Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hiv Life Cycle: Fact Sheet Number 106
Uploaded by
Nap Villarosa0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views1 pageThe document describes the 10 step life cycle of the HIV virus: 1) The virus binds to CD4 and CCR5/CXCR4 coreceptors on the cell surface and fuses with the cell. 2) The virus releases its contents into the cell. 3) The reverse transcriptase enzyme creates HIV DNA from the viral RNA. 4) The viral DNA integrates into the host cell DNA. 5) The integrated HIV DNA directs the cell to produce new HIV proteins and RNA. 6) The proteins and RNA assemble new immature viruses. 7) The immature viruses bud from the cell, acquiring a lipid envelope. 8) A protease enzyme matures the viruses by cleaving viral proteins. 9) The
Original Description:
Original Title
8_eng_106
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document describes the 10 step life cycle of the HIV virus: 1) The virus binds to CD4 and CCR5/CXCR4 coreceptors on the cell surface and fuses with the cell. 2) The virus releases its contents into the cell. 3) The reverse transcriptase enzyme creates HIV DNA from the viral RNA. 4) The viral DNA integrates into the host cell DNA. 5) The integrated HIV DNA directs the cell to produce new HIV proteins and RNA. 6) The proteins and RNA assemble new immature viruses. 7) The immature viruses bud from the cell, acquiring a lipid envelope. 8) A protease enzyme matures the viruses by cleaving viral proteins. 9) The
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views1 pageHiv Life Cycle: Fact Sheet Number 106
Uploaded by
Nap VillarosaThe document describes the 10 step life cycle of the HIV virus: 1) The virus binds to CD4 and CCR5/CXCR4 coreceptors on the cell surface and fuses with the cell. 2) The virus releases its contents into the cell. 3) The reverse transcriptase enzyme creates HIV DNA from the viral RNA. 4) The viral DNA integrates into the host cell DNA. 5) The integrated HIV DNA directs the cell to produce new HIV proteins and RNA. 6) The proteins and RNA assemble new immature viruses. 7) The immature viruses bud from the cell, acquiring a lipid envelope. 8) A protease enzyme matures the viruses by cleaving viral proteins. 9) The
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
AIDS InfoNet
www.aidsinfonet.org
Fact Sheet Number 106
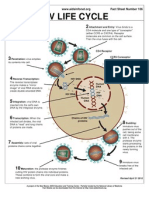
HIV LIFE CYCLE
1 Free Virus 2 Attachment and Entry: Virus binds to a
CD4 molecule and one type of "coreceptor" (either CCR5 or CXCR4). Receptor molecules are common on the cell surface. Then the virus fuses with the cell.
CD4 Receptor
3 Penetration: virus empties
its contents into cell.
CCR5 Coreceptor CXCR4 Coreceptor
4 Reverse Transcription:
The reverse transcriptase enzyme makes a mirror image of viral RNA strands to create double-stranded DNA.
HIV DNA Human DNA HIV RNA HIV DNA
5 Integration: viral DNA is
inserted into the cell's own DNA by the integrase enzyme.
Human DNA
6 Transcription: When the
infected cell divides, the viral DNA is "read" and long chains of proteins are made.
Chains of HIV proteins
8 Budding:
immature virus pushes out of the cell, taking some cell membrane with it. The protease enzyme starts processing the proteins in the newly forming virus.
7 Assembly: sets of viral
proteins chains come together.
10 Maturation: the protease enzyme finishes
cutting HIV protein chains into individual proteins. These combine to form the viral core and make a new working virus.
Immature virus breaks free of the infected cell.
Revised April 21 2010
A project of the New Mexico AIDS Education and Training Center. Partially funded by the National Library of Medicine Fact Sheets can be downloaded from the Internet at http://www.aidsinfonet.org
You might also like
- VirusesDocument1 pageVirusesChris_Barber09100% (2)
- VIRUSESDocument29 pagesVIRUSEStria nurdianaNo ratings yet
- Chapter06 LectureDocument40 pagesChapter06 Lecture7104No ratings yet
- VirusesDocument40 pagesVirusesRimayaniNo ratings yet
- 5 Basic VirologyDocument71 pages5 Basic VirologyErdemNo ratings yet
- HIV PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesHIV PathophysiologyChristian Karl B. Llanes91% (11)
- HIV - PathogenesisDocument14 pagesHIV - Pathogenesisjunaidiabdhalim100% (1)
- The HIV Life CycleDocument1 pageThe HIV Life Cycleapi-3732057100% (1)
- CH 5 - Virology 1Document60 pagesCH 5 - Virology 1Tariku TadesaNo ratings yet
- Struktur HIVDocument5 pagesStruktur HIVadwinas253No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - VirusDocument26 pagesChapter 2 - Virusshahera rosdiNo ratings yet
- Hiv Life Cycle: Fact Sheet Number 106Document1 pageHiv Life Cycle: Fact Sheet Number 106Amod KumarNo ratings yet
- Hiv Life Cycle: Fact Sheet Number 106Document1 pageHiv Life Cycle: Fact Sheet Number 106John HendyNo ratings yet
- Obat Anti Retrovirus Pada Hiv: Dr. Ni Luh Putu Eka. Skp. Mkes Jurusan Keperawatan Poltekkes MalangDocument21 pagesObat Anti Retrovirus Pada Hiv: Dr. Ni Luh Putu Eka. Skp. Mkes Jurusan Keperawatan Poltekkes MalangYohanes DavidNo ratings yet
