Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nephrolithiasis: Tarlac State University College of Nursing
Nephrolithiasis: Tarlac State University College of Nursing
Uploaded by
Miguelito Galagar GultianoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Nephrolithiasis: Tarlac State University College of Nursing
Nephrolithiasis: Tarlac State University College of Nursing
Uploaded by
Miguelito Galagar GultianoCopyright:
Available Formats
Republic of the Philippines Tarlac State University COLLEGE OF NURSING Lucinda Campus Brgy.
Ungot, Tarlac City Philippines 2300
Nephrolithiasis
Presented by: Agcaoili, Claire P. Baluyut, Donna C. Bautista, Karen L. Brojan, May Daisyree C. Bugayong, Emmanuel Dominic Raymond M. Caampued, John Matley M. Calendas, Arcelene Joy E. Capiendo, Mc Jim Emmanuel I. Cas Alyssa Daphne L. Catap, Stephanie Jill L. BSN 3A-A1 Presented to: Jonathan Cura, R.N.,C.R.N. Instructor August 13, 2010
TABLE OF CONTENTS I. II. Introduction .. Objectives . Nursing Process A. Assessment .. 1. Personal Data . a. Demographic Data b. Environmental Status ... c. Lifestyle .. 2. Family History of Health and Illness .. 3. History of Past Illness .. 4. History of Present Illness . 5. 13 Areas of Assessment ... 6. Diagnostic and Laboratory Procedures .. 7. Anatomy and Physiology .. 8. Pathophysiology .. a. Book Based . b. Client Based ... B. Planning ... Nursing Care Plans ... C. Implementation IV Fluids............................................................................................ Drug Studies. Diet.................................................................................................... III. IV. SOAPIE............................................................................................ Conclusion Recommendations .. 49 51 3 5 7 7 7 7 7 8 9 10 10 11 29 33 37 37 38 39 39 45 45
INTRODUCTION Nephrolithiasis refers to the condition of having kidney stones. The stones are solid concretions or calculi (crystal aggregation) form in the kidneys from dissolved urinary minerals. The stones are solid and are common in premature infants. (www.wikipedia.com) About 5% of women and 10% of men will have at least one episode by age 70. Kidney stones affect about 2 out of every 1000 people. Recurrence is common, and the
risk of the recurrence is greater if 2 or more episodes of kidney stones occur. (www.wikipedia.com) Some type of stones tends to run in the families. Some types may be associated with other conditions such as bowel disease, iliac bypass for obesity, or renal tubule defects. A personal or family history of stones is associated with increase of stone formation. (www.wikipedia.com) For the Filipinos who are fond of eating salty foods and fatty foods, also cigarette smoker and alcohol drinker were at risk for having this condition. In the United States, 23, 685 of its population have the incidence of Nephrolithiasis. (http://kidney.niddk.nih.gov/kudisease/pubs/kustats/) Nephritis, nephritic syndrome, kidney stone and nephrosis has the number of 11,056 or 3.6% over 100,000 populations in the Philippines. (http://www.doh.gov.ph/kp/statistics/lading motality as of 2008). a. Importance of the case study This study is significant to the nursing education of broadening the knowledge of the students skills, knowledge and attitude of the nursing practice. It supplies extensive analysis about the condition selected through research and actual observation as it serves as and guidance in developing learned skills in the assessment and management of Nephrolithiasis. Through this study, the researcher will be able to familiarize the different medical approaches toward ongoing curative phase and the holistic approach in assessing patients health will be delivered for proper intervention to be given. For the researcher to have a baseline information about nephrolithiasis, management and clinical interventions. b. Reasons of choosing the case study: The researcher choose this study to learn the detailed process of the disease nephrolithiasis associated with its prevention and treatment and somehow, help the client and his family to promote and restore support and wellness by providing proper nursing intervention. And for the researcher to have further understanding on the disease.
c. Objectives: c.1 General objective: To have a better understanding of the course of the disease, its causes, signs and symptoms, diagnoses & treatment. c.2 Specific Objectives Nurse-Centered 1. Assess properly to determine the contributing factors regarding to the clients disease and identify any present abnormalities. a. Personal Data b. Family history of health & illness c. History of past illness d. History of present illness e. 13 areas of assessment 2. Gather the needed data that can help to understand how and why the disease occurs. a. Diagnostic & Laboratory procedures b. Pathophysiology (book-based and client-based) 3. Develop an individualized plan considering client characteristics or the situation and setting specific, measurable, attainable, realistic and time-bound plan that reflects the onset, date of problem identified. a. Planning (NCP)
4. Judge the effectiveness of chosen interventions, nursing care and the quality of care provider. a. Client daily program in the hospital 5. Learn the actual cause or formation of the disease process. 6. Identify major risk on developing Nephrolithiasis
Client-Centered 1. Discuss the indications and management of the client with Nephrolithiasis 2. Discuss the implications for medications commonly prescribed for clients with Nephrolithiasis. 3. Describe nursing care for the client with Nephrolithiasis 4. Use the nursing process to provide holistic care for a client with Nephrolithiasis. 5. To comply with the health teachings provided during the hospital confinement.
II. NURSING PROCESS A. ASSESSMENT 1. Personal Data 1.a) Demographic data NAME: Mr. V AGE: 66 y/o
SEX: Male CIVIL STATUS: Married RELIGION: Roman Catholic POSITION IN THE FAMILY: Father ADDRESS: Moncada, Tarlca City DATE OF BIRTH: March 20, 1944 NATIONALITY: Filipino USUAL SOURCE OF MEDICAL CARE: Phil Health ADMITTING DIAGNOSIS: Nephrolithiasis CHIEF COMPLAINT: Flank pain DATE & TIME OF ADMISSION: July 27, 2010 / 08:04:14 PM ADMISSION #: 152879
1.b) Environmental Status Mr. V lives in unfinished house with an existing one bedroom. The back part of their house is a farm planted with corns and rice grains wherein they would also have the capacity to plant any trees or any other vegetation that they can use for other source of food. The drainage is located at 40 m. distant from their house. Their house is in close proximity to the RHU. Water pump outside their house which is owned by them is usually their source of water.
