Professional Documents
Culture Documents
FDI in India
FDI in India
Uploaded by
Amit RoyCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
FDI in India
FDI in India
Uploaded by
Amit RoyCopyright:
Available Formats
FDI IN INDIA
IN 1990
INTRODUCTION REFORMS IN
1990
FDI TRENDS AND COMPOSITION
INDIA VS CHINA
TECHNOLOGY SPILLOVERS AND BARGAINING POWER IN THIS MARKET BRAND NAMES
FDI POLICY
INTODUCTION
FDI
India followed restricted trade policy
Foreign investment is allowed only in designated industries
FERA stipulated foreign companies to hold equity up to
40%
Such policies are believed to retard domestic technical capability and loss of export opportunities
REFORMS IN
90S
Shift in strategy
FDI is seen as source of capital, technology and managerial skills Permitted foreign investments in almost all the sectors
Fiscal and Administrative reforms Financial sector reforms International trade and investment reforms Industrial sector reforms Infrastructure reforms Agricultural reforms
Privatization reforms
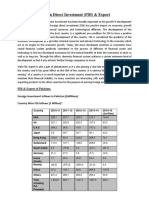
TRENDS The inflows increased from 500 crores to 55000 crores in five years The top investing countries are USA, Mauritius, UK, South Korea, Japan etc Sectors are Power generation Tele communications Service sector Food processing Chemicals etc
Sector-wise FDI inflows in India from April 2000 Dec 2009 Amount of FDI inflows Rs. Millions Service Sector 1015269 Computer Software and Hardware 423529 Telecommunication 398094 Housing and Real Estate 352550 Construction Activities 327195 Power 200993 Automobile Industry 197634 Metallurgical Industry 131178 Pertoleum and Natural Gas 112617 Chemicals 108251 Electrical Equipments 94888 Trading 87001 Hotel and Tourism 80355 Information and Broadcasting 79569 Cement and Gypsum Products 74579 Drugs and Pharmaceuticals 72533 Agriculture 71231 Consultancy 68354 Ports 66675 Industrial Sectors in India % of total FDI inflows 21.63 9.02 8.48 7.51 6.97 4.28 4.21 2.79 2.40 2.31 2.02 1.85 1.71 1.70 1.59 1.55 1.52 1.46 0.93
Ranking of Sector-wise FDI Inflows in India since April 2000 Dec2009 Industrial Sectors in India Service Sector Computer Software and Software Telecommunication Housing and Real Estate Construction Activities Power Automobile Industry Metallurgical Industry Pertoleum and Natural Gas Chemicals Electrical Equipments Trading Hotel and Tourism Information and Broadcasting Cement and Gypsum Products Drugs and Pharmaceuticals Agriculture Consultancy Ports Ranks 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19
Ranks
Country
2007-08 (AprilMarch) 44,483 (11,096) 12,319 (3,073) 4,377 (1,089) 4,690 (1,176) 2,780 (695) 3,336 (815) 3,385 (834) 2,075 (514) 583 (145) 1,039 (258)
2008-09 (AprilMarch) 50,794 (11,208) 15,727 (3,454) 8,002 (1,802) 3,840 (864) 3,922 (883) 1,889 (405) 5,983 (1,287) 2,750 (629) 2,098 (467) 1,133 (257)
2009-10 (AprilMarch) 49,633 (10,376) 11,295 (2,379) 9,230 (1,943) 3,094 (657) 4,283 (899) 5,670 (1,183) 7,728 (1,623) 2,980 (626) 1,437 (303) 3,017 (629)
2010-11 (for April 10) 2,528 (568) 1,933 (434) 404 (91) 265 (59) 312 (70) 1,455 (327) 123 (28) 102 (23) 184 (41) 31 (7)
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10.
MAURITIUS SINGAPORE U.S.A. U.K. NETHERLAN DS JAPAN CYPRUS GERMANY FRANCE U.A.E.
