females). Amoxicillin is a moderate-spectrum antibiotic active against a wide range of Gram-positive, and a limited range of Gram-negative organisms. It is usually the drug of choice within the class because it is better absorbed, following oral administration, than other beta-lactam antibiotics. Amoxicillin is susceptible to degradation by -lactamase-producing bacteria, and so may be given with clavulanic acid to increase its susceptability. The incidence of -lactamaseproducing resistant organisms, including E. coli, appears to be increasing. Amoxicillin is sometimes combined with clavulanic acid, a -lactamase inhibitor, to increase the spectrum of action against Gram-negative organisms, and to overcome bacterial antibiotic resistance mediated through -lactamase Mechanism of Action production. Amoxicillin binds to penicillin-binding protein 1A (PBP-1A) located inside the bacterial cell well. Penicillins acylate the penicillin-sensitive transpeptidase Cterminal domain by opening the lactam ring. This inactivation of the enzyme prevents the formation of a cross-link of two linear peptidoglycan strands, inhibiting the third and last stage of bacterial cell wall synthesis. Cell lysis is then mediated by bacterial cell wall autolytic enzymes such as autolysins; it is possible Absorption Half Life Route of Elimination Side Effects that amoxicllin interferes with an autolysin inhibitor. Rapidly absorbed after oral administration. 61.3 minutes
You might also like
- Amoxicillin: A Beginner's 20-Minute Quick Guide Overview on its Use Cases to Treat Bacterial Infection and Side EffectsFrom EverandAmoxicillin: A Beginner's 20-Minute Quick Guide Overview on its Use Cases to Treat Bacterial Infection and Side EffectsNo ratings yet
- AmpicillinDocument1 pageAmpicillinAhmad Happy M SNo ratings yet
- The Essential Guide to Amoxicillin: Usage, Precautions, Interactions and Side Effects.From EverandThe Essential Guide to Amoxicillin: Usage, Precautions, Interactions and Side Effects.No ratings yet
- Amoxicillin (: INN BAN β-lactam antibiotic bacterial infections microorganismsDocument17 pagesAmoxicillin (: INN BAN β-lactam antibiotic bacterial infections microorganismsNiks KanungoNo ratings yet
- Phar - Cell Wall Part 2 - Lec 8 - TheoDocument19 pagesPhar - Cell Wall Part 2 - Lec 8 - Theoسلام شاكر حميد جميل 6506No ratings yet
- Cell Wall Inhibitors: Beta-Lactams: PenicillinsDocument12 pagesCell Wall Inhibitors: Beta-Lactams: Penicillinsمحمد بن صالحNo ratings yet
- Hikma Pharmaceuticals: AmoclanDocument5 pagesHikma Pharmaceuticals: AmoclanBest ManNo ratings yet
- 10.beta Lactamase InhibitorsDocument15 pages10.beta Lactamase InhibitorsJagirNo ratings yet
- OgminDocument9 pagesOgminelcapitano vegetaNo ratings yet
- Ampicillin: Mechanism of ActionDocument2 pagesAmpicillin: Mechanism of ActionAditya GopeNo ratings yet
- OgminDocument7 pagesOgminSharar KalayliehNo ratings yet
- Beta-Lactam Antibiotics & Other Inhibitors of Cell WallDocument71 pagesBeta-Lactam Antibiotics & Other Inhibitors of Cell WallAlvin LaurenceNo ratings yet
- Classes of AntibioticsDocument7 pagesClasses of Antibioticsthoth_trismegistusNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics CologyDocument31 pagesAntibiotics CologyManthan ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Ampicillin SulbactamDocument5 pagesAmpicillin SulbactamtitiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 Chemotherapeutic AgentDocument54 pagesLecture 7 Chemotherapeutic AgentjowditzNo ratings yet
- Medication Summary: Penicillins, Natural Class SummaryDocument13 pagesMedication Summary: Penicillins, Natural Class SummaryAfifah NANo ratings yet
- Co AmoxiclavDocument2 pagesCo AmoxiclavKatrina Ponce92% (12)
- Pharmacology of AmoxicillinDocument15 pagesPharmacology of AmoxicillinWilliamNo ratings yet
- PenicillinsDocument23 pagesPenicillinsajpharmacist117No ratings yet
- EsblDocument16 pagesEsblsharmamaddy32No ratings yet
- Amoxicillin PDFDocument6 pagesAmoxicillin PDFNaveen KumarNo ratings yet
- PenicillinDocument21 pagesPenicillinnadar shahNo ratings yet
- Augmentin in JDocument15 pagesAugmentin in JChutharat SucharitNo ratings yet
- Nurse Round - AugmentinDocument15 pagesNurse Round - AugmentinkyokeungkennethNo ratings yet
- Calamox Tablets SuspensionsDocument4 pagesCalamox Tablets SuspensionsAbdurrahman DarmanNo ratings yet
- Antibacterial AntibioticsDocument13 pagesAntibacterial AntibioticsMuhamed ArsalanNo ratings yet