1.c) Lifestyle
The patients main habits at home are doing household chores such as cleaning the surroundings, washing dishes and clothes. When hes not yet married, he often drinks alcoholic beverages such as beer, redhorse and gin. He stated that 4x a week, he and his friends were having alcohol drinking session. He consumes approximately 5 bottles of gin or 10 bottles of beer and red horse every time they will have session. They often starts at 7pm and ended at 11 pm and goes home to sleep when hes already drunk and wakes up in the morning at 4 to do some household chores. He is also a cigarette smoker, usually consumes two packs per day which is equivalent to forty sticks. But, when he got married he gradually lessen his take of alcohol and cigarette, from five bottles to two bottles of gin, from ten bottles to four bottles of beer and redhorse, from two packs to one pack of cigarette per day until the day that he is not drinking alcohol and smoking cigarette anymore. He also loves salty and fatty food( example: sinigang na baboy na maraming taba or piritong baboy chicharon). He cannot eat foods without having sawsawan such as bagoong, alamang and patis. His main form of exercise is walking, doing household chores and planting; he is also fond of listening to radio when he is at rest.
2. Family History of Health and Illness
Paternal
Maternal
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
66 Nephro A&W
64 A&W
62 A&W
59 A&W
57 A&W
56 A&W
55 A&W
53 A&W
Schematic Diagram Legends:
-Deceased Male
-Living Male
-Deceased Female
-Living Female
N/A- Not Applicable Nephro- Nephrolithiasis -pertains to patient
3. History of past illness The client experienced having chicken pox and sore eyes during his childhood years and verbalized that he was unable to complete his immunization. The client doesnt have allergies to drugs, animals, insects, or any other environmental agents. He claims that whenever he gets sick he used OTC drugs such as paracetamol (biogesic and neozep).
4. History of present illness Mr. V felt the pain at first time on March 2010. He stated that he was just planting rice at that time and felt the pain on the lower quadrant on the abdomen radiating to back with a pain scale of four over ten. He just took a rest and the pain is relieved according to him. The pain occurs two times a week. The pain continued until April and he had ultrasound showing that there is a left renal cyst and medications were given. On June, the pain got worst but he can still tolerate and relieved by rest. He can do planting anymore due to pain but he can still do light activity such as washing dishes, and sweeping the floor. One week prior to admission, he can no longer tolerate the pain. He had just lied on bed and tried to overcome the pain. Few hours prior to admission, the patient was unable to walk and straighten up his body due to pain and already needs assistance.
5. 13 Areas of Assessment 1. Social Status Mr. V 66 years old married and is the eldest among eight siblings of the family, currently he is residing in Moncada, Tarlac. He works as a farmer at the back of their house. The patient verbalized that he and his family usually communicate with one another during mealtime. Every misunderstanding throughout the family is being settled immediately. Mr. V claimed that after his work he use to have bonding moments with his friends. Often times they tend to drink alcoholic beverages and consumed up to two bottles each. During the interview the patient always thinks about his health condition and when will be the operation. You can see on his face the worry he feels. Although, he is ill and experiencing pain, he still doing his best to cooperate during the interview. He used to talk to the other patients inside the ward. NORMS: Family members perform roles. Good communication within the family must be maintained to obtain a healthy relationship with one another. Social support is a perception tat one has emotional and tangible resources to call on when needed, perceived social support is being followed by the family to express the love of the family. Financial aspect is one of the normal constraints in the family. (Nursing Fundamentals by Rick Daniel; Community Health Nursing in the Philippines)
Analysis/interpretation: Mr. V has a good and harmonious relationship with the people around him. 2. Mental Status General appearance and Behavior The patient was well-groomed. He entertained every questions asked and answered willingly. He listened attentively and was cooperative. Patient manifested facial expression and affect in response to various topics of the conversation.
Level of consciousness The patient is responsive during the interaction yet as time goes by he is becoming less attentive and loss his focus on the interview. He was unable to maintain eye contact during the interview. Orientation The patient was oriented regarding his condition and his stay in the hospital. He was able to state the right time, right place and date of the interview. Speech The patient can speak Filipino and Ilocano. He conversed mostly in Tagalog and was able to express himself well. His speech was understandable and no speech defect was noted. Intellectual Functioning Mr. V was able to understand the questioned ask to him. The researchers did not have a hard time explaining anything to him. His memory is good because he did not have difficulty in recalling past events in his life including his check up. He was able to recall his activities since this morning.
NORMS: Mental status is the degree of comprehensive shown by a person in intellectual, emotional, psychological, and personality functioning.(Mosbys Pocket Dictionary of Medicine, Nursing, and Health Professions). Analysis/interpretation: The patient responded accordingly to the situation and can be considered as mentally healthy.
3. Emotional Status During the interview Mr. V is uncomfortable at times when he was experiencing pain and not able to concentrate. His wife is with home to address his needs and to provide support. He expresses his opinions and emotions as the researchers go along the conversation. NORMS: It is normal for an individual to react on the stimuli she perceives and feels. (Health Assessment and Physical Examination, Estes 2006)
Analysis/Interpretation: The patients mood was influenced by the present condition and the environment.
4. Sensory Perception
In the assessment of sensory perception, examination of vision, hearing, smell, taste and touch were included.
Vision In the examination of the eyes, extra ocular muscle movements of both eyes were examined first. To test this, the Six Fields of Gaze was used as the assessment method. Standing two feet in front of the patient, a pen was used for the patient to follow from superior, inferior, left, and right oblique angles. Both eyes of the patient symmetrically followed the pen is moved to the different locations. For the test of papillary constriction a penlight was used, light was introduced from the front to the lateral side of one and then repeated the same procedure to the eye. Both pupils constricted as light was directed to them. The patient was unable to read newspapers showed to him.
NORMS: For the test of the Cardinal Fields of Gaze, the extra ocular muscle movements are being assessed. Normally, both eyes of the patients should move smoothly and symmetrically in each of the six fields of gaze. Pupils should constrict briskly to direct and consensual light and to accommodation, reading is possible at a distance of 14inches for the assessment of near vision. (Health Assessment and Physical Examination, Estes 2006)
Analysis/Interpretation The patients, extra ocular muscle movements and papillary response are still within normal but the client has a blurred vision.
Hearing For the auditory assessment, the voice-whisper test was used. Standing two feet between the patients other ear, words and phrases were whispered and allowed the patient to repeat the words and phrases that were whispered. The procedure was then repeated to other ear. The patient was not able to repeat the words being used.
NORMS: For the auditory accuracy, the patient should be able to repeat words whispered from a distanced of two feet. (Health Assessment and Physical Examination, Estes 2006).
