Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cal Skills 1
Cal Skills 1
Uploaded by
aoasOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cal Skills 1
Cal Skills 1
Uploaded by
aoasCopyright:
Available Formats
Mathmatical skills 1
By: Ma'en Jarrar
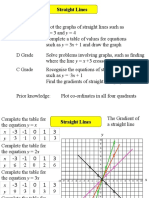
A Linear relation between two variables x & y, is when equal changes in x causes equal changes in y The general form of the equation is: y = mx+c (m & c are constants) y Example: Y=2x+3 x y
Equal changes by 1 on the x
0 3
1 5
2 7
3 9
9 7 5 3 1 1 2 3 x
Equal changes by 2on the y
A directly proportional relation between two variables x & y, is when x is increased, y is increased by same ratio and vice versa Example: Y= 2x x y 0 0 1 2
When 1 is doubled
Y 6 4 2 1
The 2 is doubled
2 4
3 6
The graph of a directly proportional relation should always be: 1straight line 2start from the origin. An inversely proportional relation, is when x increases, y decreases by the same inverse ratio Example: Y=1/x
When 1 is doubled
x y
1 1
2 1/2
The 1 is halfed
Y 3 4 1 1/3 1/4 3/4 The relation is a curve going 1/2 downwards 1/4 1 2 3 4 x
If x is inversely proportional to y, then x is directly proportional to 1/y Y=2/x x y 1/y 1 2 1/2 2 1 1 3 2/3 3/2 4 1/2 2
Y/1 2 3/2 1 1/2 x 2 3 4 x is directly proportional to 1/y 1
Y 2 3/2 1 x is inversely proportional to y 1/2 1 2 3 4 x
You might also like
- If God Had Maths Notes, They Would Be These NotesDocument9 pagesIf God Had Maths Notes, They Would Be These NotescallumkhangNo ratings yet
- Direct VariationDocument29 pagesDirect VariationRon TesoreroNo ratings yet
- DLP Direct VariationDocument8 pagesDLP Direct Variationsusan narvasNo ratings yet
- Writing and Graphing Linear Equations 1Document62 pagesWriting and Graphing Linear Equations 1Ma. Rica Mae Rosete100% (1)
- 9-1 Direct VariationDocument49 pages9-1 Direct VariationSarah Eve HaqueNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsFrom EverandMathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsNo ratings yet
- Direct Variation: Whatisitandhowdoiknowwheniseeit?Document23 pagesDirect Variation: Whatisitandhowdoiknowwheniseeit?saturnino corpuzNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 8 Linear Equations in One Variable NotesDocument4 pagesCBSE Class 8 Linear Equations in One Variable NotesShivam YadavNo ratings yet
- Direct VariationDocument25 pagesDirect VariationRey HisonaNo ratings yet
- Direct Variation 11Document30 pagesDirect Variation 11api-302577842No ratings yet
- 12 1 NotesDocument15 pages12 1 Notesapi-199670769No ratings yet
- Direct Variation: Section 5-2Document30 pagesDirect Variation: Section 5-2saturnino corpuzNo ratings yet
- Direct VariationDocument5 pagesDirect VariationNorma GamboaNo ratings yet
- Linear EquationDocument8 pagesLinear EquationkleyrgNo ratings yet
- Maths Study - GRAPHS Year 10Document2 pagesMaths Study - GRAPHS Year 10JosephNo ratings yet
- Week 3 Joint and Combined VariationDocument24 pagesWeek 3 Joint and Combined VariationJerickson NolledoNo ratings yet
- Math ReviewerDocument2 pagesMath Reviewerc44cnh8yjgNo ratings yet
- Direct Variation: This Photo CC byDocument14 pagesDirect Variation: This Photo CC byZil BordagoNo ratings yet
- Straight Lines 2 - GradientDocument13 pagesStraight Lines 2 - GradientSelva RajNo ratings yet
- Tg2 - Topic 2 - VariationsDocument4 pagesTg2 - Topic 2 - VariationsJuhari DirumponganNo ratings yet
- Variation MathDocument3 pagesVariation MathNichole Anne Competente0% (1)
- Business MathesDocument152 pagesBusiness MathesBelay MezgeboNo ratings yet
- The Equation of The Straight Line: y MX CDocument6 pagesThe Equation of The Straight Line: y MX CMarc SugrueNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document24 pagesChapter 4KelleyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1. Linear Functions & EquationsDocument11 pagesChapter 1. Linear Functions & EquationsJiregna Gadisa KumsaNo ratings yet
