Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Drug Study Emphysema
Uploaded by
Paul MagbooOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Drug Study Emphysema
Uploaded by
Paul MagbooCopyright:
Available Formats
DRUG NAME Ipratropium BromideSalbutamol Sulfate (Combivent) Classification: >bronchodilator
DOSAGE AND ROUTE >inhalation
MECHANISM OF ACTION Combivent Inhalation Solution is a combination of the anticholinergic bronchodilator, ipratropium bromide, and the beta2adrenergic bronchodilator, salbutamol sulfate. Ipratropium bromide is a quaternary ammonium derivative of atropine and is an anticholinergic drug which has bronchodilator properties. Salbutamol produces bronchodilation through stimulation of beta2-adrenergic receptors in bronchial smooth muscle, thereby causing relaxation of muscle fibres. This action is manifested by an increase in pulmonary function as demonstrated by spirometric measurements.
INDICATION For the management of bronchospasm in patients suffering from chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) who requires regular treatment with both ipratropium and salbutamol.
CONTRAINDICATION Patients with cardiac tachyarrhythmias, hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy and patients with a history of hypersensitivity to any of its components or to atropine or its derivatives.
ADVERSE REACTIONS Fatigue, abdominal pain, hypertension, dyspepsia, tachycardia, sinusitis, dysuria, and urinary retention blurred vision, taste perversion, dry mouth, paradoxical bronchospasm, bronchitis, angina, arrhythmia, lightheadedness, drowsiness, insomnia, dizziness, vertigo, CNS stimulation, weakness, itching, rash, flushing, alopecia, hypotension, increased blood pressure, gastrointestinal distress, vomiting, diarrhea, edema, constipation and urinary difficulty
NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES Assessment and Drug Effects: 1.monitor respiratory status; auscultate lungs before and after inhalation 2. report treatment failure (exacerbation of respiratory symptoms) to physician Patient and Family Education: 1. do not allow the solution/ mist to enter the eyes 2. Consult a doctor immediately in the event of acute, rapidly worsening dyspnea. In addition, the patient should be warned to seek medical advice should a reduced response become apparent. 3. The concomitant use of Combivent with other sympathomimetic agents is not recommended since such combined use may lead to deleterious cardiovascular effects. 4. Eye pain or discomfort, blurred vision, visual halos or colored images in association with red eyes from conjunctival and corneal congestion may be signs of acute narrow-angle glaucoma. Should any combination of these symptoms develop, treatment with miotic drops should be initiated and specialist advice sought immediately. 5. Allow 30-60 sec between puffs for optimum results. 6. Wait 5 min between this and other inhaled medications. 7. rinse mouth after medication puffs to reduce bitter taste
DRUG NAME Ranitidine
DOSAGE Ranitidine 50mg TIV Adult: 150mg twice a day or 300mg at once a day
MECHANISM OF ACTION Inhibits the action of histamine at the H2 receptor site located primarily in gastric parietal cells, resulting in inhibition of gastric acid secretion. In addition, ranitidine bismuth citrate has some antibacterial action against H. pylori.
INDICATION Treatment and prevention of heartburn, acid indigestion, and sour stomach.
CONTRAINDICATION Hypersensitivity, Cross-sensitivity may occur; some oral liquids contain alcohol and should be avoided in patients with known intolerance. Use Cautiously in: Renal impairment Geriatric patients (more susceptible to adverse CNS reactions) Pregnancy or Lactation
ADVERSE REACTIONS CNS: Confusion, dizziness, drowsiness, hallucinations, headache CV: Arrhythmias GI: Altered taste, black tongue, constipation, dark stools, diarrhea, drug-induced hepatitis, nausea GU: Decreased sperm count, impotence ENDO: Gynecomastia HEMAT: Agranulocytosis, Aplastic Anemia, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia LOCAL: Pain at IM site MISC: Hypersensitivity reactions, vasculitis
NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES Assess patient for epigastric or abdominal pain and frank or occult blood in the stool, emesis, or gastric aspirate. Nurse should know that it may cause false-positive results for urine protein; test with sulfosalicylic acid. Inform patient that it may cause drowsiness or dizziness. Inform patient that increased fluid and fiber intake may minimize constipation. Advise patient to report onset of black, tarry stools; fever, sore throat; diarrhea; dizziness; rash; confusion; or hallucinations to health car professional promptly. Inform patient that medication may temporarily cause stools and tongue to appear gray black.