Analysis/Interpretation: The patients auditory accuracy
Smell In assessing the sense of smell of the patient, she was instructed to close her eyes and let her smell things like orange fruit and alcohol which is present on their table. She was then instructed to recognize and name the different materials. The client was able to recognize the scent of the things being asked him to smell.
NORMS: Olfactory receptor cell are located in the upper parts if the nasal cavity, the superior nasal conchae, and on parts of the nasal septum and are covered by hair like cilia that project into the cavity. The chemical component of odors binds with the receptors, causing nerve impulses to be transmitted to the olfactory cortex located in the base of the fontal lobe. (Health Assessment and Physical Examination, Estes 2006).
Analysis/Interpretation: It denotes that the patients olfactory function transmits impulses to the frontal lobe properly.
Taste For the assessment of the sense of taste, the patient was again instructed to close his eyes and let her taste things like sugar and coffee which are present on their table then enabling him to name them. The patient named all things that he tasted.
NORMS: Four qualities of taste are found in the taste buds distributed over the surface of the tongue: bitter is located at the base, sour along the sides, and salty and sweet near the tip. (Health Assessment and Physical Examination, Estes 2006).
Analysis/Interpretation: Her taste buds that help transmit taste sensations are functioning well.
Tactile In the examination of the touch sensation of the patient was again instructed to close his eyes and let him feel things like spoon soaked from hot water and pinched his on the forearm to assess pain sensation. The patient responded to the different sensation and expressed what he felt. He verbalized that the spoon soaked from the hot water was hot and the pinch was painful.
NORMS: The skin contains receptors for pain, touch, pressure and temperature. These receptors originate in the dermis and terminate as either that are encapsulated and found
predominantly in the fingertips and lips. Sensory signals that help determine precise locations on the skin are transmitted along rapid sensory pathways, and less distinct signals such as pressure or poorly localized touch are sent via slower sensory pathways. (Health Assessment and Physical Examination, Estes 2006).
Analysis/Interpretation: The patients sensory transmission functions well.
5. Motor Stability The patient is able to ambulate from her bed. He was slouched and weak in appearance. The lower limb was not able to bear full body weight during standing and ambulation. The head and neck turn toward the included direction, followed by the rest of the body. He was not able to transfer easily from various positions. Assessment for the Range of Motion of the patient was done through instructions assistance which includes the ability of the patient to bend her shoulder farther apart. He can also move her shoulder medially (toward the midline of the body), and laterally (away the midline of the body) as well as rotating her shoulder medially and laterally. He can bend her elbows closer and farther apart or rotate it laterally to face upward and medially to face downward. Extension and flexion of his wrist can be done, and extending it beyond the neutral position. The patient can also flex and extend her knees and do dorsiflexion (flexing the foot at the ankle so that the toes moves toward the chest) or plantar flexion (moving the foot at the ankle so that the toes move away from the chest) of her ankles and feet, or titling her foot inward and outward and moving it toward away the midline of the body. The patient shows active movement against gravity.
Norms: Range of Motion standards are follows: Walking is limited in one smooth, rhythmic fashion as the heel strikes the floor body weight is then shifted to the bail of the foot, and then elevates off the floor before the nest step forward. The normal ROM for the shoulder is forward flexion, abduction, adduction, internal and external rotation. The normal ROM for the elbows is extensions, supination, pronation, and flexion. The normal ROM of the wrist is extension, hyperextension, and flexion The normal ROM for the knees is flexion, extension in some cases, hyperextension is possible. The normal ROM for the ankles and feet is dorsiflexion, plantar flexion, inversion, abduction, and adduction. (Health Assessment and Physical Examination, Estes 2006).
Scale 0 1 2 3 4 No muscular contraction Barely flicker of contraction Active movement with gravity removed Active movement against gravity Active movement against gravity and some resistance 5 Active movement against full resistance with no fatigue Scale for Muscle Strength
Analysis/Interpretation: Mr. V was able to ambulate. Both lower limbs were able to bear full body weight. Normal muscle strength allows for complete voluntary range of joint motion against both gravity and moderate to full resistance. Muscle strength is equal bilaterally. There are no observed involuntary muscle movements.
6. Body Temperature
Table 1.1 Body Temperature
Date July 28, 2010: 11-3 shift July 29, 2010: 11-7 shift 7-3shift July 30, 2010: 6:00am 8:00am 10:00am 2:00pm Norms:
Temperature 36. 8 degree celcius 36.9 degree Celcius 36. 6 degree celcius 36.0 degree Celcius 36.5 degree Celcius 36.5 degree Celcius 36.2 degree celcius
The temperature per axilla is 35.0 degress to 36.8 degress Celcius. (Health Assessment by Leasia Monahan, 2002) Analysis/Interpretation: Mr. Vs body temperature taken per axilla is within normal limits. There is uniformity in temperature of her body upon palpation.
7. Respiratory Status The following listed below were the recorded respiratory rates as per assessment:
Table 1.2 Respiratory Rate
Date July 28, 2010: 11-3 shift
Respiratory Rate 23cpm
July 29, 2010: 11-7 shift 7-3shift July 30, 2010 6:00am 8:00am 10:00am 2:00pm Norms:
21cpm 25cpm 20cpm 25cpm 23cpm 23cpm
Based on the Health Assessment and Physical Examination Third Edition (Mary Ellen Zator Estes, 2006), the normal respiratory rate for adult is 12- 20 breaths per minute, normal respiration are regular and even in rhythm, depth of inspiration is not exaggerated and effortless with the thorax rises and falls in unison in the respiratory cycle. Analysis/Interpretation: It shows that there is slight elevation on the respiration, since. He has irregular rhythm. 8. Circulatory Status Upon assessment of the blanch test results in prompt returning of pinkish color of the nail beds for two seconds. The patients skin turgor after pinching turns to its normal position. The force of the arterial pulse can be classified as in three point scale: 3+--------------fall, bounding 2+--------------normal 1+--------------weak, thready 0----------------absent
Table 1.3 Pulse Rate and Blood Pressure
Date July 28, 2010: 11-3 shift July 29, 2010: 11-7 shift 7-3shift July 30, 2010: 6:00am
Pulse rate 71 bpm 68bpm 87 bpm 81 bpm
Blood Pressure 100/70 mmHg 100/80 mmHg 120/80 mmHg 120/80 mmHg
8:00am 10:00am 2:00pm
101 bpm 90 90
120/80 mmHg 120/80 mmHg 120/70 mmHg
Laboratory reports dated July 27, 2010 reported RBC as 4.16 T/L and Hgb 122 g/L. Norms: The normal pulse rate ranges from 60-100 beats per minute and the rhythm is normal due to it is regular with equal bilateral strength upon bounding. The normal blood pressure is within the 120 to 140 systolic pressure and 80-90 diastolic pressure. (Health Assessment and Physical Examination Third Edition, Mary Ellen Zator Estes, 2006). The normal value of hemoglobin is 120 to 180g/L* and the RBC has the standard value from 4.20 to 6.30 T/L*. *Normal Values of the laboratory results are based on the normal values used in
TPH.