Cumulative Inflows (April 00 to April 10) 213,434 (47,808) 47,080 (10,625) 37,593 (8,369) 26,263 (5,944) 20,438 (4,557) 18,350 (4,041) 17,900 (3,927) 12,571 (2,822) 7,102 (1,571) 7,054 (1,556)
%age to total Inflows (in terms of US $) 43 % 9% 7% 5% 4% 4% 4% 3% 1% 1%
TOTAL FDI INFLOWS *
98,664 (24,581)
123,025 (27,331)
123,378 (25,888)
9,854 (2,214)
526,357 (117,943)
RBI BULLETIN
India Vs China
Even though our inflows are increased tremendously we are far behind of china It is due to failure of Indian reforms Reasons for our failure Reforms Infrastructure Technology Facilities Skilled labor etc
Technology spillovers FDI is considered as a source of technology
It may not be all the times It depends on extent of value addition in host economy FMCG leads to minimal externality Automobile industry can increase technical capability
Loss in bargaining power..
Many dominant international firms with their power in technology has weakened domestic players bargaining power Considering their finanancial and technical strengths many foreign firms took managerial control over domestic companies and increased their stake They found it as an inexpensive way to acquire new companies
Brand names..
It takes some time to create such intangible asset It acts as a competitive advantage Brand consciousness has started form 1990s Cola bought its competitors Pepsi bought Mangola, Dukes etc
These proved to be a costly mistake for India
FDI POLICIES
FDI is seen as integral part of National development
Foreign investment is freely permitted in all the sectors excluding some such as agriculture, retail trade, real estate etc % in power trading, processing, development of new airports, laying of natural gas pipelines, petroleum infrastructure and warehousing of coffee and rubber
100
Limit for telecoms services firms have been raised from 49 per cent to 74 per cent. Retailing industry in India is allowing 51% FDI in single brand outlet Prohibited Sectors
i. Gambling and betting ii.Lottery Business iii.Atomic Energy iv. Retail Trading v.Agricultural or plantation activities of Agriculture
Questions:
Name any five top investing sectors in India?
What are the main reasons for not attracting fdi ?
What is the reason for sudden increase in fdi ?
What is our current rank in FDI investments ? Which countr did India overtake to reach that position?
How we can reach number one? What are our advantage
You might also like
- BMGC Chapter OneDocument50 pagesBMGC Chapter Oneadithya100% (1)
- Service Manual (AT) - J Transmission (AT)Document16 pagesService Manual (AT) - J Transmission (AT)Николай КирилловNo ratings yet
- Turkish Leasing MarketDocument16 pagesTurkish Leasing Marketlévai_gáborNo ratings yet
- Tesla DCF Valuation by Ihor MedvidDocument105 pagesTesla DCF Valuation by Ihor Medvidpriyanshu14No ratings yet
- FDI Approval Procedure: - Automatic RouteDocument11 pagesFDI Approval Procedure: - Automatic RoutesudeepptrNo ratings yet
- Ybs 1Document1 pageYbs 1Thet Htar's NoteNo ratings yet
- Foreign Direct InvestmentDocument12 pagesForeign Direct InvestmentRohan KumarNo ratings yet
- Growth and Stabilization: : at Average Exchange Rate P: ProvisionalDocument17 pagesGrowth and Stabilization: : at Average Exchange Rate P: ProvisionalWaqas TayyabNo ratings yet
- Fdi Numeic DataDocument3 pagesFdi Numeic DataSuman YadavNo ratings yet
- Table 3 - Labor Productivity by Region and Sector, Philippines (At Constant 2000 Prices), 2009-2017 - 0Document7 pagesTable 3 - Labor Productivity by Region and Sector, Philippines (At Constant 2000 Prices), 2009-2017 - 0Reta Kar'ihaNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - General Safety 2005Document32 pagesModule 1 - General Safety 2005Ali KenaboiNo ratings yet
