Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Galleros
Galleros
Uploaded by
Jaicy Mae Roa RacinesOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Galleros
Galleros
Uploaded by
Jaicy Mae Roa RacinesCopyright:
Available Formats
Attention: Engr.
Rogelio Golez, MSME (Faculty Member)
Sheets 1 of 2 sheets
XAVIER UNIVERSITY College of Engineering Cagayan de Oro City
MECHANICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT ME37: A RESEARCH PAPER ON WET SCRUBBER
Submitted by: Lloyd Levi L. Galleros
Date submitted: February 14, 2012
I.
Abstract:
Air dust inhalation by mill factories can interfere lung function. The longer the workers exposed to dust the lower the lung function. One way to remove dust is by using wet scrubber. This study aims to examine the ability of wet scrubbers in reducing dust covering the media bed varation, the pressure difference, and the number of columns. This study begins with a preliminary analysis including the added weight of the substance that is being worked in the factory per running to find out the weight of dust that came off and the length of time required for each running. There are three research variables used i.e. media bed, the pressure variations, and variations in the number of columns. Variations include bed media with the porosity of 2 mm, 3 mm, and 4 mm. The variations of pressure used were 20, 30, and 40 psi. While variations in the number of columns is 1 column, 2 columns and 3 columns. Repetitions were performeds in 5 times for each variation. The parameters examined were weight of dust before and after running wet scrubber. The results showed that 2 mm porous beds had the average efficiency of removing the dust at 87.52 %, 3 mm porous bed at 76.76 %, and 4 mm porous nbed at 74.06 %. One column had the average removal efficiency of dust at 76.21 %, two colums at 78.49 %, and three colums at 83.64 %. Pressure at 20 psi had an average removal efficiency of dust at 78.73 %, 30 psi at 81.94 %, and 40 psi at 77.66 %.
You might also like
- 9-09 - Guide+16 Guide To Specifying and Selecting Dust CollectorsDocument14 pages9-09 - Guide+16 Guide To Specifying and Selecting Dust CollectorsSherif AbdelhameedNo ratings yet
- Solid / Gas Separation With Fabric FiltersDocument2 pagesSolid / Gas Separation With Fabric FiltersAhmadLuqmanNo ratings yet
- A Pilot-Scale Study of The Design and Operation Parameters of A Pulse-Jet BaghouseDocument16 pagesA Pilot-Scale Study of The Design and Operation Parameters of A Pulse-Jet Baghousereza100% (1)
- Bioresources.: Kraft, BCTMP, and TMP Dewatering Behaviour Along The Axis of A Screw PressDocument16 pagesBioresources.: Kraft, BCTMP, and TMP Dewatering Behaviour Along The Axis of A Screw Pressjanaaidaas1996No ratings yet
- Flotation of Cleaner Rejects Removes High Density StickiesDocument16 pagesFlotation of Cleaner Rejects Removes High Density Stickiespaperravi2000No ratings yet
- Experimental Study of Pleated Fabric Cartridges in A Pulse-JDocument9 pagesExperimental Study of Pleated Fabric Cartridges in A Pulse-JumanathrpNo ratings yet
- Demister EfficiencyDocument9 pagesDemister EfficiencyHastelloy Monel100% (1)
- SM - CH 7Document50 pagesSM - CH 7Angie Dorado RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Car Filters 1Document34 pagesCar Filters 1Pulak DebnathNo ratings yet
- Performance of A Venturi Scrubber in The Removal oDocument4 pagesPerformance of A Venturi Scrubber in The Removal oImen KerrouNo ratings yet
- In Uence of Push Element Geometry On The Capture Efficiency of Push-Pull Ventilation Systems in Surface Treatment TanksDocument12 pagesIn Uence of Push Element Geometry On The Capture Efficiency of Push-Pull Ventilation Systems in Surface Treatment TanksbilouNo ratings yet
- GTJ YaoDocument21 pagesGTJ Yaoingchiara85No ratings yet
- 1526970702H08TM35 QiDocument11 pages1526970702H08TM35 QiJhilik DeyNo ratings yet
- Artikel Alifia-SriDocument5 pagesArtikel Alifia-SriYochanan meisandroNo ratings yet
- Effect of Processing Parameters On Properties of LDocument7 pagesEffect of Processing Parameters On Properties of LNAJJEMBA WINNIFREDNo ratings yet
- Inspection of Waste Extracted by Different Machines of Spinning Department.Document3 pagesInspection of Waste Extracted by Different Machines of Spinning Department.Ammar Naeem BhattiNo ratings yet
- 1224fabric Dust CollectorsDocument2 pages1224fabric Dust Collectorsrmm99rmm99No ratings yet
- Sand FiltrationDocument28 pagesSand FiltrationAnonymous bHh1L1No ratings yet
- 1 PBDocument7 pages1 PBanandhra2010No ratings yet
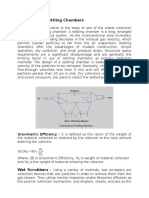
- Gravitational Settling ChambersDocument6 pagesGravitational Settling ChambersVinod KumarNo ratings yet
- SOx MeasurementDocument20 pagesSOx MeasurementShakila PathiranaNo ratings yet