Analysis/Interpretation: The pulse from the scale given above, it falls under to the 2+ which is normal. There is an occurrence of increases in the blood pressure of the patient. The laboratory findings of hemoglobin and RBC are below normal range. 9. Nutritional Status According to Mr. V, he eats three times a day. He usually eats vegetables, fish and fatty foods such as chicharon. The patient verbalized that he cannot eat foods without soy sauce and fish sauce .In terms of fluid intake, the client stated that he consumes at an average of 4-6 glasses of water per day, distributed at around 3 glasses in the morning, 4 at noon and 3 glasses at evening before and during hospitalization.
Her Body Mass Index is computed as follows:
BMI=weight in kg Height (m) BMI = 48 kg (1.68) = 17.02 Norms: Normal eating pattern is at on the minimum of 3 times per day, depending upon metabolic need and demands. Fluid intake is on the average of 8 to 10 glasses per day. Normal BMI range: <18.5...underweight 18.5 24.9..healthy 25.0 29.9..overweight 30..obesity (Physical Assessment and Health Examination IV Edition by: Carolyn Javis)
Analysis/Interpretation: There are no remarkable deviations in the clients eating pattern, frequency, and attitude. Her BMI is within normal limit as compared to the normal value which is 18.5 to 24.9 thus making her healthy. 10. Elimination Pattern Bowel Habits: Mr. V was not able to defecate for three days (from July 27- July 30, 2010). Bladder Habits: He voids 3-4 times a day with dark yellow urine in small amount (500cc for 24 hrs) and with pain during urination.
Norms:
Normal bowel movement is 1 to 3 times a day and voiding at 1200 to 1500ml/day. (Health Assessment and Physical Examination Third Edition, Mary Ellen Zator Estes, 2006). Analysis/Interpretation: Mr. V has abnormal bowel elimination for three consecutive days. His urine output is not within normal range. There is presence of difficulty in urination. 11. Reproductive Status Mr. V claims that his first coitus happened when he was 27 years old. He also claims that he does not use condoms or other contraceptives with her wife. He has 9 children. Norms: Based on Sigmund Freuds psychosexual development the genital stage is where sexual desires reemerge due to physiological changes, fluctuating hormone levels, and changing social relationship (Pediatric Nursing; Thomson Edition 2003). Analysis/Interpretation: The patients early engagement to sexual activities is normal, since his reproductive organs are not yet fully develop. 12. State or Physical Rest and Sleep The patient had stated that during his hospitalization, he experienced sleep difficulties. His hours of sleep only range three to four hours a day. He claimed that his sleep difficulties were primarily due to the pain on the abdomen and the different interactions to check his medical conditions. Norms:
Based from Daniels (2004) Fundamentals of Nursing, 8- 10 hours of sleep is needed to have an adequate rest and an environment that is conducive to health is necessary to provide comfort to an individual. Analysis/Interpretation: The client has an abnormal state of sleep and rest. Pain was the primary factor of sleep deprivation during these days. 13. State of Skin Appendages Upon inspection, the clients skin is light brown and there is a presence of palmar pallor. Texture is described as cold clammy and a presence of mild sweating, grade 3 pitting edema was found in both hands and feet and skin turgor returns promptly after pinching. Sclerae are anicteric. Nails are intact with no swelling on eponychium and are pale in color. In abdominal area, skin is uniform similar as in the body, and his abdomen show signs of tenderness. Norms: The normal generalized color for dark-skinned individuals is light to dark brown to olive with milder colored palms, soles, nail beds and lips. Texture is described as smooth, soft, warm, and dry to touch. Pinched skin to test for skin turgor should return immediately after. There should also be no swelling, pitting or edema present when pressed firmly for 5 to 10 seconds over tibia or ankle. Nails are present per distal phalanx, are in pink color, round and with a 160 degree nail base. It is also hard, immobile and firm in texture. Evidence of Pallor is seen in patients who had abortion due to blood loss. (Health Assessment and Physical Examination Third Edition, Mary Ellen Zator Estes, 2006). Analysis/Interpretation: Palmar pallor is present due to ineffectrive peripheral tissue perfussion and a grade 3 pitting edema was noted in both hands and feet.
6. Diagnostic and Laboratory Procedures Diagnostic/laboratory Date ordered and date procedures result/s Hematology Results 07-27-10
Indication/s or Purpose/s Indicates the total number of blood cells as well as the hemoglobin, hematocrit and RBC indices.
Results
Normal values ( units used in the hospital)
Analysis and interpretation of results All results are within the normal range.
1. White Blood cells a.Lymphocytes b. Monocytes c. Eosinophils 2. Red blood cells a. Hematocrit b. Hemoglobin 3. Platelets
8.6 G/L 13.2% 4.16 T/L 0.371 L/L 122 G/L 393 G/L
4.1-10.9 G/L 10.0-58.5% L 4.20-6.30 T/L 0.370-0.510 L/L 120-180 G/L 140-440 G/L
Diagnostic/laboratory procedures Ultrasound
Date ordered and date result/s 04-10-10
Indication/s or Purpose/s To visualize of the upper abdominal area for any stones or calculi formed in the kidney.
Results There is a cyst in the lateral cortex measuring 1.6 cm with two reflective structures within both measuring 0.3 cm without shadows.
Analysis and interpretation of results Left renal cyst with reflective structures with no shadowing.