- Lapangan Usaha PDRB 2007 2008 2009Document4 pagesLapangan Usaha PDRB 2007 2008 2009ghost godnessNo ratings yet
- Foreign Capital and Economic Growth of IndiaDocument23 pagesForeign Capital and Economic Growth of IndiaMitesh ShahNo ratings yet
- TABLE 1.1 Gross National Product at Constant Basic Prices of 2005-06Document12 pagesTABLE 1.1 Gross National Product at Constant Basic Prices of 2005-06sidraNo ratings yet
- 1 Pbi Ancash 2007-2019Document9 pages1 Pbi Ancash 2007-2019Alin Ayalar SalazarNo ratings yet
- TABLE B - Employment by Major Industry Group and Total Hours Worked, Philippines - 2Document6 pagesTABLE B - Employment by Major Industry Group and Total Hours Worked, Philippines - 2cotiadanielNo ratings yet
- Appendix Table 9: Foreign Direct Investment Flows To India: Country-Wise and Industry-WiseDocument1 pageAppendix Table 9: Foreign Direct Investment Flows To India: Country-Wise and Industry-WiseINDRANIL ROYNo ratings yet
- Chapter IDocument15 pagesChapter Imohsin.usafzai932No ratings yet
- XLS317 XLS EngDocument10 pagesXLS317 XLS EngWilder Atalaya ChavezNo ratings yet
- Market Structure Analysis EcoDocument9 pagesMarket Structure Analysis EcoPalak MendirattaNo ratings yet
- Table B - Employment by Major Industry Group, December 2021f, December 2022p To December 2022p (In Thousands Except Rates)Document14 pagesTable B - Employment by Major Industry Group, December 2021f, December 2022p To December 2022p (In Thousands Except Rates)PIAO ADSNo ratings yet
- AU535Document5 pagesAU535Navjivan IndiaNo ratings yet
- TABLE B - Employment by Major Industry Group and Total Hours Worked, Philippines Sept2021f, January 2022p To September 2022pDocument4 pagesTABLE B - Employment by Major Industry Group and Total Hours Worked, Philippines Sept2021f, January 2022p To September 2022pMonique TierraNo ratings yet
- Power Sector WriteupDocument17 pagesPower Sector WriteupAgha Alamdar HussainNo ratings yet
- Gross Capital Formation in Agriculture & Allied Sector (At Current Prices)Document2 pagesGross Capital Formation in Agriculture & Allied Sector (At Current Prices)Anushka GoelNo ratings yet
- Global Services-5-6 Prof. Tarun DasDocument45 pagesGlobal Services-5-6 Prof. Tarun DasProfessor Tarun DasNo ratings yet
- Name of The InstrumentDocument10 pagesName of The InstrumentShashikant SinghNo ratings yet
- Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) & ExportDocument9 pagesForeign Direct Investment (FDI) & ExportSibghaNo ratings yet
- Kor Key Indicators 2021Document11 pagesKor Key Indicators 2021Carlos CcaNo ratings yet
- Economic Forces: Montgomery CountyDocument78 pagesEconomic Forces: Montgomery CountyM-NCPPCNo ratings yet
- Electricity: Commodity BalancesDocument5 pagesElectricity: Commodity BalancesWILLIAM FRANCISCO MENDIETA BENAVIDESNo ratings yet
- Operating Profit Analysis: Tata Consultancy Services (TCS)Document43 pagesOperating Profit Analysis: Tata Consultancy Services (TCS)manju_chandelNo ratings yet
- Klem S 12072019Document209 pagesKlem S 12072019Bhagirath BariaNo ratings yet
- Kar Gaz Suppl 1994 Chapter8Document90 pagesKar Gaz Suppl 1994 Chapter8Afreen MullaNo ratings yet
- REV 1 - PPT KBRI For TEI-revDocument7 pagesREV 1 - PPT KBRI For TEI-revPanji GNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document2 pagesAssignment 1Sameh Ali - سامح عليNo ratings yet
- Fabi KoreaadbDocument30 pagesFabi KoreaadbDino Fredne FabiNo ratings yet
