Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cancer Chemotherapy
Cancer Chemotherapy
Uploaded by
firengineerCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cancer Chemotherapy
Cancer Chemotherapy
Uploaded by
firengineerCopyright:
Available Formats
CANCER CHEMOTHERAPY Principles of Cancer Chemotherapy Goal of treatment A. Cure eradication of every neoplastic cell B.
. Palliation alleviation of symptoms and avoidance of life threatening toxicity Tumor susceptibility and the growth cycle 4 Phases of the Cell Cycle 1. M phase period of mitosis (cell division) 2. G1 phase interval during which RNA, protein synthesis and cellular growth occurs 3. S phase DNA synthesis 4. G2 phase synthesis of cellular components required for mitosis 5. Go- resting state where cell is not dividing 2. Trimetrexate antimalarial agent, also a potent inhibitor of DNHFR 6 Mercaptopurine the thiol analog of the purine hypoxanthine. It is converted to the corresponding nucleotide 6-thioinosinic acid 6 TIMP which inhibits the formation of adenine and guanine from Inosinic monophosphate (IMP). Fate: 6 MP is converted to thiouric acid in the liver (this reaction is catalyzed by xanthine oxidase)
3.
4.
6- Thioguanine (6 TG)
5.
2 Types of Cancer Chemotherapeutic Agents base on its effect on cell cycle 6. -
MECH = converted to 6 thioguanine 5 Phosphate (6-thioGMP) which replace guanine nucleotide and inhibit DNA synthesis Fluorouracil (5 FU) Inhibits thymidylate synthetase thus interferes DNA production Floxuridine (FUDR or 5 FUDR) MECH= 5 FU is a pyrimidine analog. Interferes the conversion of deoxyuridylic acid to thymidylic acid. 5 FU must be converted to 5 FdUMP-( 5 Fluorodeoxyuridine monphosphate,) which competes with deoxyuridine monophosphate for the enzyme thymidylate synthetase. 5 FU is metabolized in the liver to CO2 which is then expired.
1.
Cell cycle specific drugs drugs that inhibit cell replication during a phase of a cycle. Example: Methotrexate inhibits DNA synthesis during Sphase(Antimetabolite) Others: Bleomycin, Antibiotics, Vinca Alkaloids - They are effective for Cancer with a high growth fraction (e.g hematologic cancers) Cell-cycle non specific agents that are active while the cancer cells are dividing but whose action spans more than one phase of the cycle as well as within Go. Example: Mechlorethamine, cisplatin, nitrosourceas they are effective for both high growth fraction as well as low fraction malignancies e.g solid tumors
2.
ANTI CANCER DRUG CLASSIFICATION: I. ANTIMETHABOLITES are structural analogs of naturally occurring substances inhibits DNA synthesis. They are S-phase specific (except 5FU) They act in 2 ways: a. By incorporation into a metabolite pathway and formation of a false metabolite b. By inhibition of the catalytic function of an enzyme or enzyme system Antimetabolite a) Folate antagonist : Methotrexate, Trimetrexate b) Purine derivatives : Mercaptopurine ,Thioguanine c) Pyrimidine derivative : Fluorouracil (5 FU), Floxuridine, Cytarabine 1. Methotrexate Mechanism of Action competes with folic acid for the active binding sites on dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) enzyme
7.
CYTARABINE ( CYTOSINE ARABINOSIDE, ARA C) Analog of 2 deoxycytidine S- CYCLE SPECIFIC MECHANISM OF ACTION an pyrimidine antimetabolite ,phoshorylated to the active cytotoxic nucleotide cytosine arbinase triphosphate, an inhibitor of DNA polymerase
Given parenterally ,not orally because it is deaminated to a noncytotocic product in the intestinal mucosa uses is an imporatnt component for the treatment of acute leukemias Toxicities GIT irritation , myelosuppresion , neurotoxicity (cerebellar dysfunction and peripheral neuritis)
II. ALKYLATING AGENTS are cycle phase nonspecific
Pharmacokinetic: converted to polyglutamated metabolite which also inhibits DHFR also converted to a 7-OH derivative by hydroxylation less water soluble may lead to crystalluria in acidic urine, and may cause renal damage. Major route of elimination kidneys.
MECHANISM OF ACTION form covalent bonds with nucleophilic sites on nucleic acid, phosphate, amino acid and proteins through the formation of carbonium ion which attack the N7 POSITION OF GUANINE THIS LEADS TO DNA MISREADING , ABNORMAL BASE PAIRING , DNA INTERSTRAND CROSS LINKING AND DNA STRAND BREAKAGE
9.
