Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Therapeutic Communication Outline
Uploaded by
Janry-Mae Escobar TumanengOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Therapeutic Communication Outline
Uploaded by
Janry-Mae Escobar TumanengCopyright:
Available Formats
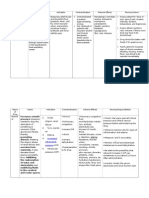
Therapeutic Communication Nursing 4206 Therapeutic Communication Any communication designed to increase the self-worth of the patient or decrease
e psychological distress Implies unconditional positive regard for the patient from the nurse and is done in a caring, concerned, empathic manner Therapeutic Nurse-Patient Relationship Therapeutic nurse-patient relationships can only occur when each views the other as a unique human being Therapeutic relationships are goal oriented, client-centered and are directed at learning and promoting growth Goals are often achieved through use of the problem-solving model Self-Awareness Process of understanding ones own beliefs, thoughts, motivations, biases, and limitations and recognizing how they affect others Crucial in developing a therapeutic nurse-patient relationship Conditions Essential for a Therapeutic Relationship Rapport Trust Respect Genuineness Empathy Phases of the Therapeutic Nurse-Patient Relationship Preinteraction Phase Explore self Learn about patient Orientation Phase Honeymoon phase Testing Phase Phases continued Working Phase Patient explores identified problems and strategies to work on them Promote client insight and perception of reality Overcome resistant behaviors Continuously evaluate progress toward goal attainment Phases continued Resolution Phase Stressful for the patient Learning is maximized Patient reactions to termination Denial Anger/hostility Feelings of rejection
Regression Variables that Influence Communication Perception Values, Attitudes, Beliefs Culture Social Status Gender Age/Developmental Level
Environment Verbal and nonverbal Communication
Verbal Communication Terminology/Word Selection Voice Tone Use of Silence Nonverbal Communication Dress and Appearance Body Movements and Psoture Touch Eye Contact Techniques to Promote Therapeutic Communication Acceptance Confrontation Doubt Interpretation Observation Open-Ended Statements Reflection Restatement Silence Validation Active Listening Self-Disclosure Barriers to Therapeutic Communication Advice Agreement Challenges Reassurance Disapproval Other Important Concepts Boundaries, Personal and Professional
Analyzing Interactions
You might also like
- Learning Feedback Diary: Rosemarie Tadena, RN, MSNDocument3 pagesLearning Feedback Diary: Rosemarie Tadena, RN, MSNJanry-Mae Escobar TumanengNo ratings yet
- OB WardDocument2 pagesOB WardJanry-Mae Escobar TumanengNo ratings yet
- MethodologyDocument3 pagesMethodologyJanry-Mae Escobar TumanengNo ratings yet
- University of Saint Louis: School of Health SciencesDocument2 pagesUniversity of Saint Louis: School of Health SciencesJanry-Mae Escobar TumanengNo ratings yet
- Vision:: "Developed Agro-Industrial Center and Improve Quality of Life of The People."Document5 pagesVision:: "Developed Agro-Industrial Center and Improve Quality of Life of The People."Janry-Mae Escobar TumanengNo ratings yet
- QwwweweDocument1 pageQwwweweJanry-Mae Escobar TumanengNo ratings yet
- Vaccines PedDocument1 pageVaccines PedJanry-Mae Escobar TumanengNo ratings yet
- LFD CommunityDocument2 pagesLFD CommunityJanry-Mae Escobar TumanengNo ratings yet
- Brooksville Mom Arrested, Accused of Killing Infant DaughterDocument1 pageBrooksville Mom Arrested, Accused of Killing Infant DaughterJanry-Mae Escobar TumanengNo ratings yet
- PAtho CholecystitisDocument2 pagesPAtho CholecystitisJanry-Mae Escobar TumanengNo ratings yet
- Discharge PlanDocument2 pagesDischarge PlanJanry-Mae Escobar TumanengNo ratings yet
- Consent FormDocument2 pagesConsent FormJanry-Mae Escobar TumanengNo ratings yet
- Cover LetterDocument1 pageCover LetterJanry-Mae Escobar TumanengNo ratings yet
- TBI DrugsDocument16 pagesTBI DrugsJanry-Mae Escobar TumanengNo ratings yet
- Care at The End of LifeDocument15 pagesCare at The End of LifeJanry-Mae Escobar TumanengNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument5 pagesDrug Name Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesJanry-Mae Escobar TumanengNo ratings yet
- Course TBIDocument1 pageCourse TBIJanry-Mae Escobar TumanengNo ratings yet
- Chole CystitisDocument5 pagesChole CystitisJanry-Mae Escobar TumanengNo ratings yet
- TBI DrugsDocument16 pagesTBI DrugsJanry-Mae Escobar TumanengNo ratings yet
- Cervical Cancer: Virus Transcript StomaDocument2 pagesCervical Cancer: Virus Transcript StomaJanry-Mae Escobar TumanengNo ratings yet
- Literature and Variable Matrix 2013Document3 pagesLiterature and Variable Matrix 2013Janry-Mae Escobar TumanengNo ratings yet
- HepaDocument4 pagesHepaJanry-Mae Escobar TumanengNo ratings yet
- Dam ItDocument1 pageDam ItJanry-Mae Escobar TumanengNo ratings yet
- Assessment ToolDocument6 pagesAssessment ToolJanry-Mae Escobar TumanengNo ratings yet
- Basic Physical Assessment 1Document62 pagesBasic Physical Assessment 1Janry-Mae Escobar TumanengNo ratings yet
- Every Liquid You See Will Probably Have Either Acidic or Basic TraitsDocument2 pagesEvery Liquid You See Will Probably Have Either Acidic or Basic TraitsJanry-Mae Escobar TumanengNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)