DRUG NAME Flutocasone
DOSAGE Fluticasone inhalation 1-2x daily
MECHANISM OF ACTION Glucocorticoid with a high topical antiinflammatory potency. It has a strong affinity for and agonist activity at human glucocorticoid receptors.
INDICATION It is used by inhalation for the prophylaxis of the symptoms of asthma; also by nasal spray for allergic rhinitis.
CONTRAINDICATION Known hypersensitivity to fluticasone propionate or any ingredient in the formulation.
ADVERSE REACTIONS Candidiasis or dryness of mouth and throat. Hoarseness. Suppression of adrenal function, growth retardation in children.
NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES ASSESSMENT Assess pts condition before therapy. Assess active infection and assess if immunocompromised Assess pulmonary and cardiac status. Monitor possible adverse reaction PLANNING Store at controlled room temperature away from direct sunlight IMPLEMENTATION Advise that the drug is for long term maintenance Instruct proper way of drug inhalation Instruct to rinse mouth after each inhalation to prevent oral candidiasis. Instructs to immediately report decreasing effect of inhaled beta agonist Instruct to report drug induced adverse reaction
DRUG NAME Ampicillin
DOSAGE 1-2 g a day in divided doses every 6 hours
MECHANISM OF ACTION Interferes with cell wall synthesis of susceptible organisms, preventing bacterial multiplication, it also renders cell wall osmotically unstable and burst due to osmotic pressure. Deactivated by betalactamase, an enzyme produced by resistant.
INDICATION Treatment of respiratory tract and soft tissue infection. Bacterial meningitis. Septicemia and gonoccocal infection caused by susceptible microorganisms; prophylaxis in rape victims and for bacterial endocarditis.
CONTRAINDICATION Hypersensitivity to penicillin, cephalosporin or imipenem.
ADVERSE REACTIONS Thromboplebitis at injection site, dizziness, fatigue, insomia, reversible hyperactivity
NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES ASSESSMENT Obtain patients history Assess signs and symptoms of infection Obtain baseline data of WBC Obtain C&S before drug therapy Assess sensitivity reactions Assess allergic reactions Monitor renal function Monitor blood studies Assess for overgrowth of infection PLANNING Give in even doses round the clock IM route reconstitute with 125mg/0.9 1.2mL; 500mg/1.2 1.8mL; 1g/2.4 7.4mL; 2g/6.8mL Give by direct IV over 3-5 mins in lower dosage IMPLEMENTATION Instruct to take medications as prescribed Advise to monitor adverse reaction Instruct pt if diarrhea with blood or pus occur notify physician
DRUG NAME Budesonide
DOSAGE Children: 12mg maintenance 0.5-1mg Adult: 0.51mg maintenance 0.25-5mg Tubuhaler: 400-1600mcg divided in 2-4 divided doses
MECHANISM OF ACTION Exerts a local anti inflammatory effect by depression of migaration of polymorphonuclear leukocytes and fibroblasts; reversal of increased capillary permeability and lysosomal stabilization. It does not suppress hypothalamus and pituitary function.
INDICATION Used for management of bronchial asthma and symptomatic management of seasonal or perennial allergic rhinitis.
CONTRAINDICATION Hypersensitivity to budesonide.
ADVERSE REACTIONS Nasal irritation/bleeding; burning; stinging; sneezing; pharingitis. GI: dry mouth, indigestion, rash, face and tongue edema, pruritus, bronchospasm.
NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES ASSESSMENT Obtain patients history Assess respiratory status Check for oral candidiasis Be alert for bronchospasm Carefully assess presence of viral infection Regularly assess intraocular pressure PLANNING Do not crush, break or chew the capsule Store at 15-39 degrees Celsius (59-86F) IMPLEMENTATION Instruct how to use nasal inhaler himself Teach pt to notify physician of pharyngitis, nasal bleeding Instruct pt not to exceed recommemded dosage; adrenal suppression may occur Instruct pt to prevent exposure to infections, especially viral.
