Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Use Case Analysis: Object Oriented Analysis and Design 07/13/01
Use Case Analysis: Object Oriented Analysis and Design 07/13/01
Uploaded by
modis777Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Use Case Analysis: Object Oriented Analysis and Design 07/13/01
Use Case Analysis: Object Oriented Analysis and Design 07/13/01
Uploaded by
modis777Copyright:
Available Formats
Object Oriented Analysis and Design
07/13/01
Use Case Analysis
When looking at the system as a whole, Use Case Analysis identifies all the major uses of the system. It is a functional description of the entire system.
Use Cases are the main tasks performed by the users of the system. Use Cases describe the behavioral aspects of the system. Use Cases are used to identify how the system will be used. Use Cases are a convenient way to document the functions that the system must support. Use Cases are used to identify the components (classes) of the system.
Use Case examples
Clerk prints a sales receipt for a video rental. Person spell checks a typed document. Receptionist schedules an appointment. Advisor registers student for classes.
Object Oriented Analysis and Design
07/13/01
Two important concepts in these analyses are:
A person is involved. (In UML, the person involved is called an actor) The actor uses the system.
Formal Definitions
Actor A role that a user can play. Examples: instructor, advisor, student.
Actors do not have to be human. An actor such as a sensor may cause a system reaction. An actor is always outside of the system boundary, an external entity. Use Cases Actions on a system initiated by an actor. These are the main tasks performed by each actor. Use cases represent complete functionality of a task. Example: Register for course.
User
Someone who uses the system. The same user can play multiple roles. Example Prof. John Doe plays the role of an instructor and the role of an advisor. A user is an instance of an actor.
Views
Two or more actors interacting with a use case. Example Register for Course involves both the Student registering for the course and the Bursar's office sending out a bill for it. Each actor views this task from a different perspective.
Object Oriented Analysis and Design
07/13/01
UML symbols
A use case is represented by an oval with the name of the use case inside.
An actor is represented as a stick figure in UML
Register for course
Registration Clerk
Connecting line shows which actors participate in which use cases
A use case is only a high-level description of an activity that will be performed on a system. It may require a sequence of individual steps to carry out the use case. There could be different sequences of individual steps for the same use case. These are called scenarios. For example, use case register for classes may have two scenarios, one for registering through an advisor and one for online registration.
Object Oriented Analysis and Design
07/13/01
UML use case relationship symbols
Generalization
Include <<include>>
Extend <<extend>>
Relationships
Use cases may be related to other use cases. A use case that is a variation on normal behavior of another use case describes a generalization relationship. These generalization use case relationships can be used to describe actions when an alternative behavior must be carried out for some reason.
Example: A use case Prerequisites Not Met describes a use case that is an alternative action for use case Register for Course. A use case may include another use case. A use case that is included is generally a common behavior that many use cases may need. One use case will use the services of another use case.
Example: Review Transcript Data use case is used by the Register for Course use case to be sure the student has met the course's prerequisites. Review Transcript Data use case is also used by Graduate Student use case to be sure that all program requirements have been met for graduation.
A use case may extend a use case by adding new actions to it.
Example: Use case Register for Distance Course may extend use case Register for Course. Additional actions must be performed when a student registers for a distance course.
Object Oriented Analysis and Design
07/13/01
Documentation
Describe each use case, actor and relationship. Describe how the use case interacts with the actor as opposed to how it will perform its task. Example: Register for Course can be described as Student completes a registration by entering the course number, section, term and year. The student's advisor indicates approval. A course registration printout of the classes this student is registered for prints. A bill for the course prints in the Bursar's office.
Object Oriented Analysis and Design
07/13/01
Use Case Diagram
A diagram used to capture the functional requirements of a system by identifying actors and use cases.
Development of a Use Case Diagram
1. Identify all of the actors who will use the system. 2. Interview these actors to identify the functions that they need to perform. (use cases) 3. Identify scenarios (sequence of steps to accomplish a use case). 4. Identify common steps within the different scenarios. Separate them into different use cases so that they can easily be included in other scenarios. 5. Identify relationships between use cases.
