Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Solution
Solution
Uploaded by
Melvin ChangOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Solution
Solution
Uploaded by
Melvin ChangCopyright:
Available Formats
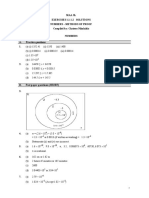
1 (a)
(i) (ii)
median = 459.5 Mean = 487 Standard deviation = 180.9540
(iii) (iv) 1(b) (i) (ii) 1(c) (i) (ii)
positively skewed 37.16% 0.003858 0.4628 0.3172 41198.84
2(a)
CV=1.6449 P=0.65 Test stat = -1.0911 Do not reject Ho.
2(b)
CVs = 2.024 Sp=7.2887 t-stat = 1.7354 Do not reject Ho.
3.(a) House Size = -1.6335 +0.4485 Family Income +4.2615 Family Size-0.6517 Education (b) SSR = SST- SSE = 3605.7736 F-ratio = MSR/MSE = 35.6353 MSR = SSR/3 = 1201.9245 MSE = SSE/36 =33.7285
(c)
R2
SSR 3605.7736 0.7481 SST 4820
There is about 74.81% of the total variation in house size can be explained by all the independent variables. (d) H0 : 1 = 2 = 3 = 0 H1 : At least one i 0
At = 0.05, critical value F0.05,3,36 = 2.866 Decision rule: Reject Ho if F > 2.866 Conclusion: Reject H0 as F = 35.6353 > 2.866. The model is useful in predicting the house size. (e) H0 : i = 0 H1 : i 0 for i = 1, 2, 3 Reject the null hypotheses if t > 2.024 or t <-2.024 Family income (X1) and family size (X2) are significant at 0.05 whereas education (X3) is not significant in explaining house size and should not be included in the model because its t-stat falls within the non-rejection area.
4.
(a)
Expected frequencies (ei) Department Sales Production Administration < 5 years 8 16 16 5 to 15 years 16 32 32 > 15 years 6 12 12
CV= 9.488 Test stat = 23 Reject Ho. 4 (b) (i) (ii) 107.56 107.67 106.56 (iii) Answer different because different weight being used.
You might also like
- Number Theory & ComputationDocument66 pagesNumber Theory & ComputationShannon Smith100% (1)
- Business Statistics: Level 3Document26 pagesBusiness Statistics: Level 3Hein Linn Kyaw100% (1)
- Decimals: STD 5 IngridDocument18 pagesDecimals: STD 5 Ingridakanshayein Fiona Maria RodriguesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Standard FormDocument9 pagesChapter 1 - Standard FormNasir RahmanNo ratings yet
- Solutions - December 2014Document3 pagesSolutions - December 2014Nurul SyafiqahNo ratings yet
- A2 CosepeDocument3 pagesA2 CosepeSean Jodi CosepeNo ratings yet
- Assignment # 6 Solution: MS MS y T y T N NDocument6 pagesAssignment # 6 Solution: MS MS y T y T N Nsulaiman_GNo ratings yet
- Doane Chap012 ASBE 7e SMDocument78 pagesDoane Chap012 ASBE 7e SMpavistatsNo ratings yet
- Econometrics Assignment 1Document6 pagesEconometrics Assignment 1Jovias KelvinsunNo ratings yet
- Practice 3 Multiple Regression 2023 03-16-09!06!38Document5 pagesPractice 3 Multiple Regression 2023 03-16-09!06!38PavonisNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Standard Form (Latest)Document72 pagesChapter 1 - Standard Form (Latest)FirdausNo ratings yet
- Assigment 2Document2 pagesAssigment 2Tran Thanh Thao (K16 DN)No ratings yet
- Sample Final Exam Answers - Summer 2022Document2 pagesSample Final Exam Answers - Summer 2022esha raisNo ratings yet
- ExamDocument90 pagesExamiqueenNo ratings yet
- Solutions To Applied Linear Regression ModelsDocument22 pagesSolutions To Applied Linear Regression ModelsXiaohanHuNo ratings yet
- 2010 Mock SolutionsDocument7 pages2010 Mock SolutionsS.L.L.CNo ratings yet
- Engineering Probability and StatisticsDocument10 pagesEngineering Probability and StatisticsRed BxNo ratings yet
- Taller Regresion MultipleDocument11 pagesTaller Regresion MultipleANDRESNo ratings yet
- Ees 404Document10 pagesEes 404beemuriithi24No ratings yet
- Problem # 01:: A) Interpretation of Number 64,100Document2 pagesProblem # 01:: A) Interpretation of Number 64,100irfan bashirNo ratings yet
- pricei = β + β sqfti + β agei + β baths + e: Question 1 (7 marks)Document11 pagespricei = β + β sqfti + β agei + β baths + e: Question 1 (7 marks)MinzaNo ratings yet
- Mathematic-Form 4 TOPIC 1: Standard Form (Bentuk Piawai)Document5 pagesMathematic-Form 4 TOPIC 1: Standard Form (Bentuk Piawai)Letchu MananNo ratings yet
- 120MSE MAY 2015-AnswersDocument3 pages120MSE MAY 2015-AnswersLexNo ratings yet