7. Anatomy and physiology
The kidney participates in whole-body homeostasis, regulating acid-base balance, electrolyteconcentrations, extracellular fluid volume, and regulation of blood pressure. The kidney accomplishes these homeostatic functions both independently and in concert with other organs, particularly those of the endocrine system. Various endocrine hormones coordinate these endocrine functions; these include renin, angiotensin II, aldosterone, antidiuretic hormone, andatrial natriuretic peptide, among others. Many of the kidney's functions are accomplished by relatively simple mechanisms of filtration, reabsorption, and secretion, which take place in the nephron. Filtration, which takes place at the renal corpuscle, is the process by which cells and large proteins are filtered from the blood to make an ultrafiltrate that will eventually become urine. The kidney generates 180 liters of filtrate a day, while reabsorbing a large percentage, allowing for only the generation of approximately 2 liters of urine. Reabsorption is the transport of molecules from this ultrafiltrate and into the blood. Secretion is the reverse process, in which molecules are transported in the opposite direction, from the blood into the urine.
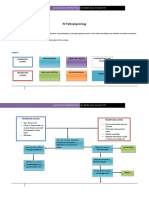
8. Pathophysiology Book Based
Client Based
B. Planning Assessment S>Masakit kapag umuihi ako O>Rated pain as 6/10, with 10 being the highest >Weak in appearance >With muscle guarding behavior on RLQ upon movement that last for 5 secs. >Complains of pain upon palpation on RLQ of abdomen >Facial grimace >Prefers to position self in side lying >Irritability and restlessness Diagnosis: Acute pain r/t presence of obstruction of cyst within the Left kidney Scientific Explanation: A cyst obstruct the Unpleasant sensory and emotional experience feeling caused by renal cyst that is obstructed within the urinary system resulting to sudden and severe abdominal or flank pain.
Planning Within 2-4 hrs. of appropriate nursing intervention the patient will be able to verbalize relief of pain from a scale of 6/10 to 4/10.
Interventions > Apply hot compress at the flank area. R: to reduce pain and provide comfort. > Assist patient in a comfortable position regularly. R: to promote feeling of comfort. > Encourage deep breathing exercise. R: to reduce muscle tension. > Provide diversional activities such as talking to relatives. R: to divert attention from pain. > Encourage or assist with frequent ambulation as indicated. R: to facilitate passage of stone to renal system. > Provide therapeutic touch such as gentle rubbing of back. R: to promote comfort.
Expected Outcome After 2-4 hours of proper nursing intervention the patients pain scale will decrease from p/s of 6/10 to 4/10.
> Administer medication as prescribed by the physician. R: to maintain acceptable level of pain.
Assessment S>hindi ako gaanong umiihi, mga 2-3 beses lang kada araw O>150cc urine collected for 8 hours >with a yellow to brownish colored urine > no crystals or blood observed > goes to comfort room twice per shift Diagnosis: Impaired urinary elimination related to decreased renal perfusion secondary to
Planning Within 6 hours of appropriate nursing intervention the patient will be able to have a urine output of 30-50 cc per hour or void in normal amounts and usual pattern.
Interventions > Monitor intake and output and characteristic of urine R: provide information about the kidney function and presence of complication. > Encourage increase fluid intake. R: to increase hydration to flushed bacteria. > Investigate reports of bladder fullness or palpate suprapubic distension. R: the urinary retention may develop causing tissue
Expected Outcome After 6 hours of appropriate nursing intervention the patient will be able to have a normal urine output and void in a normal amounts as evidenced by 30-50cc level per hour.
nephrolithiasis Scientific Explanation: Obstruction of the urinary stones(calculi) in the urinary tract causes urinary retention. Over distension of the bladder causes poor contractivity of the detrusor muscle, further imparting urination. And urinary retention causes overflow voiding or incontinence. Assessment S>Paano ba nagkakaroon ng bato O>Asking questions about his health problem >Requested for a list of contraindicated foods >Unfamiliar with the things that contributes to his health problem like eating salty foods Diagnosis: Knowledge deficit r/t lack of information regarding current health condition. Scientific Explanation: Planning Within 2 hrs. of proper nursing intervention, the patient will be able to verbalize understanding of his disease process and potential complications.
distension and potentiates risk of infection. > Document any stone expelled and send laboratory for analysis. R: retrieval of calculi allows identification of type of stones and influences choice of therapy.
Interventions >review disease process and future expectations R: provides knowledge base from on which patient can make and formed choices >encourage patient to notice dry mouth and excessive diaphoresis and to increase fluid intake whether or not feeling thirsty R: increased fluid losses/dehydration require additional intake beyond usual daily needs >encourage patient to eat * low purine diet (example:
Expected Outcome After 2 hrs. of proper using intervention, the patient is able to verbalized understanding of his disease process and potential complication
Lack of cognitive information or psychomotor skills required for health promotion, recovery and maintenance.
lean meat, legumes) R: decreases oral intake of uric acid precursors that leads to formation of uric acid calculi. *low calcium diet (limited milk, cheese, green leafy vegetables) R: reduces calcium oxalate stone formation *low oxalate diet (restrict chocolate, caffeine) R: reduce calcium oxalate stone formation >discuss medication regimen R: drugs will be given to acidify or alkalize urine
Assessment S>tatlong araw na akong di nakakapagbawas O>weak in appearance >restless >irritable >abdominal tenderness >discomfort
Planning Within 2-4 hrs of proper nursing intervention, the patient will demonstrate behaviors to relieved constipation
Diagnosis: Constipation r/t insufficient physical activity Scientific Explanation: Decrease in normal frequency of defecation accompanied by difficult or incomplete passage of stool and passage of excessively hard, dry stool.
Interventions >Monitor intake and output >Auscultate for bowel sounds >Instruct client to increase fluid intake from 4-6 glasses 68 glasses per day >instruct client to eat foods that are high in fiber such as oranges, pineapple >Encourage client to increase mobility or exercise such as walking >Administer laxative medications (Dulcolax)
Expected Outcome After 2-4 hrs. of proper nursing intervention, the patient will demonstrate behaviors to relieved constipation as evidenced by feeling of relieved and urge to defecate
Assessment S > parang puputok na ang pantog ko. O> bladder distension > small frequent voiding > urine output of 150cc within 8 hrs Diagnosis: Chronic urinary retention related to pain felt during urination secondary to obstruction of the urinary tract. Scientific Explanation: Urine retention occurs because the cl;ient experiences pain during urination, he is unable to excrete all the urine in his bladder.
