What is router: Communicates between different netwoks It provides WAN connectivity It does routing(Select best paths) It works at layer
3 It can read IP header It maintains IP routing table which contains best paths to destination networks Types of routers Software routers o Dual home system with routing enabled o Windows server 2003,2008,linux server Hardware routers Hardware device-dedicated routing Cisco router Router manufacturers Cisco DAX JUNIPER LINKSYS NOKIA D-LINK ZYXEL 3COM Types of cysco Routers: Fixed routers Fixed [Link] interfaces No hardware upgrade Cheaper
�Modular routers No. of interfaces can be increased Hardware upgrade is possible Costlier Ex:
�Attachment unit interface:
AUI pin configuration is 15 pin female. It is known as Ethernet Port or LAN port or Default Gateway. It is used for connecting LAN to the Router. Transceiver is used for converting 8 wires to 15 wires. i.e. RJ45 to 15 pin converter.
Serial port Serial pin configuration is 60 pin configuration female (i.e. 15 pins and 4 rows) and Smart Serial pin configuration is 26 pin configuration female. It is known as WAN Port It is used for connecting to Remote Locations V.35 cable is having 60 pin configuration male at one end and on the other end 18 pin configuration male.
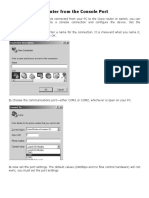
�Console Port It is known as Local Administrative Port It is generally used for Initial Configuration, Password Recovery and Local Administration of the Router. It is RJ45 Port IMP : It is the most delicate port on the Router. So make less use of the Console Port.
Console connectivity
�Connect a rollover cable to the router console port (RJ-45 connector). Connect the other end of the rollover cable to the RJ-45 to DB-9 converter Attach the female DB-9 converter to a PC Serial Port. Open Emulation Software
DB9 convertor
Internet Structure; Internet centers, companies are connected to lacal ISPs(Internet service provider) Local ISPs are connected to Regional ISPs
�Regional ISPs are connected National ISPs National ISPs are connected to Global ISPs Data flow rate is low at local ISPs and gradually increased till Global ISPs The devices at Global ISPs must be high end devices
CISCO 3-Layer Hierarchy CISCO routers are divided into 3 categories based on hardware capabilities Access Layer Distribution layer Core Layer Access Layer: Used for small organizations Data transfer speed is low Local ISPs 1600.1700 series routers Fixed routers Distribution Layer: Used for medium level Organizations Data transfer speed is medium Regional ISPs, national ISPs 2600,2800,3600 series routers Modular Routers
�Core Layer: Used for medium and high level organizations Data transfer speed is high National ISPs and Global ISPs 6000,7000,10000,12000 series routers Modular Router physical structure external components-cisco 2601
POST: Power on self test Hardware checkup RAM, CPU, Interfaces diagnosis ROM: Read only memory Bootstrap loader/ Mini IOS Finds the location of complete IOS FLASH: Complete IOS image May have multiple IOS Images Router operates with single IOS
�Eg: [Link] NVRAM: Non Volatile Random Access Memory Permanent configuration Filename:startup-config Router always uses NVRAM configuration when booting Router copies NVRAM into RAM RAM; Random Access Memory Temporary configuration Filename Running-cofig Router copies NVRAM into RAM Router always works with RAM configuration only
If there is no IOS, router uses bootstrap loader The prompt would be Router(boot)> Rommon> Router boot Sequene: Router boot sequence depends on Configuration Register Value This value decides the router to use IOS OR Bootstrap loader This value decides the router to use NVRAM or not Configuration Register value is 16 bit value
What is the Operating System in Router: Router works on IOS IOS-internetwork operating system
�Router works on single IOS image file Router configuration is Mandatory? Configuration is mandatory Router works if it is configured properly Dont connect the router without configuration Router is not a zero touch configuration device How configure the router? Use console 0 to configure the router firsttime Connect roll over cable between console 0 on router and comport on the computer / laptop
Emulation Software:
�One application is required on the laptop/system IOS and to configure router. This software is called emulation software Eg: hyper terminal, putty How to access Hyper terminal Start->programmes->Accessories->communications>Hyperterminal (or) Start->Run->type hypertrm
Type the name of the session
�Define the connection type
Define the port settings of the comport
�Note: press restore defaults
Router Modes Cisco IOS has different modes. Every modes has its own functionalities Cisco IOS is CLI (command line interface) based
� Commands are made specific Router (Config) # Router modes Prompts:-
Router> Router# Router (Config) # Router (Config-if)# # Router (Config-line) # Router modes Names:User Mode Privilege Mode Global Configuration Interface mode Line Mode Router mode Router (Configrouter) #
�User Exec router >
enab
Privilege Mode router # Confi Global Configuration router (config) # Line con 0 Router rip Line aux 0 Router igrp 10
gt
End/Ctrl+Z
Int e 0 Int s 0 Int s 1
Line vty 0 4 Router ospf 34
�Interface mode
Line Mode
Router mode
Router Modes Functionalities Commands User mode: Router >
1.