TOXICITY : adrenal insufficiency pulmonary fibrosis and skin pigmentation
STREPTOZIN- has high affinity for beta cells of islet of langerhans of pancreas
10. DACARBAZINE used in treatment regimen in hodgkins
disease as part of the abvd regimen(adriamycin, bleomycin, vinblastine,decarbazine) ALKYLATING AGENTS A. NITROGEN MUSTARD : 1. MECHLORETHAMINE 2. CHLORAMBUCIL 3. CYCLOPHOSPHAMIDE 4. MEPHALAN 5. IFOSFAMIDE B. NITROSOUREAS 1. LOMUSTINE 2. CARMUSTINE 3. STRETOZOCIN C. TRIAZINES DACARBAZINE ALKYL SULFONATE : BUSULFAN PLATINUM DERIVATIVE CISPLATIN CARBOPLATIN METHYLHYDRAZINE PROCARBAZINE MECHLORETHAMINE III -Antibiotics Binds to DNA by intercalation. Inhibit DNA or RNA synthesis cycle phase non specific 1. Dactinonomycin (Actinomycin D) focus a complex with DNA involving selective binding to and intercalation between the guanine-cytosine segments Causes also single stranded breaks in DNA
2. Plicamycin(Mithramycin) comes from Streptomyces plicatus. Toxic specific for asteoclasts and lowers serum calcium Bleomycin Sulfate derive from S. Verticillus. It is antitumor, anti viral and anti bacterial. It is a mixture of different copper chelating glycopeptide -
D.
E. F. 1.
(Similar to Dactinomycin). It inhibits the synthesis of DNA dependent RNA synthesis
3.
Binds with DNA to produce single & double stranded breaks DNA is cleaved at guanine-cytosine and guanine-thymine seq.
coverted spontaneously into a reactive cytotoxic product. acts on all phase but most sensitive is G1 and S PHASE CLINICAL USES : use in combination with other anti cancer agents in the MOPP regimen(Mechlorethamine, Oncovin or Vincristine, Procarbazine, Prednisone
2.
CYCLOPHOSPHAMIDE
A nitrogen mustard that is biotransformed by the hepatic cychrome p450 into hydroxylated intermediates : phosphoramide , the active alkylating agent (anti- cancer) and acrolein which can cause hemorrhagic cystitis TOXICITY : hemorrhagic cystitis (prevention of this is by vigorous hydration and the use of mercaptoethanesulfonate (mesna)) -cardiac dysfunction, pulmonary toxicity 4. a. Doxorubicin (adriamycin) b. Daunorubicin Are anthracycline antibiotics
3. 4.
5.
Mech. Of Action: CHLORAMBUCIL SLOWEST ACTING ALKYLATING AGENT IFOSFAMIDE A DERIVATIVE OF CYCLOPHOSPHAMIDE CARMUSTINE (BCNU) AND LOMUSTINE (CCNU) ARE NITROSOUREAS WITH HIGH LIPOPHILICITY THAT FACILITATES CNS ENTRY USE TREATMENT OF BRAIN TUMORS CISPLATIN AND CARBOPLATIN Cisplatin is given intraveneously, cleared unchanged by the kidney 2. 3.
1.
Intercalation in the DNA the drug inserts between adjacent base pairs and binds to sugar- PO4 backbone of DNA, thus blocking DNA synthesis Binds to cell membrane and alters the function of transport process Generation of Oxygen radicals or superoxide
6.
USE component in the treatment regimen for testicular carcinoma, cancers of the bladder, lung and ovary. TOXICITY : git distress ,mild hematoxicity ,but neurotoxic (pheripheral neuritis and acoustic nerve damage )and nephrotoxic . renal damage may be reduce by the use of mannitol and forced hydration . Carboplatin is less nephrotoxic ,less likely to cause tinnitus and hearing loss but has a greater myelosuppresant actions
5.
7.