- ImunodefisiensiDocument30 pagesImunodefisiensiANNIS RAHMA KUSUMA WARDANINo ratings yet
- Human Immunodeficiency VirusDocument5 pagesHuman Immunodeficiency VirusFirdaMalikaNo ratings yet
- HML 214 Lecture 6 2021Document37 pagesHML 214 Lecture 6 2021Linet KariukiNo ratings yet
- Hiv Life Cycle: Fact Sheet Number 106Document2 pagesHiv Life Cycle: Fact Sheet Number 106eviNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5Document10 pagesLecture 5Smasher AustineNo ratings yet
- U4 - Compendium Review Reproduction: Part TwoDocument15 pagesU4 - Compendium Review Reproduction: Part TwoAmandaShermanNo ratings yet
- Biology of Hiv Particle Description of HIV Particle A) Classification of HIV ParticleDocument10 pagesBiology of Hiv Particle Description of HIV Particle A) Classification of HIV ParticlevictoriousNo ratings yet
- Home Library Health Genetics Encyclopedia Human Immunodeficiency VirusDocument7 pagesHome Library Health Genetics Encyclopedia Human Immunodeficiency VirusCollins UmogbaiNo ratings yet
- Home This Page : o o o o o o o o o oDocument36 pagesHome This Page : o o o o o o o o o oTennidoxNo ratings yet
- Human Immunodeficiency Virus (Hiv)Document52 pagesHuman Immunodeficiency Virus (Hiv)AswinNo ratings yet
- Session 6 L Blood Borne Viruses HIV HVDocument62 pagesSession 6 L Blood Borne Viruses HIV HVBlendma AhmedNo ratings yet
- Virus GeneticDocument39 pagesVirus GeneticintanchairunnisaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5: VIRUS 18 - Lacap, Dixie Mae N. Lacap 02. .15Document10 pagesChapter 5: VIRUS 18 - Lacap, Dixie Mae N. Lacap 02. .15Dixie LacapNo ratings yet
- Group 2 - Activity 7CDocument3 pagesGroup 2 - Activity 7CWong Yee LingNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document12 pagesChapter 6EDLE FAITH ANDREA CATABIANNo ratings yet
- Hiv PathogenesisDocument16 pagesHiv PathogenesisjmalavanuNo ratings yet
- VocabularyDocument2 pagesVocabularyDania IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Adeno VirusDocument34 pagesAdeno Virusshikha yadavNo ratings yet
- HIV Life Cycle 03Document3 pagesHIV Life Cycle 032445legitNo ratings yet
- HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus)Document32 pagesHIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus)renirahmatNo ratings yet
- Basic Virology 2018 StudentDocument54 pagesBasic Virology 2018 StudentJulia MartinezNo ratings yet
- Edwin Mwangi Zool 143 Assgn 5Document4 pagesEdwin Mwangi Zool 143 Assgn 5nattydreadfathelahNo ratings yet
- HIV ScienceDocument2 pagesHIV ScienceKhadija PrescottNo ratings yet
- Virus Structure and ReplicationDocument42 pagesVirus Structure and Replicationtummalapalli venkateswara rao100% (2)
- Dr. Ridho - HIVDocument20 pagesDr. Ridho - HIVpenizubaediNo ratings yet
- Gangguan ReproduksiDocument16 pagesGangguan ReproduksiDerrick ThompsonNo ratings yet
- Viral ReplicationDocument26 pagesViral ReplicationJhann100% (1)
- HIV/AIDS: Biology and Treatment: Learning ObjectivesDocument10 pagesHIV/AIDS: Biology and Treatment: Learning Objectiveschrispine ochiengNo ratings yet
- Is HivDocument50 pagesIs HivRodriguez, Jhe-ann M.No ratings yet
- Viruses-Kb SCH of Nursing-MicrobiologyDocument27 pagesViruses-Kb SCH of Nursing-MicrobiologyNelson michaelNo ratings yet
- General Virology 1Document6 pagesGeneral Virology 1safiya nihaalNo ratings yet
- Disease: A Deviation of The Normal Structure/function of Any Part of The Body That Is Manifested by ADocument4 pagesDisease: A Deviation of The Normal Structure/function of Any Part of The Body That Is Manifested by ADhanaNo ratings yet
- Chapter06 LectureDocument44 pagesChapter06 Lecturepokemon123321No ratings yet
- Human Immunodeficiency Virus, HIV: Uncategorized Leave A CommentDocument8 pagesHuman Immunodeficiency Virus, HIV: Uncategorized Leave A Commentshrikantgautam2013No ratings yet
- DiscussionDocument2 pagesDiscussionBlack PastelNo ratings yet
- Viruses: Higher Human BiologyDocument18 pagesViruses: Higher Human BiologyEnis LatićNo ratings yet
- Viruses and Virus GeneticsDocument77 pagesViruses and Virus GeneticsNorman DamaaNo ratings yet
- VirusesDocument33 pagesVirusesShermaine GenistonNo ratings yet
- © 2020 by The Author(s) - Distributed Under A Creative Commons CC BY LicenseDocument10 pages© 2020 by The Author(s) - Distributed Under A Creative Commons CC BY LicenseDouglas SouzaNo ratings yet
- BT601 Virology 1.note On Herpes Virus?3Document8 pagesBT601 Virology 1.note On Herpes Virus?3Haroon IqbalNo ratings yet
- VaccineDocument2 pagesVaccineHappy Birth DayNo ratings yet
- RNA Polymerase Within Its Nucleocapsid (Fig. 20.1)Document4 pagesRNA Polymerase Within Its Nucleocapsid (Fig. 20.1)Aleksandar DimkovskiNo ratings yet
- Pathogenesis of HIVDocument11 pagesPathogenesis of HIVPeter JustinNo ratings yet
- Cancer Gene Therapy by Viral and Non-viral VectorsFrom EverandCancer Gene Therapy by Viral and Non-viral VectorsMalcolm BrennerNo ratings yet