Planning Within 4-8 hrs of proper nursing interventions the patient will be able to void in sufficient amounts with no palpable bladder distention
Interventions >evaluate hydration status >pour warm water over perineum to stimulate reflex arc >encouraged client to report problems immediately >measure amount of voided residual >determine frequency of voiding >encourage patient to use valsalva maneuver if appropriate
Expected Outcome After 4-8 hrs, of proper nursing interventions, the patient will be able to void in sufficient amounts (260 cc in 8 hrs.) with no palpable bladder status
Assessment S > Hinang-hina ako O> grade 3 pitting edema on of hands and feet > intake of six glasses of water a day > 500cc urine output in 24 hours. > increase respiratory rate 25cpm. Diagnosis: Fluid volume excess r/t to compromise renal function. Scientific Explanation: Due to impairment of the renal function fluid retention occur that lead to excessive fluid in the body.
Planning Within the 8 hours shift of proper nursing intervention the patient will stabilize fluid volume as evidence by balance intake/ output.
Interventions >Note intake and output. R: to have a baseline data of fluid intake and output. > Review intake of sodium and protein. R: to know if foods taken aggravate the condition. > Note pattern and amount of urination. R: to have a measurement of fluid output. > Observe skin and mucus membrane. R: to assess for decubitus or ulceration. > Restrict sodium fluid intake as indicated. R: to avoid further fluid retention. >Assist patient when changing position. R: to reduce pressure tissue pressure.
Expected Outcome After 8 hours shift of proper nursing intervention the patient will stabilize fluid volume as evidence by balance intake/ output.
C. IMPLEMENTATION 1. Medical Management i. IVF Medical Management/Treatment PLRS
Date ordered July 27, 2010
General Description Isotonic fluid. These solutions provide sources of water and electrolytes. Their electrolyte content resembles that of the principle ionic constituents of normal plasma. Isotonic fluid is used frequently in intravenous drips for patients who cant take fluids orally and have developed or are in danger of developing dehydration or hypovolemic. Hypotonic fluid that provides free water for intravenous KVO. Provides a modest sugar source for cellular
Indication/s or Purpose/s For replacement of acute extracellular fluid loses without disturbing normal electrolyte relationships
Clients reaction to treatment Client shows no adverse reactions
PNSS
July 29, 2010
Replacement & maintenance of fluid and electrolytes.
Client shows no adverse reactions
D5W
July 30, 2010
Used to supply water and calories to the body.
Client shows no adverse reactions
metabolism
NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES Before: During: After: Check the doctors order at the clients chart. Ensure proper identification. Assess the clients history for allergic reaction to medication. Perform hand hygiene and wear clean gloves. Inform the client about the procedure. Maintain aseptic technique. Check the doctors order for the flow rate. Inform the client not to elevate his hands to prevent back flow of blood. Assess the condition of the vein and signs of infection.
ii. Drugs Name of Drug
Date Ordered/ Date taken or given July 28, 2010
Route of administration & Dosage & Frequency of administration 1g IVP q12
Mechanism of action
GENERIC NAME: Ceftriaxone BRAND NAME: Rocephin CLASSIFICATIONS: > 3rd generation Cephalosphorin > Antibiotic
Inhibits synthesis of bacterial cell wall, causing cell death.
Clients response to medicine with actual side effect Single No side preoperative doses effects noted may decrease the incidence of post operative infections.
Indication, Purpose
NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES: Explain to the patient and family on what is the effect of drug and its action. Assess patients infection before therapy. Before giving first dose, do sensitivity test Before giving the first dose, ask patient about previous reaction to Cephalosporin or Penicillin. Assess CBC and kidney function results
Name of Drug
Date Ordered/ Date taken or given July 28, 2010
Route of administration & Dosage & Frequency of administration 30 mg IVP q6
Mechanism of action
Indication, Purpose
Clients response to medicine with actual side effect No adverse reaction noted
GENERIC NAME: Ketorolac Tromethamine BRAND NAME: Toradol CLASSIFICATIONS: NSAID, Analgesic
Antiinflammatory and analgesic activity; inhibits prostaglandin and leukotriene synthesis.
Short term management of pain
NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES: Explain to the patient and family on what is the effect of drug and its action. Assess patients infection before therapy. Monitor fluid intake and output. Check for any side effects that may occur.
Name of Drug
Date Ordered/ Date taken or given
Route of administration & Dosage & Frequency of administration
Mechanism of action
Indication, Purpose
Clients response to medicine with actual side effect No adverse reaction noted
GENERIC NAME: Bisacodyl BRAND NAME: Dulcolax CLASSIFICATIONS: Laxatives
July 30, 2010
1 tab OD PO
Has a known tendency to cause potassium depletion. Stimulates mucus secretion and synthesis contributes to the laxative action of and the part of the potassium secretion is due to mucus release.
Short term relief of constipation.
NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES: Explain to the patient and family on what is the effect of drug and its action. Assess patients infection before therapy. Monitor fluid intake and output. Check for any side effects that may occur.
iii. Diet Type of Diet Date ordered General description Indication/s, Purpose/s The full liquid diet is often used as a step between a clear liquid diet and a regular diet Specic foods taken Clients response and/or reaction to the diet No allergic reaction noted
Full Diet
July 27, 2010 July 28, 2010
Is a diet which is intermediate between the clear liquid and mechanical soft diet in characteristics. A normal diet limited to soft , easily digestible foods.
Vegetables fruits, breads
Soft Diet
July 29, 2010
Nutritionally adequate diet differs from the normal diet in having reduced fiber content soft consistency bland flavor. Low salt, low fat July 29, 2010 A diet containing limited amounts of fat and consisting chiefly of easily digestible foods of high carbohydrate content
It is commonly Banana, soup recommended for people who have GI disturbances or acute infections and those unable to tolerate a normal diet. Fruits, vegetables
No allergic reaction noted
No allergic reaction noted
3. Nursing Management (SOAPIER) S>Masakit kapag umuihi ako O>Received patient in bed at supine position >with ongoing PNSS @ R arm regulated at 30 gtts/min >awake, conscious and coherent >Rated pain as 6/10, with 10 being the highest >Weak in appearance >With muscle guarding behavior on RLQ upon movement that last for 5 secs. >Complains of pain upon palpation on RLQ of abdomen >Facial grimace >Prefers to position self in side lying >Irritability and restlessness A> Acute pain r/t presence of obstruction or movement of stones within the urinary system secondary to nephrolithiasis P>Within 2-4 hrs. of appropriate nursing intervention the patient will be able to verbalize relief of pain from a scale of 6/10 to 4/10. I> Applied hot compress at the flank area. > Increased fluid intake for atleast 3-4 glasses. > Assisted patient in a comfortable position regularly. > Encouraged deep breathing exercise. > Provided diversional activities such as talking to relatives. > Encouraged or assist with frequent ambulation as indicated. > Provided therapeutic touch such as gentle rubbing of back. > Administered medication as prescribed by the physician. E> After 2-4 hours of proper nursing intervention the patients pain scale decreased from p/s of 6/10 to 4/10.