PROCARBAZINE
Mitomycin - comes from Streptomyces Calspitosus contains quinone, a urethane and an aziridine
Active most in cell cycle in late G and early S phase. Potentiates cardiotoxic effect of Doxorubicin
MECH OF ACTION =a reactive agent that forms hydrogen peroxide ,which generates free radicals that cause dna strand scission orally active, penetrates most tissues ,including csf. eliminated via hepatic metabolism USE= component of mopp regimen for the treatment of hodgkins disease TOXICITY =myelosuppresant ,git irritation ,cns dysfunction, peripheral neuropathy and skin reactions . can cause a disulfiram like reaction with ethanol , it is also leukemogenic
IV Plant derivatives 1. Vinca Alkaloids a. Vinblastine b. Vincristine Source: periwinkle plant (vinca rose) - Both cycle and phase specific Mitotic spindle
Block mitosis in Metaphase Binds to Tubulin inhibit assembly of microtubules thus the failure of mitotic spindle cells in S phase are most sensitive
8.
BUSULFAN AN ALKYL SULFONATE
USE = treatment regimen for myelogenous leukemia
2. -
Epipodophylltoxins Etoposide (VP-16) Teniposide (VM-26) Synthetic derivatives of the extract of the American mandrake plant
Appears to arrest cells in G2 phase Cause dose dependent break on DNA strands Probably act through inhibition of DNA topoisomerase II are spindle poisons but act differently from vinca alkaloids. They prevent microtubule disassembly into tubulin monomers
Rifuximab = a monoconal antibody to a surface protien in HodgKins lymphoma cells. Trastuzumab = is a monoclonal antibody to a surface protien in breast cancers that overexpress the HER2 protien. Can cause cardiac dysfunction, including CHF Therapeutic Usefulness: ALL, chorio CA, BukKitts Lymphoma in Children, breast, neck and head CA ALL (acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia) Acute myelocytic leukemia CA of colon, breast, ovarian, pancreatic, gastric CA Acute myclogenous leukemia. Wilms tumor, chorio CA, soft tissue sarcomas ALL, HodgKins, breast and Lung CA AML Testicular tumors (w) vinblastine and cisplatin Bone tumor HodgKin (MOPP regimen Mechlorethamine, Oncovin, Prednisone, Procarbazine) BurKitts and Breast CA lymphoma malignant glioma ALL, Wilms tumor, Ewings, Soft tissues sarcoma and HodgKins testicular CA, Hodgkin malignant melanoma Hodgkins (combine with Doxorubicin)
1. Methotrexate
3.
Taxanes: Paclitaxel, docetaxel Given IV--Clinical use: used in advanced breast and ovarian cancers
2. 6 Mercaptopurine 3. 6 THioguanine 4. 5 Fu 5. Cytarabine 6. Dactinomycin 7. Doxorubicin
Toxicity: Paclitaxel: causes neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, a high incidence of peripheral neuropathy and possible hypersensitivity reactions during infusion. Docetaxel: neurotoxicity and BMS
V Miscellaneous Agent Mechanism of Action 1. Amsacrine cytotoxic, binds to DNA through intercalation and has base specificity on A-T pairs more effective in cycling cells Hydrolyzes blood asparaginase which is necessary for growth and function of cells, thus tumor cells are deprived of this nutrient required for protein synthesis.
8. Daunorubicin 9. Bleomycin 10. Plicamycin 11. Mechlorethamine
2. 2. Asparaginase (LAsparaginase) -
12. Cyclophosphamide 13.Lomustine/Carmustine 14. Vincristine 15. Vinblastine 16. Dacarbazine)
17. Streptozocin 18. Etoposide
Pancreatic cell carcinoma Oat cell carcinoma of lungs
Treatment Choices for Cancer responsive to Systemic Agents 1. Acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL) For Remission: maintenanceMethotrexare, Thioguanine 2. Acute Myelocytic and myelomonocytic leukemia 3. Chronic Myelocytic leukemia Induction: Combination Chemo Adults: Vincristine, Prednisone, Daunorubicin,Asparagin ase For children: w/o aspaginase Combination Chemo Cytarabine Daunorubicin or idarubicin Hydroxyurea; alpha interferon (Busulfan, Mercaptopurine, thioguanine, cytarabine,plicamycin) 4. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia 5. Hairy cell 6. HodgKins dis (stages III & IV) Chlorambucil+ Prednisone or fludarabine Alpha interferon cladribine Combination Chemo (ABVD) 1. Doxorubicin (Adriamycin) 2. Bleomycin 3. Vinblastin 4. Dacabazine
