Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Information System Decision-Making
Information System Decision-Making
Uploaded by
Aiswarya ShanmugamOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Information System Decision-Making
Information System Decision-Making
Uploaded by
Aiswarya ShanmugamCopyright:
Available Formats
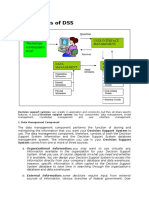
Decision support system A decision support systems (DSS) is a computer-based information system that supports business or organizational decision-making
activities. DSSs serve the management, operations, and planning levels of an organization and help to make decisions, which may be rapidly changing and not easily specified in advance.
DSS include knowledge-based systems. A properly designed DSS is an
interactive software-based system intended to help decision makers compile useful information from a combination of raw data, documents, personal knowledge, or business models to identify and solve problems and make decisions.
Decision Support Systems (DSS) are a specific class of computerized
information system that supports business and organizational decision-
making activities. A properly designed DSS is an interactive software-based
system intended to help decision makers compile useful information from raw data, documents, personal knowledge, and/or business models to identify and solve problems and make decisions.
A Decision Support System (DSS) is a collection of integrated software
applications and hardware that form the backbone of an organizations
decision making process. Companies across all industries rely on decision
support tools, techniques, and models to help them assess and resolve everyday business questions. The decision support system is data-driven, as the entire Intelligence (BI) reporting tools, processes, and methodologies are key reporting, monitoring, and data analysis. process feeds off of the collection and availability of data to analyze. Business components to any decision support system and provide end users with rich
Typical information that a decision support application might gather and present would be:
Accessing all of your current information assets, including legacy and relational data sources, cubes, data warehouses, and data marts Comparative sales figures between one week and the next
Projected revenue figures based on new product sales assumptions The consequences of different decision alternatives, given past experience in a context that is described
Typical information that a decision support application might gather and present are:
inventories of information assets (including legacy and relational data sources, cubes, data warehouses, and data marts), comparative sales figures between one period and the next,
projected revenue figures based on product sales assumptions.
Benefits 1. Improves personal efficiency
2. Speeds up problem solving in an organization 3. Facilitates interpersonal communication 4. Promotes learning or training 5. Increases organizational control
6. Generates new evidence in support of a decision
7. Creates a competitive advantage over competition
8. Encourages exploration and discovery on the part of the decision maker 9. Reveals new approaches to thinking about the problem space 10. Helps automate managerial processes
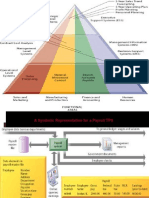
DSS components may be classified as: 1. Inputs: Factors, numbers, and characteristics to analyze user
2. User Knowledge and Expertise: Inputs requiring manual analysis by the 3. Outputs: Transformed data from which DSS "decisions" are generated 4. Decisions: Results generated by the DSS based on user criteria High-level Decision Support System Requirements:
Data collection from multiple sources (sales data, inventory data, supplier data, market research data. etc.) Data formatting and collation A suitable database location and format built for decision support based reporting and analysis Robust tools and applications to report, monitor, and analyze the data
Decision support systems have become critical and ubiquitous across all types of business. In todays global marketplace, it is imperative that companies support systems have a significant competitive advantage. respond quickly to market changes. Companies with comprehensive decision
You might also like
- This Is Me Letting You Go PDFDocument1 pageThis Is Me Letting You Go PDFAdriel Borja20% (5)
- WEBEL SRS SingleMobilePlatform 1.2Document156 pagesWEBEL SRS SingleMobilePlatform 1.2sunitsinhaNo ratings yet
- SAP Data Archiving StrategyDocument33 pagesSAP Data Archiving StrategyThaís Dalanesi100% (3)
- Exploring Bioinformatics A Project Based Approach PDFDocument2 pagesExploring Bioinformatics A Project Based Approach PDFDiana0% (2)
- Etl Architecture Best Practices PDFDocument2 pagesEtl Architecture Best Practices PDFElijahNo ratings yet
- Decision Support SystemsDocument36 pagesDecision Support SystemssindhujaNo ratings yet
- DecisionDocument6 pagesDecisionSingh GurpreetNo ratings yet
- A NARRATIVE REPORT OF Chapter16Document22 pagesA NARRATIVE REPORT OF Chapter16Mafe Angela OrejolaNo ratings yet
- Unit3-MIS DSSDocument9 pagesUnit3-MIS DSSBhavesh RathiNo ratings yet
- Information System Applications Unit IIIDocument18 pagesInformation System Applications Unit IIIHrithick BhowmickNo ratings yet
- 10 Chapter 10 Decision Support Systems DSSDocument6 pages10 Chapter 10 Decision Support Systems DSSJobaiyerNo ratings yet
- Advantages of Business Intelligence: 1. Boost ProductivityDocument4 pagesAdvantages of Business Intelligence: 1. Boost ProductivityShivansh tomarNo ratings yet
- Decision Support Systems and Business IntelligenceDocument45 pagesDecision Support Systems and Business IntelligenceNeha Priya50% (2)
- Decision Making & Information SystemDocument11 pagesDecision Making & Information SystemArchitNo ratings yet
- d22244ddssss NolannDocument17 pagesd22244ddssss Nolannrobee.sumatraNo ratings yet
- MIS MergedDocument58 pagesMIS MergedArzoo BanoNo ratings yet
- CL585Document7 pagesCL585marcusfdm69No ratings yet
- Ponents of DSSDocument7 pagesPonents of DSSDeep BhalodiaNo ratings yet
- Types of Decision Support Systems (DSS) : by Dan PowerDocument7 pagesTypes of Decision Support Systems (DSS) : by Dan PowermylesNo ratings yet
- DSS - Ch01 Decision Support System Lecture NotesDocument7 pagesDSS - Ch01 Decision Support System Lecture Notescoolco270No ratings yet
- 12.2 Marketing Information Systems (Figure 12.2 & Figure 12.3)Document7 pages12.2 Marketing Information Systems (Figure 12.2 & Figure 12.3)Premendra SahuNo ratings yet
- Too Many Cooks Spoil The CRM System CRM: When Should Customer Service Run The Show?Document18 pagesToo Many Cooks Spoil The CRM System CRM: When Should Customer Service Run The Show?PanAcatloverNo ratings yet
- DSSDocument6 pagesDSSMohit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Business Intelligence and Applications Question Paper-2009 PREPARED BY: Simranjeet (019), Gunjan Garg (042), Aanchal GargDocument27 pagesBusiness Intelligence and Applications Question Paper-2009 PREPARED BY: Simranjeet (019), Gunjan Garg (042), Aanchal GargGunjan Happy BansalNo ratings yet
- 12.1 Supporting Business Functions in An Enterprise With InformationDocument26 pages12.1 Supporting Business Functions in An Enterprise With InformationCharis ClarindaNo ratings yet
- Decision Support Systems (DSS)Document13 pagesDecision Support Systems (DSS)wasiuddinNo ratings yet
- What Are The Types of Information System ApaDocument16 pagesWhat Are The Types of Information System ApaAbeer AlshebamiNo ratings yet
- Mis Module 3Document38 pagesMis Module 3Tinku JoyNo ratings yet
- Compare - Dss and Bi PDFDocument6 pagesCompare - Dss and Bi PDFSharmila SaravananNo ratings yet
