Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Arenes
Arenes
Uploaded by
cjcmoneyOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Arenes
Arenes
Uploaded by
cjcmoneyCopyright:
Available Formats
Arenes
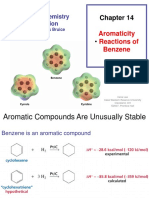
Weekly learning outcomes Students should be able to: y y y y y y y y Explain the terms: arene and aromatic. Describe and explain the models used to depict the structure of benzene. Review the evidence for a delocalised model of benzene. Describe the delocalised model of benzene. Describe the electrophilic substitution of arenes with concentrated nitric acid. Describe the electrophilic substitution of arenes with a halogen in the presence of a halogen carrier. Outline the mechanism of electrophilic substitution in arenes. Outline the mechanism for the mononitration and monohalogenation of benzene. Addition reaction Substitution reaction Halogen carrier Reaction mechanism Electrophilic substitution Mononitration Monohalogenation Benzene Orbital overlap Catalyst
Key words Arene Aromatic -electron -bond Curly arrow
Delocalisation Electrophile
Weekly learning outcomes Students should be able to: y y y y y y Explain the relative resistance to bromination of benzene compared with alkenes. Describe the reactions of phenol with aqueous alkalis and with sodium to form salts. Discuss the role of phenol as an early antiseptic. Describe the reactions of phenol with bromine to form 2,4,6-tribromophenol. Explain the relative ease of bromination of phenol compared with benzene. State the uses of phenols.
Key words Cyclohexene Addition Electrophile Substitution Acidbase Phenol Phenoxide Delocalisation Activation
You might also like
- BenzeneDocument14 pagesBenzeneJueeli More100% (1)
- Experiment 1 OrgChem Lab 2Document5 pagesExperiment 1 OrgChem Lab 2John Harvey Santos100% (2)
- Bi FunctionalDocument40 pagesBi FunctionalMirza TatsuyaNo ratings yet
- ARENES AND PHENOLS (Autosaved)Document85 pagesARENES AND PHENOLS (Autosaved)dodoNo ratings yet
- Summary of HaloalkaneDocument10 pagesSummary of HaloalkaneTai PanNo ratings yet
- AlcoholDocument8 pagesAlcoholSri DharshanNo ratings yet
- Prelab-Amines 2Document3 pagesPrelab-Amines 2piapetkovNo ratings yet
- Organic HydrocarbonsDocument20 pagesOrganic HydrocarbonsOmar Samir0% (1)
- Alkenes and AlkynesDocument4 pagesAlkenes and Alkynesespiritumikhailehayah28No ratings yet
- C Chem-201Document3 pagesC Chem-201Abdullah Mukhtar MirzaNo ratings yet
- OutlineDocument1 pageOutlineOmar Enrique DiazNo ratings yet
- 11 Alcohols, Phenol and Ether 28Document28 pages11 Alcohols, Phenol and Ether 28Aryan POONIANo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry II: UC-Berkeley Extension x36B Spring 2012Document56 pagesOrganic Chemistry II: UC-Berkeley Extension x36B Spring 2012klm112088No ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry Imp Haloalkanes Haloarenes MixDocument21 pages12 Chemistry Imp Haloalkanes Haloarenes MixRajesh ChinniahNo ratings yet
- Aromatic HydrocarbonsDocument37 pagesAromatic HydrocarbonsMae Rose PicaranaNo ratings yet
- PRGR Him2022Document8 pagesPRGR Him2022BoyanaNo ratings yet
- Physical Properties and Chemical Reactions ofDocument9 pagesPhysical Properties and Chemical Reactions ofTUANA DURMAYÜKSELNo ratings yet
- Carbonyl: For Carbonyl As A Ligand, SeeDocument5 pagesCarbonyl: For Carbonyl As A Ligand, SeemeritnasaNo ratings yet
- Review & Preview BDocument38 pagesReview & Preview BhobbitbookwormNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7-2-110-2Document78 pagesChapter 7-2-110-2徐敏珊No ratings yet
- Experiment 2 Alcohols and PhenolsDocument3 pagesExperiment 2 Alcohols and PhenolsJustine MarieNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document38 pagesChapter 4iB13eNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2.5 Aromatic CompoundDocument38 pagesChapter 2.5 Aromatic Compound0JTINGNo ratings yet
- 18 Aromatic SubstitutionsDocument67 pages18 Aromatic SubstitutionsJun LyNo ratings yet
- Chem31.1 ATQ9 Santos PDFDocument2 pagesChem31.1 ATQ9 Santos PDFClaire SantosNo ratings yet