- Phar - Cell Wall Inhibitor - Lec 7 - TheoDocument20 pagesPhar - Cell Wall Inhibitor - Lec 7 - Theoسلام شاكر حميد جميل 6506No ratings yet
- 3 The B-Lactamase ThreatDocument8 pages3 The B-Lactamase ThreatAnfalNo ratings yet
- Gram Negative Bacterial ResistanceDocument49 pagesGram Negative Bacterial Resistancesaraabolghasemi1No ratings yet
- List of Antibiotics - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument11 pagesList of Antibiotics - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaRamesh KumarNo ratings yet
- AugmentinDocument7 pagesAugmentinImran KhanNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Therapy: A) Anti-BacterialDocument9 pagesAntimicrobial Therapy: A) Anti-BacterialUnor KnownNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of Action of Penicillin & CephalosporinDocument7 pagesMechanism of Action of Penicillin & CephalosporinshahabahmadNo ratings yet
- Cell Wall Synthesis Inhibitors: Pharmacology Seminar Group: A1Document113 pagesCell Wall Synthesis Inhibitors: Pharmacology Seminar Group: A1Lola KhatimNo ratings yet
- Beta Lactam AntibioticsDocument28 pagesBeta Lactam AntibioticsHassan.shehri100% (11)
- Clamo Powder For Oral Suspension 312.5mg/5ml Drug InteractionDocument2 pagesClamo Powder For Oral Suspension 312.5mg/5ml Drug InteractionRania T. SabriNo ratings yet
- AntibioticsDocument115 pagesAntibioticspmm21d229No ratings yet
- Introduction To Beta Lactam AntibioticsDocument31 pagesIntroduction To Beta Lactam AntibioticsVishaal BhatNo ratings yet
- Extended Spectrum PenicillinsDocument80 pagesExtended Spectrum PenicillinsSunanda mohanNo ratings yet
- OrganicDocument27 pagesOrganicمحمد رحمان محمد الدليميNo ratings yet
- Antibacterial: Topics: 1. Cell Wall Synthesis InhibitorDocument26 pagesAntibacterial: Topics: 1. Cell Wall Synthesis InhibitorMusfira YaseenNo ratings yet
- Name Amoxicillin Accession Number DB01060 (APRD00248) Type GroupsDocument12 pagesName Amoxicillin Accession Number DB01060 (APRD00248) Type GroupsHilyaNo ratings yet
- AugmentinDocument24 pagesAugmentinKaren Ann M. EstradaNo ratings yet
- Penicillins: 6-Amino Pencillanic Acid (6-APA)Document14 pagesPenicillins: 6-Amino Pencillanic Acid (6-APA)ThileepNo ratings yet
- Beta Lactams 1Document44 pagesBeta Lactams 1C E princeyNo ratings yet
- Amoxicillin + Clavulanic AcidDocument1 pageAmoxicillin + Clavulanic AcidAditya GopeNo ratings yet
- An Update On Newer - Lactamases: Review ArticleDocument11 pagesAn Update On Newer - Lactamases: Review ArticleBev YuNo ratings yet
- Pseudomonas Aeruginosa. Effective: Antibiotics by ClassDocument4 pagesPseudomonas Aeruginosa. Effective: Antibiotics by ClassDocFrankNo ratings yet
- Beta-Lactam Antibiotics Kul Nov 2014Document44 pagesBeta-Lactam Antibiotics Kul Nov 2014Sahala Louis AlexanderNo ratings yet
- BED12 - Antibiotics PharmacologyDocument2 pagesBED12 - Antibiotics PharmacologyAmir AmirulNo ratings yet
- Ampicillin: Mechanism of ActionDocument2 pagesAmpicillin: Mechanism of ActiongamhaelNo ratings yet
- AntibioticsDocument24 pagesAntibioticsAlba GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial AgentsDocument29 pagesAntimicrobial Agentsyaya mohaNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic 1-Terminology: 1. Inhibition of Cell Wall SynthesisDocument12 pagesAntibiotic 1-Terminology: 1. Inhibition of Cell Wall SynthesismidoNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Pharmacologyforthe Neonatalfoal: K. Gary MagdesianDocument19 pagesAntimicrobial Pharmacologyforthe Neonatalfoal: K. Gary MagdesianCristhian Jover CastroNo ratings yet
- 2-Cell Wall Inhibitor Antibitics-I Oct 15th 2018Document28 pages2-Cell Wall Inhibitor Antibitics-I Oct 15th 2018Leena AlateeqNo ratings yet
- Antibacterial AgentsDocument44 pagesAntibacterial Agentsbelindasithole965No ratings yet
- Penicillin's: Jagir R. Patel Asst Professor Dept. PharmacologyDocument29 pagesPenicillin's: Jagir R. Patel Asst Professor Dept. PharmacologyJagirNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics PDFDocument8 pagesAntibiotics PDFSarah JaneNo ratings yet
- The Game Will Be Set in England in 2150Document2 pagesThe Game Will Be Set in England in 2150Anthony BrookNo ratings yet
- KPA QuizDocument2 pagesKPA QuizAnthony BrookNo ratings yet
- KPA Quiz 08-02-11Document2 pagesKPA Quiz 08-02-11Anthony BrookNo ratings yet
- KPA Quiz 05-10-10Document2 pagesKPA Quiz 05-10-10Anthony BrookNo ratings yet
- KPA Quiz 05-10-10Document2 pagesKPA Quiz 05-10-10Anthony BrookNo ratings yet