- Chap013 SolutionsDocument21 pagesChap013 SolutionsDiane Katz ZiegmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Standard FormDocument6 pagesChapter 1 - Standard Formkhai_83No ratings yet
- WB 1 CH 4 (Estimation and Approximation)Document8 pagesWB 1 CH 4 (Estimation and Approximation)Abdulkasim AkhmedovNo ratings yet
- Assignment Number 1 Introduction To Statistics MATH 1131Document9 pagesAssignment Number 1 Introduction To Statistics MATH 1131AVATAR88No ratings yet
- HomeworkDocument25 pagesHomeworkPhuong Uyen Du NgocNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Standard Form Exercise 2: M&S Learning CentreDocument4 pagesChapter 1: Standard Form Exercise 2: M&S Learning CentreyokekeannNo ratings yet
- Elementary Statistics 2nd Edition Navidi Solutions ManualDocument22 pagesElementary Statistics 2nd Edition Navidi Solutions Manualberthakha3lw100% (31)
- Ebook Elementary Statistics 2Nd Edition Navidi Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument43 pagesEbook Elementary Statistics 2Nd Edition Navidi Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDouglasRileycnji100% (12)
- MIS770A CH 08 Even Sol PDFDocument7 pagesMIS770A CH 08 Even Sol PDFZijun LiNo ratings yet
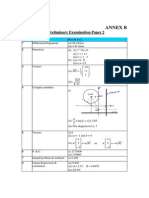
- NJC h2 Math p2 Annex BDocument2 pagesNJC h2 Math p2 Annex BjimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- STA302 Mid 2010FDocument9 pagesSTA302 Mid 2010FexamkillerNo ratings yet
- Jawapan PPT Math Ting 3 (Modul 2)Document6 pagesJawapan PPT Math Ting 3 (Modul 2)Yan WahabNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Significant FiguresDocument11 pages1.1 Significant FiguresMadihah RamlyNo ratings yet
- 4024 w08 Ms 2Document9 pages4024 w08 Ms 2mstudy123456No ratings yet
- Sitesdefaultfiles201702130732253 PDFDocument4 pagesSitesdefaultfiles201702130732253 PDFWissam HakawatiNo ratings yet
- DI SolutionDocument8 pagesDI SolutionSunil GaikwadNo ratings yet
- Answer Key Homework 8 (Due Date: April 8, 2005, Friday in Class)Document3 pagesAnswer Key Homework 8 (Due Date: April 8, 2005, Friday in Class)Rain MalabananNo ratings yet
- Jawapan PPT Math Ting 3 2023Document6 pagesJawapan PPT Math Ting 3 2023Yan WahabNo ratings yet
- Estimation and Significant FiguresDocument5 pagesEstimation and Significant FiguresZonish BakshNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Standard Form (Part 1)Document2 pages1.2 Standard Form (Part 1)mansourvcxNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document4 pagesAssignment 1Bhavik BohraNo ratings yet
- MAA SL 1.1-1.2 NUMBERS - METHODS OF PROOF - SolutionsDocument3 pagesMAA SL 1.1-1.2 NUMBERS - METHODS OF PROOF - SolutionsShivSantosh JhaNo ratings yet
- Solutions Chapter 6Document29 pagesSolutions Chapter 6IyadAitHouNo ratings yet
- Math 6 SummativeDocument5 pagesMath 6 SummativeNANIETA NACARNo ratings yet
- Ajc h2 Math p2 Annex BDocument2 pagesAjc h2 Math p2 Annex BjimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- Assignments (Course Requirement) : Misamis University Graduate SchoolDocument7 pagesAssignments (Course Requirement) : Misamis University Graduate SchoolGraciously ElleNo ratings yet
- G1 - Exercise On 19.9Document11 pagesG1 - Exercise On 19.9tanimaNo ratings yet
- V I ExerciseAnswersDocument95 pagesV I ExerciseAnswersRony Pestin0% (1)
- 6062 Resumption TestDocument2 pages6062 Resumption TestRasheed AhmedNo ratings yet
- Exercise 2B: 1 A 700 G, As This Is The Most Often Occurring. B 500 + 700 + 400 + 300 + 900 + 700 + 700 4200Document15 pagesExercise 2B: 1 A 700 G, As This Is The Most Often Occurring. B 500 + 700 + 400 + 300 + 900 + 700 + 700 4200drsus78No ratings yet
- 5 6291747757128417359Document77 pages5 6291747757128417359joeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Standard Form (1) - 4ADocument8 pagesChapter 1 Standard Form (1) - 4ACheng WLNo ratings yet
- Chap 1 Worksheet + Answer KeyDocument4 pagesChap 1 Worksheet + Answer KeyJudy EidNo ratings yet
- Class 3Document3 pagesClass 3Vithia Yalini PalanyNo ratings yet
- Solutions - December 2013Document3 pagesSolutions - December 2013Nurul SyafiqahNo ratings yet