Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Name of The Drug
Name of The Drug
Uploaded by
AgnesRendonOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Name of The Drug
Name of The Drug
Uploaded by
AgnesRendonCopyright:
Available Formats
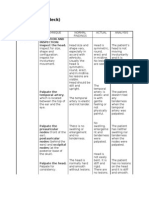
NAME OF THE DRUG Ampicillin 200mg IVTT Q6 NST (2-8) CLASSIFICATION: Antibiotics MECHANISMS OF ACTION: Interferes with cell
wall synthesis of susceptible organisms, preventing bacterial multiplication, it also renders the cell wall osmotically unstable and burst due to osmotic pressure. Deactivated by beta-lactamase, an enzyme produced by resistant bacteria. INDICATION: Treatment of respiratory tract and soft tissue infections, bacterial meningitis, septicemia, and gonococcal infections caused by susceptible microorganisms. CONTRAINDICATION: Hypersensitivity to penicillins, cephalosporins or imipenem. Oral form not used to treat severe pneumonia, emphysema, bacteremia, pericarditis, and purulent or septic arthritis during acute stage. ADVERSE REACTION: Thrombophlebitis at injection site, fatigue, insomnia, reversible hyperactivity, neurotoxicity (lethargy, neuromuscular irritability, hallucinations, convulsions, seizures) urticaria, maculopapular to exfoliative dermatitis, vesicular eruptions, skin rashes, diarrhea, pseudomembranous, colitis, iinterstitial nephritis (e.g., oliguria, proteinuria, hematuria, hyaline casts, pyuria) decreased Hgb, Hct, WBC, RBC, neutrophis, eosinophils and platelets, pain at injection site, hyperthermia. NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES: 1. Obtain patient history of infection before and during therapy to assess response. 2. Assess patient for signs and symptoms of infection. Fever, characteristics of wounds, sputum, urine, stool, earache,and WBC count >10,000/mm3, obtain baseline information and during treatment. 3. Otain C & S before drug therapy to identify if correct treatment has been initiated. 4. Assess history of previous sensitivity reactions to penicillins or other cephalosporins. Crosssensitivity between penicillins and cephalosporins is common fever; joint pain, pruritus and rash. Angioedema may occur a few days after therapy begins. Epinephrine ad resuscitation equipment should be on unit for anaphylactic reaction. 5. Monitor blood studies: CBC, Hct 6. Assess for overgrowth infection: perineal itching, fever, malaise, redness, pain, swelling,
drainage, rash, diarrhea or change in character of cough and sputum.
NAME OF THE DRUG Ranitidine 3mg IV Q8h CLASSIFICATION: Histamine2 (H2) antagonist, antacid MECHANISM OF ACTION: Ranitidine blocks histamine H2-receptors in the stomach and prevents histamine-mediated gastric acid secretions. It does not affect pepsin secretion, pentagastrin-stimulated factor secretion or serum gastrin. INDICATIONS: Short-term treatment of active duodenal ulcer, maintenance therapy for duodenal ulcer at reduced dosage, short-term treatment of active benign gastric ulcer, short-term treatment of GERD, pathologic hypersecretory conditions (e.g.,Zollinger-Ellison syndrome) treatment of erosive esophagitis, and treatment of heartburn, acid indigestion, and sour stomach. CONTRAINDICATIONS: Hypersensitivity. History of acute porphyria. Long-term therapy. ADVERSE REACTION: Headache, dizziness. Rarely hepatitis, thrombocytopenia, leucopenia, hypersensitivity, confusion, gynecomastia, impotence, somnolence, vertigo, and hallucinations. NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES: 1. Decrease doses in renal and liver failure. 2. Administer IM dose diluted, deep into large muscle group. 3. Provide concurrent antacid therapy to relieve pain. 4. Arrange for regular follow-up, including blood tests to evaluate effects. Report fever, unusual bruising or bleeding, headache, muscle or joint pain.