Vl Hormones mainly Palliative Antagonize or lower concentration of normally occuring hormones in hormone dependent tumors 1. Adrenocorticosteroids useful in acute leukemia in children and malignant lymphoma. 2. Aminogluthethimide (cytadren) inhibits synthesis of adrenocorticosteroids when administered with hydrocortisone can effectively reduce estradiol levels useful in advanced carcinoma of the breast (estrogenreceptor(+) tumors 3. Mitotane(O,P DDD) (Lysodren) Selectively attacks adrenocortical cells use in palliative treatment of inoperable adrenocortical carcinoma 4. Progestins useful in the management of endometrical CA. (Hydroxy Progesterone Megestrol) 5. Estrogens use to treat prostatic CA. (estradiol, diethylstilbesterol) Estramustine a nitrogen mustard linked to estradiol, use as a palliative treatment of advanced prostatic carcinoma. 6. Androgens - use to treat carcinoma of the breast in both premenopausal and past menopausal women. (Testosterone fluoxymesterone) 7. Tamoxifen antiestrogen competes with estrogen for binding with receptor - use in CA of breast, estrogen(+) receptors 8. Gonadotropin reduces circ. Gonadotropins and testosterone. Effective in prostatic carcinoma. VII- Aromatase Inhibitors: Anastrozole and letrozole inhibit aromatase, the enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of androstenedione (an androgenic precursor) to estrone (an estrogenic hormone) Uses: Advanced breast cancer Toxicity: Nausea, diarrhea, hot flashes, bone and back pain, dyspnea and peripheral edema. VIII- Monoclonal Antibodies:
Combination Chemo (MOPP) 1. 2. 3. 4. Mechlorethamine Vincristine Prednisone 4. Procarbazine
7. Non HodgKins lymphoma
Combination Chemotheraphy - Cyclophosphamide - Vincristine - Doxorubicin - Prednisone
8.Multiple Myeloma
Combination Chemotherapy - Melaphalan + Prednisone or 1. Melaphalan
2. Cyclophosphamide 3. Carmustine 4. Vincristine 5. Doxorubicin 6. Prednisone 9. Waldenstrom's Macroglobulinemia Chlorabucil or Combination Chemotherapy 1.Cyclophosphamide 2. Vincristine 3. Prednisone 10. Polycythemia Vera 11. carcinoma of Lung (small cell) Hydroxyurea Combination Chemotherapy Cisplatin and etoposide (palliative Radiation) 12. Non-small cell Lung CA 113. Carcinoma of the head and neck 14. Carcinoma of the Esophagus Advance Cisplatin + Vinorelbine Localized Cisplatin + Vinblastin Combination Chemotherapy 1. Cisplatin and 5 FU Combination Chemotherapy 1. 5 FU 2. Cisplatin 15. Carcinoma of the Stomach and Pancreas Stomach Etoposide: 5FU w/ leucovorin (ELF) Pancreas 5 FU or ELF 16. Carcinoma of the colon Colon - Fuorouracil + levamisole (adjuvant) or w/ leucovorin Rectum 5FU w/ radiation therapy (adjuvant) 17. Carcinoma of the kidney 18.Carcinoma of the bladder Vinblastine Combination Chemotherapy 1. Methotrexate 2.Vinblastine 3. Doxorubicin 4. Cisplatin CMF regimen: Cyclophosphamide plus 19. Breast Carcinomamethotrexate& fluoouracil, or doxorubicin (stages I &II) for methotrexate CAF regimen: tamoxifen if hormone receptor positive 20. Breast carcinoma (stages III & IV) - As above paclitaxel, plus trastuzumab(if HER2 protein) w/ or w/o aromatase inhibitors
15. Vinblastine 16. Progesterone 17. Tamoxifen 18. Estrogen 19. Busulfan 20. Cisplastin 21. Procarbazine 22. L-asparaginase 23. Etoposide 24. Fluoxmesterone
- BMS - fluids retention, hypertension - nausea and vomiting - thromboembolic accidents - skin pigmentation, pulmonary fibrosis, adrenal insuffiency - Nephrotoxicity (renal toxicity) and acoustic nerve dysfunction - BMS, CNS depression - Allergic reactions, fever, pancreatitis, thrombocytopenia BMS, allergic reaction - Cholestatic jaundice
Principles of Combination Therapy 1. Each drug should be active when used alone against the particular cancer. 2. The drugs should have different mechanism of action. 3. Cross resistance between drugs should be minimal. 4. The drugs should have different toxic effects. Combination Chemotherapy 1. HodgKin's disease a. MOPP regimen Mechlorethamine, Oncovin (vincristine), Procarbazine, Prednisone b. ABVD regimen, Adriamycin, (Doxorubicin) Bleomycin, Vinblastine, Decarbazine 2. 3. 4. a. Non-Hodgkins Lymphoma COP regimen Cyclophosphamide, Oncovin, Prednisone Testicular Cancer PVB regime, Plationol, Vinblastine, Bleomycin Breast Cancer CMF regimen Cyclohosphamide, Methotrexate, Fluorouracil with or without Tamoxifen b. CAF in which Adriamycin(Doxorubicin) replaces Methotrexate
Additional Strategies for cancer Chemotherapy
1.