S>hindi ako gaanong umiihi, mga 2-3 beses lang kada araw O>Received patient in bed at supine position >with ongoing PNSS @ R arm regulated at 30 gtts/min >awake, conscious and coherent >150cc urine collected for 8 hours >with a yellow to brownish colored urine > no crystals or blood observed > goes to comfort room twice per shift A>Impaired urinary elimination related to decreased renal perfusion secondary to nephrolithiasis P>Within 6 hours of appropriate nursing intervention the patient will be able to have a urine output of 25-35 cc per hour or void in normal amounts and usual pattern. I> Monitored intake and output and characteristic of urine > Encouraged increase fluid intake. > Investigated reports of bladder fullness or palpate suprapubic distension. > Documented any stone expelled and send laboratory for analysis. E> After 6 hours of appropriate nursing intervention the patient had a normal urine output and void in a normal amounts as evidenced by 25cc level per hour.
S>Paano ba nagkakaroon ng bato O>Received patient in bed at supine position >with ongoing PNSS @ R arm regulated at 30 gtts/min >awake, conscious and coherent >Asking questions about his health problem >Requested for a list of contraindicated foods >Unfamiliar with the things that contributes to his health problem like eating salty foods A>Knowledge deficit r/t lack of information regarding current health condition. P>Within 2 hrs. of proper nursing intervention, the patient will be able to verbalize understanding of his disease process and potential complications. I>reviewed disease process and future expectations >stressed the importance of increased fluid intake(3-4 L/day) >encouraged patient to notice dry mouth and excessive diaphoresis and to increase fluid intake whether or not feeling thirsty >encouraged patient to eat * low purine diet (example: lean meat, legumes) *low calcium diet (limited milk, cheese, green leafy vegetables) *low oxalate diet (restrict chocolate, caffeine) >discussed medication regimen R>After 2 hrs. of proper using intervention, the patient verbalized understanding of his disease process and potential complication
S>tatlong araw na akong di nakakapagbawas O>Received patient in bed at supine position >with ongoing PNSS @ R arm regulated at 30 gtts/min >awake, conscious and coherent >weak in appearance >restless >irritable >abdominal tenderness >discomfort A>Constipation r/t insufficient physical activity P> Within 2-4 hrs of proper nursing intervention, the patient will demonstrate behaviors to relieved constipation I>Monitored intake and output >Auscultated for bowel sounds >Instructed client to increase fluid intake from 4-6 glasses 6-8 glasses per day >instructed client to eat foods that are high in fiber such as oranges, pineapple >Encouraged client to increase mobility or exercise such as walking >Administered laxative medications (Dulcolax) R> After 2-4 hrs. of proper nursing intervention, the patient demonstrated behaviors to relieved constipation as evidenced by feeling of relieved and urge to defecate
S> parang puputok na ang pantog ko. O>Received patient in bed at supine position >with ongoing PNSS @ R arm regulated at 30 gtts/min >awake, conscious and coherent > bladder distension > small frequent voiding > urine output of 150cc within 8 hrs A>Chronic urinary retention related to pain felt during urination secondary to obstruction of the urinary tract. P> Within 4-8 hrs of proper nursing interventions the patient will be able to void in sufficient amounts with no palpable bladder distention I>evaluated hydration status >poured warm water over perineum to stimulate reflex arc >encouraged client to report problems immediately >measured amount of voided residual >determined frequency of voiding >encouraged patient to use valsalva maneuver if appropriate R> After 4-8 hrs, of proper nursing interventions, the patient voided in sufficient amounts (260 cc in 8 hrs.) with no palpable bladder status
III. CONCLUSION In doing this study, the group had met all the nursing and client objectives that were formulated. The group was able to practice the skills and observed and applies the theories and concept that were learned during lecture days. In addition to this, dealing with a client with Nephrolithiasis gave opportunity to review the different body systems involved and the possible manifestations that would appear on a client with this kind of disease process. The group also became familiarized with various tests and diagnosis of the disease. As student nurses, the group was able to apply the proper nursing interventions and assessment. With regards to the client centered objectives, the client acquires knowledge about the current condition and carries out actions independently. IV. RECOMMENDATION: After stone passage or successful medical/surgical treatment, patient should be evaluated metabolically with serum studies and a 24 hr urine profile to determine whether any metabolic abnormalities exist that predispose to stone formation. Patients can be placed on the appropriate medication or alter their diet/lifestyle if needed. Periodic 24 hr urine monitoring should be performed to assess the efficacy of dietary/ lifestyle changes and medication. Imaging with non contrast CT scan or KUB should be carried out every six to twelve months to monitor for recurrence or increased in the size of existing stones.