- AS Chemistry OCR Module 4, Chapter 13 HLDocument9 pagesAS Chemistry OCR Module 4, Chapter 13 HLVikki McIntoshNo ratings yet
- 5.4 - Organic Independat OtesDocument5 pages5.4 - Organic Independat Otesvarda9877No ratings yet
- 20.1 Electrophilic Substitution and Reduction Reactions PDFDocument21 pages20.1 Electrophilic Substitution and Reduction Reactions PDFJoshua VincentNo ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument79 pagesOrganic ChemistrySiti Nurul AfifahNo ratings yet
- Aldehyde Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsDocument21 pagesAldehyde Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsAnupam 4622No ratings yet
- Protic & Aprotic SolventsDocument2 pagesProtic & Aprotic Solventslaibaasimsoomro21No ratings yet
- 2 NitribenzeneDocument6 pages2 NitribenzeneHasrilia BeskaraNo ratings yet
- Study of Acidic Nature of Alcohol and PhenolDocument11 pagesStudy of Acidic Nature of Alcohol and PhenolrejeenfullelNo ratings yet
- Aroma Tizac I OnDocument62 pagesAroma Tizac I OnJotaro KujoNo ratings yet
- 6.1 Aromatic Compounds Carbonyls and AcidsDocument1 page6.1 Aromatic Compounds Carbonyls and AcidsmasterlukamfNo ratings yet
- Curs 3 EnglezaDocument25 pagesCurs 3 EnglezaFlaviu TomuțaNo ratings yet
- Heloalkanes and HeloarenesDocument8 pagesHeloalkanes and HeloarenesPuneet K UppalNo ratings yet
- 5294 H+i Assignment No 2 M WaseemDocument6 pages5294 H+i Assignment No 2 M WaseemM WaseemNo ratings yet
- A Nucleophilic Aromatic Displacement Reactions of Aryl HalidesDocument5 pagesA Nucleophilic Aromatic Displacement Reactions of Aryl HalidesSAGNIK PALNo ratings yet
- Hydrolysis of Esters: Reaction Type: Nucleophilic Acyl SubstitutionDocument4 pagesHydrolysis of Esters: Reaction Type: Nucleophilic Acyl SubstitutionManoj RungtaNo ratings yet
- Benzene & Aromatic CompoundsDocument61 pagesBenzene & Aromatic CompoundsAisyahAzaliNo ratings yet
- Reasoning QuestionsDocument2 pagesReasoning QuestionsHarishmaNo ratings yet
- Aromatic HydrocarbonDocument31 pagesAromatic HydrocarbonCamille Solana100% (1)
- Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers 2Document167 pagesAlcohols, Phenols and Ethers 2Omkar Singh ShekhawatNo ratings yet
- Acyl Chlorides and PhenolDocument8 pagesAcyl Chlorides and PhenolPurpleMyself25No ratings yet
- Lecture 7-8 Term 3, AY 22-23Document31 pagesLecture 7-8 Term 3, AY 22-23LujainNo ratings yet
- BenzeneDocument18 pagesBenzeneYossef AmrNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4-Aromatic CompoundsDocument69 pagesChapter 4-Aromatic CompoundsNURUL BALQIS DZULKIFLINo ratings yet
- Acids and Bases in Organic Chemistry: 1. An Arrhenius Acid Is A Source of HDocument13 pagesAcids and Bases in Organic Chemistry: 1. An Arrhenius Acid Is A Source of HAndile VeziNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of Organic ChemistryDocument112 pagesBasic Concepts of Organic ChemistryNavya KuchanaNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of Organic ChemistryDocument112 pagesBasic Concepts of Organic ChemistryPakardan TeaNo ratings yet
- CHEM111 Alcohol, Phenol, EtherDocument26 pagesCHEM111 Alcohol, Phenol, EtherAgatha joy MadrazoNo ratings yet
- Assignment - Aromatic HydrocarbonDocument2 pagesAssignment - Aromatic Hydrocarbonnirupama7meherNo ratings yet
- Alcohol, Phenol and EtherDocument9 pagesAlcohol, Phenol and Etherayush22singh34No ratings yet
- Exam Questions 2012/2013Document2 pagesExam Questions 2012/2013Georgios PlethoNo ratings yet
- Benzene and Aromaticity: John E. McmurryDocument40 pagesBenzene and Aromaticity: John E. McmurryafafNo ratings yet
- Unsaturated HydrocarbonsDocument31 pagesUnsaturated HydrocarbonsFelicia GunawanNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and Salts with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and Salts with AnswersNo ratings yet
- Polymerization of Heterocycles (Ring Opening): International Union of Pure and Applied ChemistryFrom EverandPolymerization of Heterocycles (Ring Opening): International Union of Pure and Applied ChemistryS. PenczekNo ratings yet