- Document 2Document4 pagesDocument 2Ridhi JainNo ratings yet
- Decision Support SystemDocument19 pagesDecision Support SystemClassic WheelsNo ratings yet
- Structure of MIS: Decision Support SystemDocument19 pagesStructure of MIS: Decision Support SystemAnkur RajputNo ratings yet
- Bi Unit ! CH 2Document26 pagesBi Unit ! CH 2skyverma0709No ratings yet
- What Is A Decision Support System (DSS) ?Document6 pagesWhat Is A Decision Support System (DSS) ?Kritt BillkinNo ratings yet
- Decision Support SystemDocument55 pagesDecision Support Systemsudha_adventNo ratings yet
- Tugas Ekotek Desicion Support System (DSS)Document11 pagesTugas Ekotek Desicion Support System (DSS)bima wpNo ratings yet
- Table 4.1: Business Value of Enhanced Decision MakingDocument20 pagesTable 4.1: Business Value of Enhanced Decision MakingGabrielle Joshebed AbaricoNo ratings yet
- Management Information System Chapter 12 NotesDocument3 pagesManagement Information System Chapter 12 Notesgut78No ratings yet
- Knowledge Management Unit-1 NotesDocument8 pagesKnowledge Management Unit-1 Notesloyof97175No ratings yet
- Decision Support SystemDocument4 pagesDecision Support SystemNickyGuptaNo ratings yet
- A Journey From Data To Information IntelligenceDocument20 pagesA Journey From Data To Information IntelligenceSwati HansNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document49 pagesUnit 2Malavika ThampyNo ratings yet
- Lecture One Introduction and Basics of DSSDocument6 pagesLecture One Introduction and Basics of DSSUmmu AhmedNo ratings yet
- Decision Support Systems: Practical No. 3Document8 pagesDecision Support Systems: Practical No. 3Suvarna LangadeNo ratings yet
- Prof K.G.Muralidhra: Submitted ToDocument26 pagesProf K.G.Muralidhra: Submitted TorajendrajhaNo ratings yet
- Questions For MISDocument11 pagesQuestions For MISKaran ShahNo ratings yet
- Decision Support Systems DefinitionDocument7 pagesDecision Support Systems DefinitionDivisha AgarwalNo ratings yet
- 3.mis Chapter Three Computer Based IsDocument36 pages3.mis Chapter Three Computer Based IsEndash HaileNo ratings yet
- System Analysis DesignDocument4 pagesSystem Analysis DesignZila Parishad RanchiNo ratings yet
- Describe Various Ways That Knowledge Management Systems Could Help Firms With Sales and Marketing or With Manufacturing and ProductionDocument1 pageDescribe Various Ways That Knowledge Management Systems Could Help Firms With Sales and Marketing or With Manufacturing and ProductionJia WongNo ratings yet
- Decision Support SystemDocument4 pagesDecision Support SystemEllen MaskariñoNo ratings yet
- What Is Data-Driven Decision-Making?Document3 pagesWhat Is Data-Driven Decision-Making?Sock the CatNo ratings yet
- Bilal BestDocument20 pagesBilal BestNaabaa 30No ratings yet
- Components of A DSS: SoftwareDocument3 pagesComponents of A DSS: Softwareaisolamaddy86No ratings yet
- QNDocument6 pagesQNdoctor andey1No ratings yet
- MIS Tim UNIT 2Document40 pagesMIS Tim UNIT 2Vishnu R NairNo ratings yet
- What Is MIS?: DEFINITION of 'Decision Support System - DSS'Document29 pagesWhat Is MIS?: DEFINITION of 'Decision Support System - DSS'Annu BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Decision Support Sytem1Document2 pagesDecision Support Sytem1Yadvender YadavNo ratings yet
- Decision Support SystemDocument60 pagesDecision Support SystemYashaswini KnNo ratings yet
- Management Information System: The Business School, University of JammuDocument10 pagesManagement Information System: The Business School, University of Jammuanon_945457258No ratings yet
- System and Its ComponentsDocument2 pagesSystem and Its ComponentsGokulNo ratings yet
- Full Value of Data: Maximizing Business Potential through Data-Driven Insights and Decisions. Part 2From EverandFull Value of Data: Maximizing Business Potential through Data-Driven Insights and Decisions. Part 2No ratings yet