Pulse therapy involves intermittent treatment with very high doses of an anti-cancer drug-are too toxic to be used continuously. Intensive drug treatment is every 3-4 weeks. This type of regimen is used in therapy of: 1. acute leukemia 2. testicular CA 3. Wilms tumor Recruitment and Synchrony the strategy of recruitment involves initial use of CCNS drug to achieve a significant log kill, which results in the recruitment into cell division of previously resting cells in the GO phase. With subsequent administration of CCS drug that is achieve against dividing cells. Syncrony example the use of vinca alkaloids to holds cancer cell in the M phase and subsequent treatment of another CCS drug such as the S-phase specific Cytarabine which results in a greater killing effect on the neoplastic cell population
2.
Dose limiting adverse effects of Chemotherapetic agents 1. Methotrexate - Bone marrow suppression (BMS) - oral and GI ulceration - acute renal failure - hepatotoxicity 2. 6 Mercaptopurine 3. 6 Thioguanine 4. 5 FU 5. Cytarabine 6. Dactinomycin 7. Doxorubicin 8. Bleomycin 9. Plicamycin 10. Mitomycin 11. Mechlorethamine 12. Cyclohosphamide 13. Nitrosoureas 14. Vincristine - BMS, oral and GI ulcers - BMS - BMS, oral and GI ulcers dacryocystitis - BMS, CNS toxicity - BMS, stomatitis, oral ulcers - BMS, cardiotoxicity - Pneumonitis, pulmonary fibrosis - BMS, hemorrhagic cystitis - BMS, trombocytopenia, leukopenia - BMS - BMS, hemorrhagic cystitis - Thrombocytopenia, leukopenia - Peripheral neuropathy
3.
Rescue Therapy use to alleviate toxic effects of anticancer drugs.
a.
b. c.
Leucovorin bypasses the dihydrofolate steps reductase in folic acid synthesis thus reducing toxicity of antifolate agents. Mercaptoethanosulfonate(mesna) - Traps acrolein released from Cyclophosphamide thus reducing hemorrhagic cystitis. Dexrazoxane a free radical trapper that protect against cardiac toxicity due to anthracyclines (doxorubicin)
You might also like
- Oncology DrugsDocument6 pagesOncology DrugslindsayparvessNo ratings yet
- Tracheostomy Sizing Chart: Current As at 23/02/2015Document3 pagesTracheostomy Sizing Chart: Current As at 23/02/2015Febri BayuNo ratings yet
- Nursing StandardsDocument16 pagesNursing StandardsPabhat KumarNo ratings yet
- Primary Chemotherapy: Adjuvant Chemotherapy: Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy: Treatment RegimensDocument7 pagesPrimary Chemotherapy: Adjuvant Chemotherapy: Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy: Treatment RegimensNoelani-Mei AscioNo ratings yet
- Anti Cancer DrugsDocument15 pagesAnti Cancer DrugsdatlaNo ratings yet
- ChemotherapyDocument1 pageChemotherapyGerardLum100% (2)
- 11 Cancer Chemotherapy, Naim Kittana PDFDocument126 pages11 Cancer Chemotherapy, Naim Kittana PDFZaina MasriNo ratings yet
- Oncology Handouts PDFDocument21 pagesOncology Handouts PDFPhilip Simangan100% (1)
- Anti Cancer Drugs...Document62 pagesAnti Cancer Drugs...KwirimeNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology - CANCER FinalDocument18 pagesPharmacology - CANCER FinalCarol NavidadNo ratings yet
- Anti-Cancer Drugs: Done By: Mukul TambeDocument42 pagesAnti-Cancer Drugs: Done By: Mukul TambeSushant Rathod100% (1)
- ChemotherapyDocument44 pagesChemotherapyJohn Mark ParacadNo ratings yet
- Cancer ChemotherapyDocument9 pagesCancer ChemotherapyJennicaNo ratings yet
- Oncology LectureDocument92 pagesOncology Lecturerustie26No ratings yet
- Anticancer ChemotherapyDocument40 pagesAnticancer Chemotherapyanon_3901479100% (1)
