Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Calculo Volume Gás Comprimido Recipiente
Calculo Volume Gás Comprimido Recipiente
Uploaded by
FernandoVizzottoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Calculo Volume Gás Comprimido Recipiente
Calculo Volume Gás Comprimido Recipiente
Uploaded by
FernandoVizzottoCopyright:
Available Formats
Calculate the storage volume of a compressed gas
The storage volume for a compressed gas can be calculated using Boyle's Law: pa Va = pc Vc (1) where pa = atmospheric pressure (14.7 psi, 101.325 kPa) Va = volume of the gas at atmospheric pressure (cubic feet, cubic meter) pc = compressed pressure (psi, kPa) Vc = volume of the gas at compressed pressure (cubic feet, cubic meter) Volume of free gas in a Storage Volume The amount of free gas at atmospheric pressure in a given volume as a cylinder storage can be calculated my modifying (1) as: Va = pc Vc / pa (1) Gas can be stored in high-pressure cylinders ranging to 6000 psig (410 bar), normal-pressure cylinders ranging between 2000 and 2500 psig (140 and 175 bar) and low-pressure cylinders ranging up to 480 psig (34 bar). Example - Volume of Air in a Cylinder Storage
The standard atmospheric air in a 250 cubic feet cylinder at 2000 psig (2014.7 psia) can be calculated as: Va = 2,014.7 (psia) 250 (cubic feet) / 14.7 (psig) = 34,264 (cubic feet)
You might also like
- Pe04025 QaDocument15 pagesPe04025 QaSona Sith20% (5)
- Chapter 2 PDFDocument39 pagesChapter 2 PDFjeedNo ratings yet
- Piping - Design - Chemical - Engineering - Robert Kern - Articles 1974 67pDocument67 pagesPiping - Design - Chemical - Engineering - Robert Kern - Articles 1974 67pJhon Coello100% (1)
- Assignment 5Document2 pagesAssignment 5avavwatocputct0% (1)
- Volume of Gas in CylinderDocument1 pageVolume of Gas in Cylinderyouni_2005No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 FluidsDocument21 pagesChapter 2 FluidsRafaella ManaloNo ratings yet
- Metabolic Rate and Alveolar VentilationDocument9 pagesMetabolic Rate and Alveolar VentilationSimran SukhijaNo ratings yet
- Essential Respiratory Calculation: Lung Volumes, Dead Space, and Alveolar VentilationDocument6 pagesEssential Respiratory Calculation: Lung Volumes, Dead Space, and Alveolar VentilationHéctor GarcíaNo ratings yet
- AlphaDocument7 pagesAlphaJojenNo ratings yet
- 5 - 2 Help For Hydrodistillation Lab ExperimentDocument1 page5 - 2 Help For Hydrodistillation Lab ExperimentAlessandroNo ratings yet
- Ventilation and PerfusionDocument2 pagesVentilation and PerfusionJayricDepalobosNo ratings yet
- Assigement 1 Pete OlmecaDocument2 pagesAssigement 1 Pete OlmecaleeNo ratings yet
- Blood GasDocument31 pagesBlood GasHusna Nur FitrianaNo ratings yet
- AbgDocument66 pagesAbgindyaphdNo ratings yet
- Homework. - # 7: Ideal GasDocument14 pagesHomework. - # 7: Ideal GasNes ThanutNo ratings yet
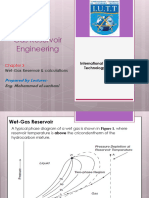
- Chapter 3 Wet-Gas ReservoirDocument22 pagesChapter 3 Wet-Gas ReservoirMohammed BahramNo ratings yet
- Flow Coefficient (CV) and Calculation of Flow Through ValvesDocument7 pagesFlow Coefficient (CV) and Calculation of Flow Through ValvesMikeCroNo ratings yet
- Accounting For Dissolved Gases in Pump DesignDocument7 pagesAccounting For Dissolved Gases in Pump DesignnirbhaiaNo ratings yet
- Leyes de Los GasesDocument31 pagesLeyes de Los GasesRodolfo YanaNo ratings yet
- Gas Laws Worksheet #2 Boyles Charles and CombinedDocument3 pagesGas Laws Worksheet #2 Boyles Charles and CombinedJeromeNo ratings yet
- Cap 2Document4 pagesCap 2Marcia Gaby CruzNo ratings yet
- Gas Exchange, Transport of O2 and Co2 in The BloodDocument81 pagesGas Exchange, Transport of O2 and Co2 in The Bloodspitzmark2030No ratings yet