Object Oriented Analysis and Design
07/13/01
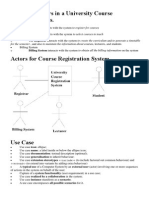
Use Case Diagram Example for College Registration System
A student may register for classes during a specified registration period. To register, a student must see their advisor. The advisor must approve each course that the student has selected. The advisor will use the registration system to determine if the student has met the course prerequisites, is in good academic standings and is eligible to register. If the advisor approves the courses, the advisor enters the student's college id into the course registration system. The course registration number for each course is entered. The course description, course number and section for those courses will automatically display. The system will check for schedule conflicts before saving the registrations. A bill for the courses will print in the Bursar's office. The student should proceed to pick it up. Faculty can use the registration system to check enrollments in their classes, get a class list, check a student's transcript, look up a student's phone number and other such student information. The registrar can use the registration system to enter new classes for an upcoming semester, cancel a class, and check conflicts in classroom/faculty assignments. Admissions use the registration system to add new students. Enrollment services use the registration system to report on retention, update student information, and check fulfillment of graduation requirements for those students planning to graduate.
Object Oriented Analysis and Design
07/13/01
College Registration System Use Case Diagram
Check enrollments Make classroom assignments Add a course
Registrar
Check Prerequisites Met Register Student for course
Faculty
Cancel a course <<Includes>> Look up Student Information Retention Report Advisor <<Includes>> Check Graduation requirements Update Student Information
System Boundaries
Add a student Admissions
Enrollment Services
Object Oriented Analysis and Design
07/13/01
Process high priority use cases first .
High priority use cases: Use cases that are the primary element of the business functionality. Use cases that contain high risk factors (time critical, technology intensive, new technology) Use cases that promise high level of progress for least amount of effort. Use cases that promise lower operating costs or increased revenue.
Why use Use Case modeling diagrams:
They offer a disciplined way to develop a system and deal with its complexity. They are great test cases for the system. They provide quantifiable progress. They provide a strong base for formulation of other models.
Use Case Diagram to Class Diagram
Develop a class diagram from the nouns that are used in the use cases. Develop the class diagram from the highest priority use cases first.
Object Oriented Analysis and Design
07/13/01
Exercises
1. Contrast the following terms: a. b. actor; use case extends relationship; includes relationship
2.
Capture the functionality for a system that accepts a tuition payment from students as a use case.
3.
Extend the use case diagram in exercise #2 to capture the situation where employees of the college are not billed for tuition. Their spouses do not get a full tuition waiver, but pay for only 25 percent of the total tuition. Draw a use-case diagram for a college that would like to keep track of each graduate. In order to maintain strong ties to its alumni, the college holds various events. The college needs to keep track of which graduates have attended which events. The college keeps in contact with graduates by mail, email, telephone and fax to announce each event and keep graduate information up to date. The college would like to be able to produce a report showing the latest information about a graduate and the events the graduate attended. An auto rental company wants to develop an automated system that would handle car reservations, customer billing, and car auctions. Usually a customer reserves a car, picks it up, and then returns it after a certain period of time. At the time of pick up, the customer has the option to buy or waive collision insurance on the car. When the ca is returned, the customer receives a bill and pays the specified amount. In addition to renting out cars, every six months or so, the auto rental company auctions the cars that have accumulated over 20,000 miles. Draw a usecase diagram for capturing the requirements of the system to be developed. Include an abstract use case for capturing the common behavior among any two use cases. Extend the diagram to capture corporate billing, where corporate customers are not billed directly; rather the corporations they work for are billed and payments are make sometime later.
4.
5.