- Anticancer Drugs ClassificationDocument19 pagesAnticancer Drugs ClassificationMuhammad Raza100% (1)
- Pharm Chemo Drugs SauldDocument6 pagesPharm Chemo Drugs Sauldneal100% (1)
- General Principles of Combination ChemotherapyDocument40 pagesGeneral Principles of Combination Chemotherapyoncology KMC-KnlNo ratings yet
- Drugs Used in ChemotherapyDocument4 pagesDrugs Used in ChemotherapyArman Leal Bernardo100% (1)
- Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy, in Its Most General Sense, Refers To Treatment of Disease byDocument42 pagesChemotherapy: Chemotherapy, in Its Most General Sense, Refers To Treatment of Disease byMalueth AnguiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To TransplantationDocument3 pagesIntroduction To TransplantationGerardLumNo ratings yet
- Oncology-Study of Cancer Cellular AbberationDocument43 pagesOncology-Study of Cancer Cellular AbberationIrwan M. IskoberNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology ChemotherapyDocument28 pagesPharmacology ChemotherapyDartiguesNo ratings yet
- Basic OncologyDocument42 pagesBasic Oncologybudiagungnugraha100% (1)
- Basic Principles of Cancer ChemotherapyDocument2 pagesBasic Principles of Cancer ChemotherapyGerardLum100% (2)
- Blood DisordersDocument21 pagesBlood Disordersapi-448398971No ratings yet
- Cancer DrugsDocument5 pagesCancer DrugsLinh HoangNo ratings yet
- Chemo MedsDocument17 pagesChemo MedsSophia Smartz100% (1)
- 03-Anti-Cancer Drugs - FST PDFDocument77 pages03-Anti-Cancer Drugs - FST PDFRyan RachmawanNo ratings yet
- Antineoplastic Agents 2011 Dental MARCH-1Document41 pagesAntineoplastic Agents 2011 Dental MARCH-1BinayakSwainNo ratings yet
- B. Pathophysiology: Clinical Aspects of Cancer DiagnosisDocument10 pagesB. Pathophysiology: Clinical Aspects of Cancer DiagnosisAbigael Patricia GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Anti-Coagulants, Anti-Platelets, FibrinolyticsDocument1 pageAnti-Coagulants, Anti-Platelets, FibrinolyticsGerardLum100% (1)
- Anticancer DrugsDocument117 pagesAnticancer DrugsKishore Chandra Korada100% (2)
- Chemotherapy AgentsDocument14 pagesChemotherapy Agents찬열박100% (1)
- Cell Cycle ChemotherapyDocument5 pagesCell Cycle ChemotherapyVictoria Alessandra BrownNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic Chart FINALDocument2 pagesAntibiotic Chart FINALjoed34543No ratings yet
- Carboplatin PaclitaxelDocument6 pagesCarboplatin PaclitaxelNida Auliya RahmahNo ratings yet
- Ami Ashariati - Immunotherapy in CancerDocument142 pagesAmi Ashariati - Immunotherapy in CancersarijuicyNo ratings yet
- Oncology Nursing Part 1 2Document51 pagesOncology Nursing Part 1 2fleur harrisonNo ratings yet
- Anticancer Drugs Anticancer Drugs: Tasneem Smerat Tasneem SmeratDocument118 pagesAnticancer Drugs Anticancer Drugs: Tasneem Smerat Tasneem Smeratanwar jabari100% (1)
- Chemotherapy - Alkylating AgentsDocument33 pagesChemotherapy - Alkylating AgentsNolan100% (1)
- Nursing OncologyDocument131 pagesNursing Oncologyapi-3818438100% (5)
- Anticancer Drugs: DR Niva Kashyap DNB Ent PGTDocument51 pagesAnticancer Drugs: DR Niva Kashyap DNB Ent PGTNivaKashyapNo ratings yet
- Anti Cancer DrugsDocument56 pagesAnti Cancer DrugsTimothy David50% (2)
- Introduction To Oncology NursingDocument35 pagesIntroduction To Oncology NursingDesh Deepak100% (1)
- Onco PharmacologyDocument9 pagesOnco Pharmacologyarn0ld21No ratings yet
- Antiviral AgentsDocument14 pagesAntiviral AgentsKate MendozaNo ratings yet