- Trade in Services in India: Implications For Poverty and InequalityDocument20 pagesTrade in Services in India: Implications For Poverty and InequalityMandeep Singh BirdiNo ratings yet
- Table B.8 Expenditure Program, by Department/Special Purpose, by General Expense Class, Fy 2017 - 2019 (In Thousand Pesos)Document4 pagesTable B.8 Expenditure Program, by Department/Special Purpose, by General Expense Class, Fy 2017 - 2019 (In Thousand Pesos)peejayNo ratings yet
- Research Notes: Division of Research and StatisticsDocument15 pagesResearch Notes: Division of Research and StatisticsLou GulinoNo ratings yet
- Summary Constant Q2 2010 30nov09 PDFDocument9 pagesSummary Constant Q2 2010 30nov09 PDFPalash DubeyNo ratings yet
- Agriculture PlanDocument151 pagesAgriculture Planpushpen5115No ratings yet
- Country Wise Net FDIDocument4 pagesCountry Wise Net FDIChussMaarsNo ratings yet
- Kotak Consolidated Earnings EstimatesDocument50 pagesKotak Consolidated Earnings EstimatesAnkit JainNo ratings yet
- CMES Annual 2014.15 Table-52Document51 pagesCMES Annual 2014.15 Table-52Aakriti AdhikariNo ratings yet
- Philippines Key Indicators 2019Document12 pagesPhilippines Key Indicators 2019Mustaffah KabelyyonNo ratings yet
- 37GRDP R13 2019Document4 pages37GRDP R13 2019Jacket TralalaNo ratings yet
- R&D, Advertisement and Market Share: Telecommunications Industry in IndiaDocument34 pagesR&D, Advertisement and Market Share: Telecommunications Industry in IndiadebajyotimondalNo ratings yet
- Adb IndoDocument35 pagesAdb IndoHoang Giang NguyenNo ratings yet
- Basic LQ SSDocument18 pagesBasic LQ SSSarah Jasmine RiadiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: The Macroeconomy: A. AssessmentDocument14 pagesChapter 2: The Macroeconomy: A. AssessmentJaiDomeyegNo ratings yet
- Eaton KortumDocument39 pagesEaton KortumBlanca MecinaNo ratings yet
- FII Buying / Selling Sector Wise SummaryDocument1 pageFII Buying / Selling Sector Wise SummaryWealth Maker BuddyNo ratings yet
- 3rd Week AssignmentDocument2 pages3rd Week AssignmentSameh Ali - سامح عليNo ratings yet
- 500 Largest Us Corporations: FORTUNE Magazine. June 15, 2017Document11 pages500 Largest Us Corporations: FORTUNE Magazine. June 15, 2017AlexElesvanPurihuamanCubasNo ratings yet
- Project Report: Foreign Direct Investment in India & Telecommunication SectorDocument14 pagesProject Report: Foreign Direct Investment in India & Telecommunication SectorPrincely ImmanuelNo ratings yet
- Macro Economic Situation of Nepal 2009-2010Document52 pagesMacro Economic Situation of Nepal 2009-2010Chandan SapkotaNo ratings yet
- Australia v1.3Document81 pagesAustralia v1.3Hà Kiều OanhNo ratings yet
- Tata Motors FM - Chintan HasnaniDocument26 pagesTata Motors FM - Chintan Hasnanianser lalNo ratings yet
- Capmas Statistical Yearbook 2017 Industry and EnergyDocument52 pagesCapmas Statistical Yearbook 2017 Industry and EnergyMariam M. WilliamNo ratings yet
- Perú: Producto Bruto Interno Según Actividad Económica (Nivel 14), 1994-2017 Valores A Precios Corrientes (Millones de Soles)Document6 pagesPerú: Producto Bruto Interno Según Actividad Económica (Nivel 14), 1994-2017 Valores A Precios Corrientes (Millones de Soles)Carlos NavarreteNo ratings yet
- Birla SunlifeDocument19 pagesBirla SunlifeSatish AddaNo ratings yet
- Memo and Memo ReportsDocument19 pagesMemo and Memo ReportsSatish AddaNo ratings yet
- Marketing Research Project: by Varun, Sanath, Azra, NaveenDocument10 pagesMarketing Research Project: by Varun, Sanath, Azra, NaveenSatish AddaNo ratings yet
- Career PathDocument7 pagesCareer PathSatish AddaNo ratings yet
- Mib DelhiDocument1 pageMib DelhiSatish AddaNo ratings yet