- Effect of Pile Density On Physical Properties of Terry Towel FabricDocument4 pagesEffect of Pile Density On Physical Properties of Terry Towel FabricshobsundarNo ratings yet
- Experimental Study of Clogging in Drainage Systems: January 2010Document5 pagesExperimental Study of Clogging in Drainage Systems: January 2010Mykael ArevaloNo ratings yet
- Particulates Not Otherwise Regulated, Respirable 0600Document6 pagesParticulates Not Otherwise Regulated, Respirable 0600paulazanforlinNo ratings yet
- Flakiness Index, Elongation, Aggregate Crushing ValueDocument6 pagesFlakiness Index, Elongation, Aggregate Crushing ValueAshadi HamdanNo ratings yet
- CycloneDocument15 pagesCycloneTheyvan T-van0% (2)
- Experimental Study of The Squeezing of A Leather Semi-Finished Product by Roller Pairs of Different DiametersDocument11 pagesExperimental Study of The Squeezing of A Leather Semi-Finished Product by Roller Pairs of Different DiametersOpen Access JournalNo ratings yet
- A Study On Development of Cracks On PaintingsDocument13 pagesA Study On Development of Cracks On PaintingsNatasa IlicNo ratings yet
- 9.0 Dust Collection SystemsDocument15 pages9.0 Dust Collection SystemsNol BarandonNo ratings yet
- Ijerph 16 00247 PDFDocument19 pagesIjerph 16 00247 PDFsinghashish35No ratings yet
- Textiles For FiltrationDocument37 pagesTextiles For FiltrationBebi WakaNo ratings yet
- Effects of Processing Condition On The Filtration Performances of Nonwovens For Bag Filter MediaDocument6 pagesEffects of Processing Condition On The Filtration Performances of Nonwovens For Bag Filter Mediaapi-3733260No ratings yet
- CFD Simulations of Fiber-Fiber Interactions in A Hollow Fiber Membrane Bundle: Fiber Distance and Position MattersDocument31 pagesCFD Simulations of Fiber-Fiber Interactions in A Hollow Fiber Membrane Bundle: Fiber Distance and Position MattersNaeem owaisNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of The Performance of Elastic Band Used ForDocument5 pagesEvaluation of The Performance of Elastic Band Used ForMaria MirandaNo ratings yet
- 22 591.fullDocument15 pages22 591.fullpriyaNo ratings yet
- Fabric Science I: National Institute of Fashion TechnologyDocument10 pagesFabric Science I: National Institute of Fashion TechnologySHASHANK ROHITNo ratings yet
- Air Pollutants & Control TechnicquesDocument25 pagesAir Pollutants & Control TechnicquesStan MacapiliNo ratings yet
- B6 Lab ReportDocument17 pagesB6 Lab ReportLim Chien Chiang100% (1)
- 9634 37102 1 PBDocument9 pages9634 37102 1 PBali4300136No ratings yet
- Doaa 2020Document7 pagesDoaa 2020ahmed aboamerNo ratings yet
- Stretching The Skin SurfaceDocument13 pagesStretching The Skin SurfaceAthenaNo ratings yet
- Niosh 0500Document3 pagesNiosh 0500sreen2r100% (1)
- INTRODUCTION Spray ChamberDocument5 pagesINTRODUCTION Spray Chamberhilm0% (1)
- Review - Spray DryerDocument4 pagesReview - Spray DryerGusmannNo ratings yet
- E 1728 - 03 - Rte3mjgDocument4 pagesE 1728 - 03 - Rte3mjgEric GozzerNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Different Collection Efficiency Models For Venturi ScrubbersDocument10 pagesComparison of Different Collection Efficiency Models For Venturi ScrubbersPassmore DubeNo ratings yet
- Abrasion Resistance Property of Woven FabricsDocument3 pagesAbrasion Resistance Property of Woven FabricsJothi Vel Murugan100% (1)
- SSPC Guide 16 PDFDocument15 pagesSSPC Guide 16 PDFkishorekumar.animu100% (1)
- SSPC Guide 16Document13 pagesSSPC Guide 16mithileshNo ratings yet
- D 6767 - 02Document6 pagesD 6767 - 02luis-12No ratings yet
- TAPPI Felt Conditioning ArticleDocument6 pagesTAPPI Felt Conditioning ArticleSoma Nathan0% (1)
- Niosh 0600Document6 pagesNiosh 0600Jonathan CárcamoNo ratings yet
- Roadmap to Sustainable Textiles and Clothing: Environmental and Social Aspects of Textiles and Clothing Supply ChainFrom EverandRoadmap to Sustainable Textiles and Clothing: Environmental and Social Aspects of Textiles and Clothing Supply ChainNo ratings yet
- Exposure Assessment and Safety Considerations for Working with Engineered NanoparticlesFrom EverandExposure Assessment and Safety Considerations for Working with Engineered NanoparticlesNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Innovations in Recycled TextilesFrom EverandSustainable Innovations in Recycled TextilesNo ratings yet
- Roadmap to Sustainable Textiles and Clothing: Eco-friendly Raw Materials, Technologies, and Processing MethodsFrom EverandRoadmap to Sustainable Textiles and Clothing: Eco-friendly Raw Materials, Technologies, and Processing MethodsNo ratings yet
- Technologic Papers of the Bureau of Standards No. 153 - Area Measurement of LeatherFrom EverandTechnologic Papers of the Bureau of Standards No. 153 - Area Measurement of LeatherNo ratings yet