- Principles of OncologyDocument26 pagesPrinciples of OncologyDr Shahzad Alam ShahNo ratings yet
- Chemotherapy MedicinesDocument2 pagesChemotherapy Medicinesr_mckenrick0% (1)
- Pharmacy Oncology Pharmacology OutlineDocument39 pagesPharmacy Oncology Pharmacology OutlineMatthew Lei100% (1)
- Neoplasia I - RecordingDocument6 pagesNeoplasia I - RecordingIS99057No ratings yet
- Introduction of Clinical OncologyDocument52 pagesIntroduction of Clinical OncologyThis is Pony100% (1)
- Chemo PrinciplesDocument3 pagesChemo PrinciplesSze Hui OoiNo ratings yet
- The Genetic Basis of CancerDocument31 pagesThe Genetic Basis of Cancerapi-418176886No ratings yet
- I. Cellular Adaptations:: Cellular Injury, Cell Adaptation & Cell Death 1. Hyperplasia 3. AtrophyDocument4 pagesI. Cellular Adaptations:: Cellular Injury, Cell Adaptation & Cell Death 1. Hyperplasia 3. AtrophyShuaib SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- OncologyDocument15 pagesOncologyapi-3840195100% (5)
- AntineoplasticsDocument4 pagesAntineoplasticsahmed montaserNo ratings yet
- Cancer: A Proliferative Disease.: Cancer Is Classified On The Basis of The Tissue From Which It DevelopedDocument42 pagesCancer: A Proliferative Disease.: Cancer Is Classified On The Basis of The Tissue From Which It DevelopedMartin RongenNo ratings yet
- Cancer Chemotherapy by MaryamDocument51 pagesCancer Chemotherapy by MaryammaryamNo ratings yet
- Med Chem Exam 2Document80 pagesMed Chem Exam 2Morrigan DearmanNo ratings yet
- Anticancer Drugs: Pharm 3620 Human Pharmacology and Therapeutic PrinciplesDocument34 pagesAnticancer Drugs: Pharm 3620 Human Pharmacology and Therapeutic Principleszj5bnxbymzNo ratings yet
- Aliphatic and Aromatic HydrocarbonsDocument13 pagesAliphatic and Aromatic HydrocarbonsdhaineyNo ratings yet
- Chelating AgentsDocument24 pagesChelating AgentsdhaineyNo ratings yet
- Thorax To RectumDocument35 pagesThorax To RectumdhaineyNo ratings yet
- Abdominal PainDocument12 pagesAbdominal Paindhainey100% (2)
- Anti TB DrugsDocument2 pagesAnti TB DrugsdhaineyNo ratings yet
- TrematodesDocument5 pagesTrematodesdhaineyNo ratings yet
- The Intestinal NematodesDocument9 pagesThe Intestinal NematodesdhaineyNo ratings yet
- Physical Examination of The SkinDocument3 pagesPhysical Examination of The Skindhainey100% (1)
- Parasitology PicturesDocument4 pagesParasitology Picturesdhainey100% (1)
- BT ReactionsDocument14 pagesBT ReactionsdhaineyNo ratings yet
- Anti Helminthic DrugsDocument3 pagesAnti Helminthic Drugsdhainey100% (2)
- Intestinal FlagellatesDocument5 pagesIntestinal Flagellatesdhainey100% (3)
- Parasitology Pictures Part 2Document22 pagesParasitology Pictures Part 2dhaineyNo ratings yet
- Female Sex HormonesDocument29 pagesFemale Sex Hormonesdhainey100% (5)
- Chest and Lungs ExaminationDocument75 pagesChest and Lungs Examinationdhainey100% (10)
- ParathyroidDocument2 pagesParathyroiddhaineyNo ratings yet
- Coagulants and Anti CoagulantsDocument22 pagesCoagulants and Anti Coagulantsdhainey100% (2)
- Cervical PolypDocument82 pagesCervical Polypdhainey100% (1)
- Toxoplasma Pneumocystis Microsporidia BabesiaDocument40 pagesToxoplasma Pneumocystis Microsporidia BabesiadhaineyNo ratings yet
- AlcoholsDocument23 pagesAlcoholsdhaineyNo ratings yet
- Happy Birthday Hergin: by Dhainey GirlDocument38 pagesHappy Birthday Hergin: by Dhainey GirldhaineyNo ratings yet
- ImmunizationsDocument21 pagesImmunizationsdhaineyNo ratings yet
- Red Blood Cell Disorders - PsaDocument96 pagesRed Blood Cell Disorders - Psadhainey100% (2)