- FormulasDocument2 pagesFormulasJen NeeNo ratings yet
- Arterial Blood Gas InterpretationDocument65 pagesArterial Blood Gas InterpretationDaniel AryanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 StudentDocument25 pagesChapter 1 StudentAbdalhady JoharjiNo ratings yet
- MI-106 Tut ThermoDocument37 pagesMI-106 Tut ThermoDhananjayLekshmiNarayan100% (7)
- Sheet 1Document2 pagesSheet 1Ahmed Rabie Abd ElazeemNo ratings yet
- AP Chemistry Chapter 10Document87 pagesAP Chemistry Chapter 10Debalina DassNo ratings yet
- PDF Document MathDocument1 pagePDF Document MathGonzalo Isidro NavarroNo ratings yet
- Thermo Sheet 1Document2 pagesThermo Sheet 1Kerro MankoNo ratings yet
- Gas ConversionDocument3 pagesGas ConversionKarim MuhammedNo ratings yet
- Pneumatica ROSSDocument16 pagesPneumatica ROSSHorea CordunianuNo ratings yet
- Biology For NursesDocument3 pagesBiology For NursesМозг ВселеннойNo ratings yet
- Determination of Certified Relieving Capacities: 1.0 GeneralDocument0 pagesDetermination of Certified Relieving Capacities: 1.0 GeneralSIVANo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Classification, Types and Dry-Gas ReservoirDocument40 pagesChapter 2 Classification, Types and Dry-Gas ReservoirMohammed BahramNo ratings yet
- 3 Properties of Refrigerants On P-H DiagramDocument7 pages3 Properties of Refrigerants On P-H DiagramJustin MercadoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Wet-Gas ReservoirDocument22 pagesChapter 3 Wet-Gas ReservoirMohammed Bahram100% (1)
- Chapter 10 Powerpoint - Student VersionDocument95 pagesChapter 10 Powerpoint - Student VersionAnj LTNo ratings yet
- Gas Law HomeworkDocument6 pagesGas Law Homeworkneo cultureNo ratings yet
- Ideal Gas Compilation Problems 2018 FinalDocument1 pageIdeal Gas Compilation Problems 2018 Finalkent bediaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Questions 1111Document6 pagesTutorial Questions 1111Fahmy Muhd100% (1)
- Chapter 3 PDFDocument21 pagesChapter 3 PDFjeedNo ratings yet
- Nitorus OxideDocument7 pagesNitorus Oxidemirco marastoniNo ratings yet
- 201 Volumetric CalculationsDocument5 pages201 Volumetric Calculationsrai rodriguezNo ratings yet
- تمرینات بخش سیالات تراکم پذیرDocument2 pagesتمرینات بخش سیالات تراکم پذیرBaba DookNo ratings yet
- Gas Laws Worksheet 2 Boyles Charles and Combined - CompressDocument2 pagesGas Laws Worksheet 2 Boyles Charles and Combined - CompressZar ArhNo ratings yet
- 352 ML of Chlorine Under A Pressure of 680Document5 pages352 ML of Chlorine Under A Pressure of 680EllaAdayaMendiolaNo ratings yet
- 3 Gases IdealesDocument1 page3 Gases IdealesToNi IbañezNo ratings yet
- VCTDS-01061 Sizing of Tank Blanketing System-EnDocument3 pagesVCTDS-01061 Sizing of Tank Blanketing System-EnvipinNo ratings yet
- Modelling Vacuum Cooling Process of Cooked Meat-Part 1: Analysis of Vacuum Cooling SystemDocument8 pagesModelling Vacuum Cooling Process of Cooked Meat-Part 1: Analysis of Vacuum Cooling SystemMohammad ArhamNo ratings yet
- حساب حجم الغازDocument3 pagesحساب حجم الغازهندسة العقولNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 - Gas LawsDocument55 pagesChapter 11 - Gas Lawsjim tannerNo ratings yet
- Boyle's LawDocument5 pagesBoyle's LawKyle Ambis SyNo ratings yet
- Arterial Blood Gas InterpretationDocument66 pagesArterial Blood Gas InterpretationlenafitriyaniNo ratings yet
- Density of Air - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument8 pagesDensity of Air - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaLeonardo CostaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Monitoring in Mechanical Ventilation: Techniques and ApplicationsFrom EverandRespiratory Monitoring in Mechanical Ventilation: Techniques and ApplicationsJian-Xin ZhouNo ratings yet