Pamantasan ng Lungsod ng Pasay College of Nursing and School of Midwifery
EMPHYSEMA
Submitted by: Madeliene Kae R. Estanislao BSN IV-2 Submitted to: Mrs. Bautista
You might also like
- Top 300 Drugs Pocket Reference Guide (2021 Edition)From EverandTop 300 Drugs Pocket Reference Guide (2021 Edition)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyGail SantosNo ratings yet
- Ampicillin Sulbactam 1.5 gm, Clindamycin Hydrochloride, Clopidogrel Bisulfate 75 mg tab, Furosemide 40mg IV, Ipratropium Bromide, Paracetamol 500mg, Tramadol Hydrochloride 500mg IV drug infoDocument10 pagesAmpicillin Sulbactam 1.5 gm, Clindamycin Hydrochloride, Clopidogrel Bisulfate 75 mg tab, Furosemide 40mg IV, Ipratropium Bromide, Paracetamol 500mg, Tramadol Hydrochloride 500mg IV drug infoVictor BiñasNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Medications ReviewDocument4 pagesRespiratory Medications ReviewKevin VillaranteNo ratings yet
- Ventolin Nebulizer for Bronchospasm ReliefDocument10 pagesVentolin Nebulizer for Bronchospasm ReliefmidskiescreamzNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Clindamycin, Ipatropium BromideDocument8 pagesDrug Study Clindamycin, Ipatropium Bromidepaupaulala100% (2)
- Complete Drugs StudyDocument13 pagesComplete Drugs StudyPeace Andong PerochoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyAysaaa DCNo ratings yet
- Neuropathic Pain Diabetic Peripheral NeuropathyDocument7 pagesNeuropathic Pain Diabetic Peripheral NeuropathyJomabee TuArNo ratings yet
- Indications For Ferrous Sulfate: Mechanism of ActionDocument4 pagesIndications For Ferrous Sulfate: Mechanism of ActionErelle John Vasquez EscaraNo ratings yet
- Ward6 Drug StudyDocument6 pagesWard6 Drug StudyMichael Lloyd T. SabijonNo ratings yet
- Drug 25Document17 pagesDrug 25carol_gigliotti24100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument14 pagesDrug StudyVal FielNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Grand Case Val GenDocument6 pagesDrug Study Grand Case Val GenRoselene Mae MarasiganNo ratings yet
- Name of DrugDocument10 pagesName of DrugBianx PradoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyRoselle SorianoNo ratings yet
- Compliled DrugstudyDocument15 pagesCompliled DrugstudyApril Jan D. Alagon0% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDrug StudyKaloy KamaoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyNajmah Saaban100% (1)
- Drug Study (Pedia)Document7 pagesDrug Study (Pedia)Caurrine Monsalud100% (1)
- Generic Name: Albuterol Brand Name: Salbutamol, Proventil, Ventolin, Accuneb, Airet, Novo-SalbutamolDocument26 pagesGeneric Name: Albuterol Brand Name: Salbutamol, Proventil, Ventolin, Accuneb, Airet, Novo-SalbutamolAnna Joy Antone100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudysarahtotNo ratings yet
- 5th Draft DrugsDocument7 pages5th Draft DrugsShayne Jessemae AlmarioNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Cap RHPDocument7 pagesDrug Study Cap RHPJan DeeNo ratings yet
- Drug StudiesDocument16 pagesDrug Studiesvitcloud23100% (2)
- Drug Action Indication Adverse Effects Contraindications Nursing Considerations Ketorolac TromethamineDocument8 pagesDrug Action Indication Adverse Effects Contraindications Nursing Considerations Ketorolac TromethamineAiryn CanonNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug StudyFritzie Beatrice NomusNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyRachel PerandoNo ratings yet
- Chlorpheniramine Maleate: (klor-fen-AIR-uh-meen MAL-ee-ate)Document4 pagesChlorpheniramine Maleate: (klor-fen-AIR-uh-meen MAL-ee-ate)Nurginayah RusliNo ratings yet
- Drug Study OR AreaDocument7 pagesDrug Study OR AreaVal FielNo ratings yet
- Drug Studies PsychDocument12 pagesDrug Studies PsychAnna Mendiola-BasbasNo ratings yet
- DrugsDocument11 pagesDrugsElisa Libo-onNo ratings yet
- DuaventDocument9 pagesDuaventAjurs UrsabiaNo ratings yet
- Celecoxib uses, dosage, side effectsDocument4 pagesCelecoxib uses, dosage, side effectsAbigail LonoganNo ratings yet