- Decision Support System: Fundamentals and Applications for The Art and Science of Smart ChoicesFrom EverandDecision Support System: Fundamentals and Applications for The Art and Science of Smart ChoicesNo ratings yet
- Business Analytics: Leveraging Data for Insights and Competitive AdvantageFrom EverandBusiness Analytics: Leveraging Data for Insights and Competitive AdvantageNo ratings yet
- Data-Driven Business Strategies: Understanding and Harnessing the Power of Big DataFrom EverandData-Driven Business Strategies: Understanding and Harnessing the Power of Big DataNo ratings yet
- Dengue Fever Prediction A Data Mining Problem 2153 0602 1000181 PDFDocument5 pagesDengue Fever Prediction A Data Mining Problem 2153 0602 1000181 PDFmathi0000No ratings yet
- SELECT DISTINCT Empname FROM EmptableDocument10 pagesSELECT DISTINCT Empname FROM Emptablesaumitra ghogaleNo ratings yet
- 48 UX Researcher Interview Questions (With Example Answers)Document1 page48 UX Researcher Interview Questions (With Example Answers)leon4bernardNo ratings yet
- The Game in Wall Street and How To Play It Successfully by Hoyle PDFDocument99 pagesThe Game in Wall Street and How To Play It Successfully by Hoyle PDFBhaskar Agarwal100% (1)
- Teradata Physical Database Design PDFDocument7 pagesTeradata Physical Database Design PDFpuneetswarnkarNo ratings yet
- Literature Review On Electronic Health RecordsDocument6 pagesLiterature Review On Electronic Health Recordsea2167ra100% (1)
- DBMS Course FileDocument193 pagesDBMS Course Fileabdul rehmanNo ratings yet
- MicheletDocument253 pagesMicheletjpscabralNo ratings yet
- SQL Server Error Message: What and Why "This Error"Document30 pagesSQL Server Error Message: What and Why "This Error"indiadigitNo ratings yet
- Automating CPM-GOMS: Bonnie John, Alonso Vera, Michael Matessa, Michael Freed, and Roger RemingtonDocument8 pagesAutomating CPM-GOMS: Bonnie John, Alonso Vera, Michael Matessa, Michael Freed, and Roger RemingtonJuliaVuNo ratings yet
- What Is Chatgpt? (And How To Use It)Document5 pagesWhat Is Chatgpt? (And How To Use It)guruict2021No ratings yet
- Distributed Database - Unit 5Document4 pagesDistributed Database - Unit 5PreethiVenkateswaranNo ratings yet
- Module Title Module 1: Database Environment Learning ObjectivesDocument6 pagesModule Title Module 1: Database Environment Learning ObjectivesVideo MusicNo ratings yet
- Proposal Spotify Recommendation SystemDocument13 pagesProposal Spotify Recommendation SystemAmarjeet VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Uploading Instructions:: Assignment No. 02 Semester: Spring 2020 Total Marks: 20Document7 pagesUploading Instructions:: Assignment No. 02 Semester: Spring 2020 Total Marks: 20ALI SUFYANNo ratings yet
- Sistem Informasi Pelaporan Dan Penanganan Kerusakan Fasilitas Kelas Studi Kasus: Universitas Kristen Duta WacanaDocument10 pagesSistem Informasi Pelaporan Dan Penanganan Kerusakan Fasilitas Kelas Studi Kasus: Universitas Kristen Duta Wacanait regarNo ratings yet
- AI Class 10 Sample Paper 1Document6 pagesAI Class 10 Sample Paper 1tribhuvanr138100% (1)
- E Drive ManagementDocument30 pagesE Drive ManagementAshitha AshNo ratings yet
- Lectures 1 - Drug InformationDocument16 pagesLectures 1 - Drug Informationmohamed hanyNo ratings yet
- Non-Disclosure Agreement Apportugal2Document14 pagesNon-Disclosure Agreement Apportugal2Melina AnsonNo ratings yet
- D78846GC20 sg2Document356 pagesD78846GC20 sg2FORMATION ORADISTNo ratings yet
- 00001Document2 pages00001C GreeshmaNo ratings yet
- Atlas Copco - Parts Online - User ManualDocument25 pagesAtlas Copco - Parts Online - User ManualRamon SanhuezaNo ratings yet
- Oscm 2014Document13 pagesOscm 2014goutam1235No ratings yet
- 882 Question PaperDocument1 page882 Question PaperSPARSH JAYRAJ PATHAKNo ratings yet