- BurnsDocument5 pagesBurnsdhainey67% (3)
- Abortion, Myoma, H Mole, EctopicDocument93 pagesAbortion, Myoma, H Mole, Ectopicdhainey100% (4)
- BurnsDocument65 pagesBurnsdhainey100% (1)
- Neuro Tract Lesions Ps230114Document16 pagesNeuro Tract Lesions Ps230114সোমনাথ মহাপাত্রNo ratings yet
- Dry Needling Article PMRDocument8 pagesDry Needling Article PMRRo KohnNo ratings yet
- JSY School-Age Practical Approach Handout - 2021 - 2-Hour PDFDocument8 pagesJSY School-Age Practical Approach Handout - 2021 - 2-Hour PDFMaha SelawiNo ratings yet
- Pyoderma GangrenosumDocument35 pagesPyoderma GangrenosumkylieverNo ratings yet
- Haad Topics To READDocument39 pagesHaad Topics To READBem Templonuevo100% (1)
- Panduan Praktik Klinis Ugd PopoolivDocument49 pagesPanduan Praktik Klinis Ugd PopoolivrusliNo ratings yet
- HypophosphatemiaDocument11 pagesHypophosphatemiaFlorygene Kris DisagonNo ratings yet
- Acute and Chronic Chorea in Childhood: Donald L. Gilbert, MD, MSDocument6 pagesAcute and Chronic Chorea in Childhood: Donald L. Gilbert, MD, MSKalindraParahitaNo ratings yet
- Vitamin K (Phytomenadione) 2016: Indication Action Drug Type Trade Name Presentation Dosage / IntervalDocument3 pagesVitamin K (Phytomenadione) 2016: Indication Action Drug Type Trade Name Presentation Dosage / IntervalDeni Yuda Adi SaputraNo ratings yet
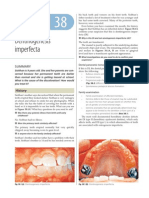
- Dentinogenesis ImperfectaDocument4 pagesDentinogenesis Imperfectamirfanulhaq100% (1)
- ParacetamolDocument3 pagesParacetamolMasta MastaNo ratings yet
- Chronic Illness Acute Illness: CharacteristicsDocument4 pagesChronic Illness Acute Illness: CharacteristicsFerdinand Sherwin MorataNo ratings yet
- Lasuna RasayanaDocument35 pagesLasuna RasayanaAnonymous x3RsIfNo ratings yet
- Clinical Social Work Manager in New York City Resume Janet SierzegaDocument3 pagesClinical Social Work Manager in New York City Resume Janet SierzegaJanetSierzegaNo ratings yet
- 8 PDFDocument4 pages8 PDFGilang IndraNo ratings yet
- Abdominal ParacentesisDocument5 pagesAbdominal ParacentesisSivaprasad S100% (1)
- The Miracle Question Steve de ShazerDocument2 pagesThe Miracle Question Steve de ShazerBeatriz Mafra Soares0% (1)
- Relining in RPD!Document33 pagesRelining in RPD!sarah50% (2)
- Pediatric Advanced Life Support (PALS) - 19-8-19Document36 pagesPediatric Advanced Life Support (PALS) - 19-8-19RimaWulandari50% (2)
- Common Principles of Couple TDocument3 pagesCommon Principles of Couple TMarius AndreiNo ratings yet
- Effective Trance Techniques - SurveyDocument26 pagesEffective Trance Techniques - Surveyرونقالحياة100% (2)
- Cleft Lip & PalateDocument43 pagesCleft Lip & PalateKanjiMasroor100% (2)
- Bronchial Asthma and ManagementDocument43 pagesBronchial Asthma and ManagementMarius-Sorin CionteaNo ratings yet
- Symbicort 80/4.5: Inhalation AerosolDocument14 pagesSymbicort 80/4.5: Inhalation AerosolAndrei MihaiNo ratings yet
- Ansin Leopold FixDocument4 pagesAnsin Leopold FixLvnalosaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Trials For Tuberculosis in India - Soumya SwaminathanDocument53 pagesClinical Trials For Tuberculosis in India - Soumya SwaminathanShailly GuptaNo ratings yet
- Ms. Ann Female 48 Years Old Diabetes Mellitus Foot/diabetes Mellitus Joseph MDocument10 pagesMs. Ann Female 48 Years Old Diabetes Mellitus Foot/diabetes Mellitus Joseph MFielMendozaNo ratings yet
- Minor Periodontal Surgery in OrthoDocument6 pagesMinor Periodontal Surgery in OrthoJuanCarlosViverosCórdovaNo ratings yet