- To Prepare A 3C Report On Future Retail GroupDocument11 pagesTo Prepare A 3C Report On Future Retail GroupSatish AddaNo ratings yet
- Inter Metal Construction Doo: InvoiceDocument1 pageInter Metal Construction Doo: InvoiceMiodrag Miki NedeljkovicNo ratings yet
- Group 10 - Chapter 12 - Group Assignment No. 10 Exercises 1 & 2 Pages 331 - 334Document31 pagesGroup 10 - Chapter 12 - Group Assignment No. 10 Exercises 1 & 2 Pages 331 - 334Carla TalanganNo ratings yet
- 3 International Standard AuditDocument10 pages3 International Standard AuditDwi Puji AstutiNo ratings yet
- Imitation Jewellery Cluster, MachilipatnamDocument6 pagesImitation Jewellery Cluster, Machilipatnamkumar53366No ratings yet
- Product Costing and Cost Accumulation in A Batch Production EnvironmentDocument56 pagesProduct Costing and Cost Accumulation in A Batch Production Environmentsunanda mNo ratings yet
- w1 Fabmii Review of Basic Bookkeeping Skills Part2Document18 pagesw1 Fabmii Review of Basic Bookkeeping Skills Part2Mizuki YamizakiNo ratings yet
- 01Document106 pages01Tanya VermaNo ratings yet
- Tax 302 Business and Transfer Tax Finals Answer PDFDocument29 pagesTax 302 Business and Transfer Tax Finals Answer PDFsunthatburns00No ratings yet
- Group Assignment Acc116Document9 pagesGroup Assignment Acc116Nurul AzlinNo ratings yet
- Flash Loan Code 3Document2 pagesFlash Loan Code 3Carlos GrafitoNo ratings yet
- Nec3 Contract - Ort Main Incomer UpgradeDocument41 pagesNec3 Contract - Ort Main Incomer UpgradedevNo ratings yet
- Applied Economics Basic Economic Problems and The Philippine Socio - Economic Development in The 21 CenturyDocument33 pagesApplied Economics Basic Economic Problems and The Philippine Socio - Economic Development in The 21 CenturyBretana joanNo ratings yet
- Class: 6: Paper Code: UN479Document20 pagesClass: 6: Paper Code: UN479virajNo ratings yet
- Swagelok Ss Tbp8Document1 pageSwagelok Ss Tbp8claudia nilNo ratings yet
- ETA 17-1056 Rebar Connection With Fischer Injection System FIS EM Plus (22 January 2021)Document26 pagesETA 17-1056 Rebar Connection With Fischer Injection System FIS EM Plus (22 January 2021)Dona Dwi SaputroNo ratings yet
- 2538.5 Randalls Gold - A4903 Mixtec Agitators - May 2009Document17 pages2538.5 Randalls Gold - A4903 Mixtec Agitators - May 2009Dhruv PatelNo ratings yet
- Syllabous-UConn Spring 2021 On Line M and BDocument7 pagesSyllabous-UConn Spring 2021 On Line M and BJames PritchardNo ratings yet
- Transfer Certificate of Title No. 319819Document1 pageTransfer Certificate of Title No. 319819michael lumboyNo ratings yet
- Macro 203Document448 pagesMacro 203Bin WangNo ratings yet
- 56 Accesories enDocument2 pages56 Accesories enSyed AsadullahNo ratings yet
- Arithmetic Mean, Median and ModeDocument9 pagesArithmetic Mean, Median and ModeSaadNo ratings yet
- CONSO FS Cost MethodDocument21 pagesCONSO FS Cost MethodMaurice AgbayaniNo ratings yet
- Point of View Research Accounting and Auditing: Saida Said Mustari SDocument8 pagesPoint of View Research Accounting and Auditing: Saida Said Mustari SSeevaniska AmandaNo ratings yet
- Edvardsson 2005Document13 pagesEdvardsson 2005Marcelo Pereira DemilisNo ratings yet
- Mumbai Abu Dhabi: Nfiu7L CompleteDocument4 pagesMumbai Abu Dhabi: Nfiu7L CompleteFizan NaikNo ratings yet
- Normal Distribution and Standardization 1Document14 pagesNormal Distribution and Standardization 1Samwel MagomaNo ratings yet
- Machinelist 16.november 2020Document15 pagesMachinelist 16.november 2020Luis Alberto Salazar CarrilloNo ratings yet
- Nerolac Perma Waterproof Premium PuttyDocument2 pagesNerolac Perma Waterproof Premium PuttyrajaNo ratings yet