NAME OF THE DRUG Metronidazole 45mg IVTT CLASSIFICATION: Antibiotic MECHANISM OF ACTION: Direct-acting amebicide/trichomonacide. It binds to bacterial and protozoal DNA to cause loss of helical structure, strand breakage, inhibition of nucleic acid synthesis and cell death. INDICATIONS: Infections in the intra-abdominal, skin and skin structure, bone and joint, gynecologic, bacterial, bacterial septicemia, CNS, lower respiratory system and endocarditis. Treatment of susceptible protozoal infections and in the treatment and prophylaxis of anaerobic bacterial infections. Anaerobic infections, trichomoniasis, amoebiasis, giardiasis. CONTRAINDICATIONS: Blood dyscrasias. Active CNS diseases. Hypersensitivity to imidazole. Tuberculosis of mucous membranes and certain viral conditions. ADVERSE REACTION: Convulsive seizures; peripheral neuropathy; rash, pruritus. GI discomfort, anorexia, nausea, furred tongue, dry mouth and unpleasant metabolic taste, headache, less frequently vomiting, diarrhea, weakness, dizziness and darkening of the urine. Leucopenia. NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES: 1. Obtain baseline information on patient s infection: fever, characteristic of wounds, WBC count (>10,000/mm3) and regularly assess during treatment. 2. Obtain patient history of infection before and during therapy to identify if correct treatment has been initiated. 3. Assess for allergic reactions: rash, urticaria, pruritus. 4. Monitor bowel pattern, discontinue drug if severe diarrhea occurs.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5814)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (845)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Chapter 3 Anatomy and Physiology For PhlebotomyDocument23 pagesChapter 3 Anatomy and Physiology For PhlebotomyMark Matthew ImpasNo ratings yet
- P.A. 1Document6 pagesP.A. 1SamSarah BongolanNo ratings yet
- Ped A Internship 1517300917 PDF 2Document13 pagesPed A Internship 1517300917 PDF 2dariasuslowaNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis and Prevention of Iron Deficiency and Iron-Deficiency Anemia in Infants and Young ChildrenDocument16 pagesDiagnosis and Prevention of Iron Deficiency and Iron-Deficiency Anemia in Infants and Young ChildrenAnwesa Priyadarsini PradhanNo ratings yet
- Med-Surg Final Exam Study Guide Fall 2010Document3 pagesMed-Surg Final Exam Study Guide Fall 2010Lynn Suening100% (1)
- Nonneoplastic Dermatopathology 2Nd Edition Brian J Hall Full ChapterDocument67 pagesNonneoplastic Dermatopathology 2Nd Edition Brian J Hall Full Chaptermichael.sheston932100% (8)
- Edit Dafpus TK 1-1Document3 pagesEdit Dafpus TK 1-1annewidiatmoNo ratings yet
- How To Pass MRCP Part 1 (Complete Guidelines) - Passing MRCP Part 1Document1 pageHow To Pass MRCP Part 1 (Complete Guidelines) - Passing MRCP Part 1Kendra GreyNo ratings yet
- Scientific Point of ViewDocument2 pagesScientific Point of Viewpavans EnglishNo ratings yet
- Determining Research Questions On Health Risks by People With Learning Disabilities, Carers and Care-WorkersDocument10 pagesDetermining Research Questions On Health Risks by People With Learning Disabilities, Carers and Care-WorkersashjdhksNo ratings yet
- Nutrition and DementiaDocument88 pagesNutrition and Dementiatimea_gheneaNo ratings yet
- FLCCC Protocols - A Guide To The Management of COVID 19Document61 pagesFLCCC Protocols - A Guide To The Management of COVID 19Tina SangreaNo ratings yet
- Anti D Injections For Women With Rhesus Negative Blood A019 PDFDocument2 pagesAnti D Injections For Women With Rhesus Negative Blood A019 PDFهدير عبدالمطلب حمزةNo ratings yet
- YAWS: Elimination To EradicationDocument5 pagesYAWS: Elimination To EradicationShrutiNo ratings yet
- Draft OrdinanceDocument2 pagesDraft OrdinanceGrace Managuelod GabuyoNo ratings yet
- Rheumatic Conditions in Patients With Diabetes Mellitus: Review ArticleDocument7 pagesRheumatic Conditions in Patients With Diabetes Mellitus: Review ArticleYadira SantosNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Models-2 PDFDocument38 pagesTherapeutic Models-2 PDFDhen MarcNo ratings yet
- Candidiasis: Armie Jade S. Gante, RNDocument18 pagesCandidiasis: Armie Jade S. Gante, RNAnnapurna DangetiNo ratings yet
- 3X-Study Material English 2022-23 (Final)Document199 pages3X-Study Material English 2022-23 (Final)Puja BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Part I - Sample Questions: Representative in Format and Phrasing Style of The Types of Questions Found in The QualifyingDocument16 pagesPart I - Sample Questions: Representative in Format and Phrasing Style of The Types of Questions Found in The Qualifyingitsshuvro100% (2)
- HIV EssayDocument1 pageHIV EssayLymberth BenallaNo ratings yet
- Mood-Stabilizing AgentsDocument9 pagesMood-Stabilizing AgentsRoci ArceNo ratings yet
- Listeria Species Occurrence and Associated Risk Factors andDocument11 pagesListeria Species Occurrence and Associated Risk Factors andEndrias ZewduNo ratings yet
- Management of Cancer Therapy - Associated Oral Mucositis: Timothy J. Brown, MD and Arjun Gupta, MDDocument8 pagesManagement of Cancer Therapy - Associated Oral Mucositis: Timothy J. Brown, MD and Arjun Gupta, MDranievadewiNo ratings yet
- Surgery Lecture 1st PatookDocument81 pagesSurgery Lecture 1st PatookPranjali WeladiNo ratings yet
- Coclia EyelidDocument5 pagesCoclia EyelidFaradila HakimNo ratings yet
- New Zealand Data Sheet: 1. Product NameDocument12 pagesNew Zealand Data Sheet: 1. Product NameMaizura Syahirah MohtadaNo ratings yet
- Gouty Arthritis PathophysiologyDocument1 pageGouty Arthritis PathophysiologyKooksNo ratings yet
- Furosemide Drug ProfileDocument34 pagesFurosemide Drug ProfileNur Ilmi SofiahNo ratings yet
- GAMMA-GT Carboxy GPNA: BiolaboDocument2 pagesGAMMA-GT Carboxy GPNA: BiolaboFariz KasyidiNo ratings yet