Functiuons To check the connectivity It has limited fucntionality Commands Command telnet ip Ping ip Traceroute ip Enable Function To telnet into a device To check connectivity To trace the path To enter privilege mode Privilage mode: Router # View entire configuration Backup & recovery
2.
Functions:
�Command Show run Show start Show int s 0 Show ip route Show version
Functions To see temporary configuration To see permanent configuration Displays into about interface s 0 Displays routing table Displays version config register value Show flash Displays flash contents/ios image Show ip protocols Displays configured routing protocols Show ip int brief Displays interface ip information Show controllers serial 0 Displays hardware info of s0 DCE/DTE Reload Restarts the router Config t Enters into global configuration mode Copy run start/write Save RAM contents to NVRAM Global configuration mode Functions: To do entire configuration Commands Commands No logging console Hostname hostname Enable Password Cisco Enable secret Cisco Function Turns off logging (logging messages) Changes the host name Set privilege mode password Set secret password for privilege mode
�Ip routing No ip routing Config-register 0*2102 Ip route Int s 0 Int s 1 Int e 0 Line con 0 Line aux 0 Line vty 0 4 Router rip Router eigrp 23 Router ospf 56
Enable routing table Disable routing table Set the config register value to 2102 To configure static route To interface mode To line mode To router mode
Interface Mode (router- config-if) # Functions: Configuration of interfaces Commands:-
Commands Ip address <ip><subnetmask> No shutdown Encapsulation hdlc
Function To configure ip address for interface Activate the interface Set L2 encapsulation for wan ports
�Clock rate 64000 Bandwidth 64
Set clock rate (DCE interface) Set interface bandwidth
5. Line mode router (config-line) # Functions: Authenciation of lines Configuring console 0, aux 0, vty 0 4 Commands Command Password <password> Login Function To configure password for line To set login type
6. router mode (config-router ) # Functions
To configure dynamic routing protocols.
Commands Command Network <network address> Auto summary Function To advertise networks in routing Auto summarize networks
�Tips in IOS usage: Use ? to get the help. Use tab to get the complete command after entering unique characters of a command Use no keyword along qith the command for reverse results Use q or ctrl+c to terminate output. Router and Switch Properties: Switch in lan: We can communicate only same network related systems Router in lan We can communicate different networks What is default Gateway: Entry or Exit point of a network This is the ip address used to communicate with different networks Default gateway is typically the ip address of the router Default gateway is not required within the network Default gateway mustbe configured in every computer to communicate with different networks What is routing Table? This list of networks that router knows Router can reach only those networks which are presented in its routing table Routing table contains only the best paths to reach networks
� Routing table includes network address, exit interface Network Design Rules All connected interfaces must be different networks All the lans must be different networks Lan and default gateway must be in same network Two directly connected interfaces must be same network
Router Initial configuration: Router is not a zero-touch configuration device It must be configured with proper ip address. If not, it wont work Router configuration includes 4 steps [Link] changes [Link] router [Link] interfaces [Link] and save 1. Hostname changes: Router> enable Router# configure terminal Router (config)#hostname vja 2. Secure Router: Vja(config)# enalble password cisco Vja(config)# enable secret ccna Vja(config)#line console 0 Vja(config)#password cisco Vja(config)#login Vja(config)#exit Vja(config)#line
�ROUTING:-
What is routing?
Communication between two different networks Router can communicate with those networks presented in its routing table By default routing table maintains connected networks information If there is no information in the routing table about a destination Network router drops all the packets for that destination So Destination networks must be added to the routing table This process is called routing
Router(config)#no ip routing --- To disable routing Process Router(config)#ip routing --- To enable routing process Router#show ip route ---------- To view routing table
Routing can be done in two ways
static Routing Dynamic Routing Static Routing:
Manual Routing Administrative work is more It is suitable for small networks Suitable for fixed networks Administrative distance is 1 Single change may effect all the router configuration
Dynamic Routing:
Routing happens dynamically (auto) by using routing protocols Administrative work is less
It is suitable for large networks Suitable for scalable networks Administrative distance depends on routing protocol single change will not effect the remaining routers configuration Destination network information is obtained and updated Automatically
syntax:
1. Router(config)#ip route <network> <subnetmask> <exit int> or 2. Router(config)#ip route <network> <subnet mask> <next hop> 3. Exit interface: Interface on the home router which forwards the data to the next router 4. Next hop ip address: Interface IP address of next immediate router towards the destination