- 8 6 VariationDocument25 pages8 6 Variationapi-233527181No ratings yet
- Application of TangentDocument9 pagesApplication of Tangentyokekeann100% (2)
- Correlation: DefinitionsDocument24 pagesCorrelation: DefinitionsBhawna JoshiNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Linear Equations and Word ProblemsDocument36 pagesFundamentals of Linear Equations and Word Problemsmichelle.okoye2009No ratings yet
- Examples of Linear EquationsDocument7 pagesExamples of Linear Equationsapi-126876773No ratings yet
- 08b Graphical Relationships in Physics HandoutDocument2 pages08b Graphical Relationships in Physics HandoutmrschnellteacherNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Other Forms of Direct ProportionsDocument23 pages1.3 Other Forms of Direct Proportionshang yinNo ratings yet
- Direct, Joint, and Inverse Variation: Section 9-4Document17 pagesDirect, Joint, and Inverse Variation: Section 9-4Edwin P. CuizonNo ratings yet
- M1 - Intro To DE 8 9 PDFDocument8 pagesM1 - Intro To DE 8 9 PDFsubyNo ratings yet
- What Is A Linear Function?Document23 pagesWhat Is A Linear Function?Fernando Lipardo Jr.No ratings yet
- Writing and Graphing Linear Equations 1Document62 pagesWriting and Graphing Linear Equations 1Sabreena RataniNo ratings yet
- 1 Chapter 1 Linear Equeation EditedDocument9 pages1 Chapter 1 Linear Equeation EditeduuuNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Community College of Gingoog CityDocument8 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Community College of Gingoog CityJohn LiamNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument4 pagesUntitled DocumentJun UkaNo ratings yet
- G9 Math Q2 Week 1 Types of VariationDocument16 pagesG9 Math Q2 Week 1 Types of Variationrin63563No ratings yet
- Direct VariationsDocument2 pagesDirect VariationsLeeanna ElhizNo ratings yet
- Direct VariationDocument57 pagesDirect VariationGheneva Mhey JuanNo ratings yet
- q2 Direct Variation GclassDocument31 pagesq2 Direct Variation GclassDhienneNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes 1Document23 pagesLecture Notes 1Lucas ZogbiNo ratings yet
- Untitled PresentationDocument10 pagesUntitled PresentationAyesha MurtazaNo ratings yet
- Chapter One MathsDocument11 pagesChapter One Mathsየገጠር ልጅNo ratings yet
- Equations in General: Degree Present in The EquationDocument3 pagesEquations in General: Degree Present in The EquationizumiNo ratings yet
- Ratio, Proportion and VariationDocument19 pagesRatio, Proportion and VariationChristian DacilloNo ratings yet
- Chapter PDFDocument55 pagesChapter PDFWonde BiruNo ratings yet
- Maths For ManagementDocument53 pagesMaths For ManagementMwalimu Hachalu FayeNo ratings yet
- A Gallery of Graphs: ObjectivesDocument15 pagesA Gallery of Graphs: ObjectivesNeoneoDuNo ratings yet
- Quiz Maker SingleDocument3 pagesQuiz Maker Singleberniecortez200913No ratings yet
- G9 MODULE 3 Lesson 1 (Part 2)Document42 pagesG9 MODULE 3 Lesson 1 (Part 2)Yoradel RempilloNo ratings yet
- Please Excuse My Dear Aunt Sally: EquationsDocument6 pagesPlease Excuse My Dear Aunt Sally: Equationsniranjankumar79No ratings yet
- Cubical DilationDocument5 pagesCubical DilationChintu Kishen KMNo ratings yet
- Find The Relationship: An Exercise in Graphing Analysis: ComputerDocument9 pagesFind The Relationship: An Exercise in Graphing Analysis: ComputerGeonhun LeeNo ratings yet
- Chapter-9-Simple Linear Regression & CorrelationDocument9 pagesChapter-9-Simple Linear Regression & CorrelationSimeon solomonNo ratings yet
- Linear FunctionsDocument31 pagesLinear FunctionsSJNHS SANTANNo ratings yet
- First Order Differential EquationsDocument17 pagesFirst Order Differential Equations20S1002 Joel DsouzaNo ratings yet
- Statics Chapter 999Document9 pagesStatics Chapter 999tarekegnworku5No ratings yet