References
Fowler, M. 1997. UML Distilled: Applying the standard Object Modeling Language. Reading, MA: Addison-Wesley. Hoffer, George, Valacich 1998. Modern Systems Analysis & Design Addison-Wesley
You might also like
- Requirements Analysis and System Design Maciaszek 3rd EditionDocument47 pagesRequirements Analysis and System Design Maciaszek 3rd EditionLeonard RumisovNo ratings yet
- Lect 07 Use Case DiagramDocument14 pagesLect 07 Use Case DiagramMuhammad Hamid100% (1)
- Chapter 1Document302 pagesChapter 1preeti198615No ratings yet
- Introduction To UML: Software Engineering BIT-8Document29 pagesIntroduction To UML: Software Engineering BIT-8gopalgupta3No ratings yet
- Slides3 UseCaseModelingDocument23 pagesSlides3 UseCaseModelingDũng Nguyễn ThànhNo ratings yet
- UsecasemodelDocument20 pagesUsecasemodelAshish KumarNo ratings yet
- SE Lecture 06 - Use Case Modeling 27042021 121950pmDocument45 pagesSE Lecture 06 - Use Case Modeling 27042021 121950pmMohammad TaimurNo ratings yet
- S03 - Requirement Modeling (Use Case Diagram)Document34 pagesS03 - Requirement Modeling (Use Case Diagram)mashNo ratings yet
- Lec 8 INT ModelDocument26 pagesLec 8 INT ModelStatus LifeNo ratings yet
- Object Oriented Analysis: Ey Ne Ed ToDocument36 pagesObject Oriented Analysis: Ey Ne Ed ToChala GetaNo ratings yet
- Use Case Diagrams-IDocument39 pagesUse Case Diagrams-IRahul LokeshNo ratings yet
- CasoRegistroCurso UMLDocument12 pagesCasoRegistroCurso UMLEel DdeNo ratings yet
- Slides7 RequirementsDocument29 pagesSlides7 RequirementsLong Nguyễn HoàngNo ratings yet
- Use Case Diagram-1Document42 pagesUse Case Diagram-1shubham tiwariNo ratings yet
- Object-Oriented Analysis and Design: Lecture 3: Requirements OverviewDocument32 pagesObject-Oriented Analysis and Design: Lecture 3: Requirements Overviewho0ng000c0minhNo ratings yet
- OO Concept Chapt3 Part2 (deeperViewOfUML)Document62 pagesOO Concept Chapt3 Part2 (deeperViewOfUML)scodrashNo ratings yet
- Advance System Analysis: Agile Model-Driven Development (AMDD), Usage ModelingDocument23 pagesAdvance System Analysis: Agile Model-Driven Development (AMDD), Usage Modelingapi-19822376No ratings yet
- CS5002NI WK16 L UseCaseDiagram Descriptions 153809Document35 pagesCS5002NI WK16 L UseCaseDiagram Descriptions 153809Ishan ThakuriNo ratings yet
- OOSE - Week 4 - Use Case DiagramsDocument43 pagesOOSE - Week 4 - Use Case DiagramsInnoxentDollNo ratings yet
- Example: Actors in A University Course Registration SysDocument10 pagesExample: Actors in A University Course Registration Sysgoingforward77No ratings yet
- Producing Use Cases and Use Case PointsDocument24 pagesProducing Use Cases and Use Case Pointserojas100% (2)
- Basic Use CasesDocument20 pagesBasic Use CasesbelisaNo ratings yet
- Theme An Approach For Aspect-Oriented Analysis and DesignDocument10 pagesTheme An Approach For Aspect-Oriented Analysis and DesignYøh KenNo ratings yet
- LectureNotes03 SlidesDocument22 pagesLectureNotes03 SlidesmaryamNo ratings yet
- Basic Use CasesDocument16 pagesBasic Use CasesMalik Umer FarooqNo ratings yet
- Lab 3 SCDDocument13 pagesLab 3 SCDMuqadas HassanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To UML: Use Case DiagramDocument33 pagesIntroduction To UML: Use Case DiagramAashis PanjiyarNo ratings yet