- Subjective: "Nahihirapan Ako Huminga" As Verbalized by The Patient. ObjectiveDocument4 pagesSubjective: "Nahihirapan Ako Huminga" As Verbalized by The Patient. Objectivechaoz09No ratings yet
- Nursing Considerations Assessment: History: Infections Kidney Disease Liver Disease, Hypothyroidism UlcerativeDocument5 pagesNursing Considerations Assessment: History: Infections Kidney Disease Liver Disease, Hypothyroidism UlcerativeSophia limNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug Studysarah1217No ratings yet
- Cardiac Arrhythmias Drug AmiodaroneDocument7 pagesCardiac Arrhythmias Drug AmiodaroneMarie Angeline ManzanoNo ratings yet
- MEDICATION: Garamycin, Garamycin Ophthalmic, Genoptic Classifications: Antiinfective Aminoglycoside Antibiotic ActionDocument4 pagesMEDICATION: Garamycin, Garamycin Ophthalmic, Genoptic Classifications: Antiinfective Aminoglycoside Antibiotic ActionLea Mae HandayanNo ratings yet
- Ciprofloxacin, Bactroban, Algesia, Losartan, Paracetamol, Ketorolac, Tetanus Toxoid, HTIG Drug StudyDocument34 pagesCiprofloxacin, Bactroban, Algesia, Losartan, Paracetamol, Ketorolac, Tetanus Toxoid, HTIG Drug StudygecalianNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (GBS)Document16 pagesDrug Study (GBS)Mary Rose Verzosa LuisNo ratings yet
- COPD Drug Study: Ipratropium Bromide and Albuterol SulfateDocument9 pagesCOPD Drug Study: Ipratropium Bromide and Albuterol SulfateShane Arroyo100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyFloramae Celine BosqueNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Paracetamol Ambroxol Ascorbic Acid CefuroximeDocument6 pagesDrug Study Paracetamol Ambroxol Ascorbic Acid CefuroximeJaymark LambinoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study DengueDocument3 pagesDrug Study DengueiamELHIZANo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyJaylean Abrigo AguinaldoNo ratings yet
- final pharmaDocument22 pagesfinal pharmaVelado Alessandra Loraine B.No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug Studypaulkris_14100% (1)
- phharmaDocument21 pagesphharmaVelado Alessandra Loraine B.No ratings yet
- Central Nervous System Drug StudyDocument11 pagesCentral Nervous System Drug StudySanny L Asim Jr.No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug Studyanon_11638632No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument33 pagesDrug StudyLag Lag AlbercaNo ratings yet
- Albuterol sulfate for asthma reliefDocument19 pagesAlbuterol sulfate for asthma reliefCamille PinedaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument19 pagesDrug StudyNorma CordovaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudiesDocument32 pagesDrug StudiesKelly ChanNo ratings yet
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesFrom EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- 4 Classifications: Dx. ExamDocument1 page4 Classifications: Dx. ExamPaul MagbooNo ratings yet
- 4 Classifications: Dx. ExamDocument1 page4 Classifications: Dx. ExamPaul MagbooNo ratings yet
- 4 Classifications: Dx. ExamDocument1 page4 Classifications: Dx. ExamPaul MagbooNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument34 pagesDrug Studyirismirzig100% (2)
- 4 Classifications: Dx. ExamDocument1 page4 Classifications: Dx. ExamPaul MagbooNo ratings yet
- Tetralogy of FallotDocument9 pagesTetralogy of FallotPaul MagbooNo ratings yet
- Think, Talk, Write Directions and QuotesDocument44 pagesThink, Talk, Write Directions and QuotesPaul MagbooNo ratings yet
- ViewSupportDoc MusicDocument18 pagesViewSupportDoc MusicPaul MagbooNo ratings yet
- My Case Study of Liver CirrhosisDocument14 pagesMy Case Study of Liver CirrhosisPaul MagbooNo ratings yet
- (Abacavir Sulfate) Tablets and Oral Solution: Adult PatientsDocument2 pages(Abacavir Sulfate) Tablets and Oral Solution: Adult PatientsChoco MuchoNo ratings yet
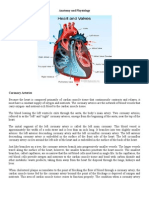
- Anatomy and Physiology of The HeartDocument3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The HeartSteffi MerzNo ratings yet