You might also like
- Pharmaco TherapeuticsDocument19 pagesPharmaco TherapeuticsJareena BegumNo ratings yet
- Geria ReviewerDocument7 pagesGeria ReviewerCarl John ManaloNo ratings yet
- FundaDocument81 pagesFundatzuquinoNo ratings yet
- COA OB WardDocument17 pagesCOA OB WardChristian PasiliaoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Phinma University of PangasinanDocument4 pagesDrug Study: Phinma University of PangasinanBrythym De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- IV PathophysiologyDocument5 pagesIV PathophysiologyJanedear Pasal100% (1)
- Complications During Pregnancy - Chapt 5Document93 pagesComplications During Pregnancy - Chapt 5klyde_evangelistaNo ratings yet
- Part 1 RenalDocument8 pagesPart 1 RenalKatherine ApostolNo ratings yet
- FERRER, GIENELLE SJ. (Job Description-HEAD NURSE) 4BSN2Document2 pagesFERRER, GIENELLE SJ. (Job Description-HEAD NURSE) 4BSN2Gienelle Susana San Juan FerrerNo ratings yet
- GastroDocument82 pagesGastroZhailyn Joy DumlaoNo ratings yet
- Nephrolithiasis PDFDocument16 pagesNephrolithiasis PDFApriany Cordias Arlita SilalahiNo ratings yet
- Ob QuestionsDocument7 pagesOb Questionslbordonada100% (1)
- Caesarian: Saint John Colleges Calamba, City College of NursingDocument37 pagesCaesarian: Saint John Colleges Calamba, City College of NursingaudreylineNo ratings yet
- Nursing Leadership and ManagementDocument13 pagesNursing Leadership and ManagementKhatlene Joy Raymundo100% (1)
- Name: - Score: - Year and SectionDocument12 pagesName: - Score: - Year and SectionSteve EstebanNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Chamberlain College of NursingDocument5 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Chamberlain College of NursingHugsNo ratings yet
- Crestor (Rosuvastatin Calcium) : Abbreviations Abbrev Definitions Dictionary ICD9 Codes Equipment Hospitals Drugs More.Document2 pagesCrestor (Rosuvastatin Calcium) : Abbreviations Abbrev Definitions Dictionary ICD9 Codes Equipment Hospitals Drugs More.Aidi RahmanNo ratings yet
- NCMB 419 Week 11 CU10Document23 pagesNCMB 419 Week 11 CU10GERALDINE GONZALESNo ratings yet
- St. Paul University Dumaguete: College of Nursing Nursing Local Board Review 2021Document16 pagesSt. Paul University Dumaguete: College of Nursing Nursing Local Board Review 2021Gee Angela Zozobrado100% (1)
- Anemia in PregnancyDocument7 pagesAnemia in PregnancyLenrok AdrianNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Ureteral CalculiDocument14 pagesPathophysiology of Ureteral CalculiEdmel Pamplona DuquesaNo ratings yet
- MI LABS ExplainedDocument3 pagesMI LABS Explainedjrubin83669No ratings yet
- Professional AdjustmentDocument3 pagesProfessional Adjustmentkamae_27No ratings yet
- Nursing Management Pancreatic CancerDocument2 pagesNursing Management Pancreatic CancerKit NameKo100% (2)
- EclampsiaDocument56 pagesEclampsiagalihtrimuninggarNo ratings yet
- Obstetric Case Study CesarianDocument16 pagesObstetric Case Study CesarianRazan NasereddineNo ratings yet
- BY: Amy Rose Abueva, Karyll Chelsea GulfanDocument19 pagesBY: Amy Rose Abueva, Karyll Chelsea GulfanAmy Rose AbuevaNo ratings yet
- Determine The Gestational AgeDocument18 pagesDetermine The Gestational AgeMomshie Felaih Binasoy Dela Cruz100% (1)
- Avandia RosiglitazoneDocument1 pageAvandia RosiglitazoneCassieNo ratings yet
- Atun Maricris Jorre Ca2 Au Legarda Leadership Managemet Research DownloadableDocument2 pagesAtun Maricris Jorre Ca2 Au Legarda Leadership Managemet Research DownloadableCharissa Magistrado De LeonNo ratings yet
- Rle Week 13Document8 pagesRle Week 13Roselyn Yu QuintoNo ratings yet
- Anemia in PregnancyDocument13 pagesAnemia in PregnancyHerliyaNo ratings yet
- Care of Adults 26 Endocrine ManagementDocument26 pagesCare of Adults 26 Endocrine ManagementGaras AnnaBerniceNo ratings yet
- Tetanus CaseDocument12 pagesTetanus CasePam RomeroNo ratings yet
- Esarean Ction: Cadalin, Fremelen Rose Cedamon, CarloDocument18 pagesEsarean Ction: Cadalin, Fremelen Rose Cedamon, CarloMonette Abalos MendovaNo ratings yet
- Recalls 7 CompilationDocument117 pagesRecalls 7 CompilationReka LambinoNo ratings yet
- NCM 107 SwotDocument7 pagesNCM 107 SwotpauchanmnlNo ratings yet
- The Nusing Process PDFDocument18 pagesThe Nusing Process PDFMae Anne MarceloNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Acute CholecystitisDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Acute CholecystitisKush KhannaNo ratings yet
- GROUP 3. Peripheral Arterial Occlusive Diseases PAODDocument73 pagesGROUP 3. Peripheral Arterial Occlusive Diseases PAODLeslie Anne Oayan DaulayanNo ratings yet
- Electrolyte ImbalanceDocument4 pagesElectrolyte ImbalanceDoneva Lyn MedinaNo ratings yet
- PlateletDocument16 pagesPlateletArgene Rose MilletNo ratings yet
- ImmunedisorderDocument3 pagesImmunedisorderDyan LazoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Process Focus Clients Receiving Ferrous Sulfate (Feosol, Others)Document1 pageNursing Process Focus Clients Receiving Ferrous Sulfate (Feosol, Others)TracyNo ratings yet
- Post Cesarean Section DeliveryDocument5 pagesPost Cesarean Section Deliveryᒙᕧᖇᕦᙏᖻ ᗴᔛᓦᗩᖆᗩNo ratings yet
- Wound Essentials 2 The Treatment of Pressure Ulcers From Grade 1 To Grade 4Document5 pagesWound Essentials 2 The Treatment of Pressure Ulcers From Grade 1 To Grade 4archanaNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Test QuestionsDocument6 pagesMultiple Choice Test QuestionsNicole MaeNo ratings yet
- Cefadroxil: Antibiotic ClassDocument2 pagesCefadroxil: Antibiotic ClassTariNo ratings yet
- Coreg (Carvedilol)Document1 pageCoreg (Carvedilol)Adrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- Practice Summary Paper For PortfolioDocument9 pagesPractice Summary Paper For Portfolioapi-290938460No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyGian Era100% (1)
- Diffrent Types of IVFDocument2 pagesDiffrent Types of IVFGail SantosNo ratings yet
- Factors Associated With The Perceptions of Physicians and Patients Regarding Disclosure of Death and Poor Prognosis in Zamboanga City Medical Center-Soliven 2016Document86 pagesFactors Associated With The Perceptions of Physicians and Patients Regarding Disclosure of Death and Poor Prognosis in Zamboanga City Medical Center-Soliven 2016Moritz SolivenNo ratings yet
- PotassiumDocument2 pagesPotassiumNinoska Garcia-Ortiz100% (18)
- COMPREHENSIVE NURSING ACHIEVEMENT TEST (RN): Passbooks Study GuideFrom EverandCOMPREHENSIVE NURSING ACHIEVEMENT TEST (RN): Passbooks Study GuideNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to Parathyroid Adenoma, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Parathyroid Adenoma, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Group 2 - NCA-To The Bone (Anorexia)Document109 pagesGroup 2 - NCA-To The Bone (Anorexia)Ruthangela GarciaNo ratings yet