- CS 470 - Week 9 - Session 2Document16 pagesCS 470 - Week 9 - Session 2Fahama Bin EkramNo ratings yet
- Slides4 UseCaseModelingDocument12 pagesSlides4 UseCaseModelingAI WarlockNo ratings yet
- Slides4 UseCaseModelingDocument12 pagesSlides4 UseCaseModeling21020781No ratings yet
- Slides4 UseCaseModelingDocument12 pagesSlides4 UseCaseModelingNguyen THNo ratings yet
- Mastering Object-Oriented Analysis and Design With UMLDocument32 pagesMastering Object-Oriented Analysis and Design With UMLjame morganNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 UmlDocument59 pagesUnit 2 Umlgayathri.engineeringNo ratings yet
- Lab 03-Use Cases Diagram: Object-Oriented Analysis & DesignDocument9 pagesLab 03-Use Cases Diagram: Object-Oriented Analysis & DesignFahim khanNo ratings yet
- 2b Writing Good Use CasesDocument62 pages2b Writing Good Use Casescuongvh3No ratings yet
- Software EngineeringDocument22 pagesSoftware EngineeringSanket KharatNo ratings yet
- Ooase UNIT 3Document92 pagesOoase UNIT 3G.AkshayaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document35 pagesChapter 4Puvanan21No ratings yet
- An Introduction To Use Case ModelingDocument44 pagesAn Introduction To Use Case ModelingHira AghaNo ratings yet
- IBM Software GroupDocument43 pagesIBM Software GroupJuni GobiNo ratings yet
- Scenarios and Use CasesDocument68 pagesScenarios and Use CasesJohnLuceNo ratings yet
- 13-Case Tools - Class Diagram, Usecase Diagram, Sequence Diagram, Collaboration Diagram-24-01-2024Document48 pages13-Case Tools - Class Diagram, Usecase Diagram, Sequence Diagram, Collaboration Diagram-24-01-2024aryanrathore040No ratings yet
- Unit 1 Uml Diagrams: Vel Tech High Tech Dr. Rangarajan Dr. Sakunthala Engineering CollegeDocument79 pagesUnit 1 Uml Diagrams: Vel Tech High Tech Dr. Rangarajan Dr. Sakunthala Engineering CollegevanithaNo ratings yet
- LAB1Document4 pagesLAB1amjaaad996No ratings yet
- CS8592-OOAD Question Bank With AnsDocument14 pagesCS8592-OOAD Question Bank With Anssaran SanjayNo ratings yet
- Ch-2 UML EdittedDocument73 pagesCh-2 UML EdittedMintesnot AbebeNo ratings yet
- Use Case DiagramsDocument42 pagesUse Case Diagramssrikanthkg100% (3)
- Requirements Modeling (DFD, ERD, Use Case Diagram)Document53 pagesRequirements Modeling (DFD, ERD, Use Case Diagram)bitf20m550-Senir JustinNo ratings yet
- OOSAD Chapter 5Document19 pagesOOSAD Chapter 5HD HDNo ratings yet
- Use Case DiagramsDocument22 pagesUse Case Diagramsapi-3834497100% (8)
- Use Case Diagram in Detail: CT1414 By: Fatimah Alakeel Reviwed By: Asma AlzaidDocument45 pagesUse Case Diagram in Detail: CT1414 By: Fatimah Alakeel Reviwed By: Asma AlzaidZarrar KhanNo ratings yet
- USE Case DesignDocument34 pagesUSE Case DesignAnteNo ratings yet
- Basic Behavioral Modeling: Use Cases 1Document33 pagesBasic Behavioral Modeling: Use Cases 1praba karanNo ratings yet
- CIS380 Free BookDocument56 pagesCIS380 Free Bookjskinner3No ratings yet
- Business Process and Functional ModelingDocument26 pagesBusiness Process and Functional ModelingLim Soong XIanNo ratings yet
- Use Case DiagramDocument26 pagesUse Case DiagramHamid AliNo ratings yet
- IT Technical best practices: How to Reduce Agile cycle time with reusable code?From EverandIT Technical best practices: How to Reduce Agile cycle time with reusable code?No ratings yet