Professional Documents
Culture Documents
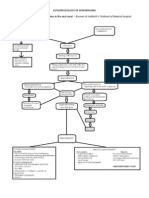
Dysphagia
Uploaded by
mainehoonaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Dysphagia
Uploaded by
mainehoonaCopyright:
Available Formats
Treatment and management of Dysphagia 1. Congenital abnormalities e.g congenital atresia of oesophagus and trachea_oesophageal fistula are associated.
Mostly its the lower segment that communicates with the trachea. Newborn suffers from attacks of coughing and cyanosis on feeding. Treatment Includes corrective surgery straight after diagnosis. If the distance between the two ends is long then there is no need for surgery. Instead its usual to wait for several weeks so that the two ends of the oesophagus can grow towards each otherreducing the distance. During this period the child is fed through a gastrostomy tube. Operation Thoracotomy is performed where the lower segment is divided at its entrance into the trachea and the fistula closed. 2. Foreign bodies arrested in the oesophagus Are mostly removed by endoscopy i.e flexible endoscopy is the method of choice and most of the objects can be extracted with grasping forceps, a snare or a basket. If the object is seems to injure on withdrawal an overtube should be used. N/B button batteries are a particular worry since they are difficult to grasp and its tempting to push them into the stomach. 3. Paraoesophageall (rolling) hiatus hernia Is a hernia in which the cardia remains in its normal anatomical position as majority of rolling hernias usually result in the cardia getting displaced into the chest.Most common sypmtoms of rolling hernias are mostly due to twisting and distortion of the oesophagus and stomach. Dysphagia is common. It always recquires surgical repair as its potentially dangerous! Patients who present as an emergency with acute chest pain may be initially treated by nasogastric tube to relieve the distention that caused thepain followed by repair. If pain is not relieved or perforation is suspected immediate operation is mandatory. 4. Carcinoma of oesophagus Whereby dysphagia is the usual presenting feature and is generally a sign of advanced disease. Here a gastrosomy should never be carried out! It is important to provide relief of dysphagia, as the patient should not be submitted to needlessly aggressive treatment. Surgery.curative surgery involves resection of an appropriate length of the oesophagus. The access to the oesophagus through the right chest is the best approach. The azygos vein is divided allowing easy acess to the whole intrathoracic oesophagus. A thoracotomy with entry above the 5th rib gives best access to mid-mediastinum and the thoraicic inlet. The oesophagus is divided just below the thoracic inlet giving adequate clearance since most lesion are in the middle third or lower third. The oesophagus is opened to check if the lesion is circumscribed or diffusely infiltrating.
Radiotherapyproduces long-term survival in oesophageal cancer though at present surgical resection produces the best survival rates and quality of life. The survival figures show that neither surgery not radiotherapy are particularly effective treatments. Chemotherapy.never cures, but shrinks the disease in upto60% of the cases. Intubation..with various types of expanding metal stents which produce a better lumen for swallowing though they are quite expensive. Endoscopic laser treatment may be used to core a channel through the tumour causing an improvement in swallowing. Though it does have a disadvantage of being repeated every few weeks. 5. Achalasia The two main methods of treatment are forceful dilatation of cardia and hellers myotomy. Forceful dilatationinvolves stretching the cardia with a balloon (plastic type with a fixed external diameter) to disrupt the muscle and render it less competent. Perforation is a complication, where the risk increases with bigger balloons. curative in about 75-85%cases. Results are best in people aged more than 45yrs. Hellers myotomyinvolves cutting the muscle of the lower oesophagus and cardia. The major complication is gastro-oesophageal reflux. Successful in more than 90% cases and maybe used after failed myotomy. 6. other non-neoplastic conditions Oesophagitis due to candida albicans may present with dysphagia, in patients taking steroids. Endoscopy shows numerous white plaques that cannot be moved. Treatment is with nystatin lozenges or other anti-fungal agents. Schatzkis ring Is a circular ring I the distal oesophagus. The core of the ring consists of variable amounts of fibrous tissue and cellular infiltrate. Some are associated with dysphagia and a single dilatation is curative.
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Case Study - HemorrhoidsDocument4 pagesCase Study - HemorrhoidsBianca Freya Porral100% (4)
- 441120719divya PushparajDocument139 pages441120719divya PushparajDipali MaliNo ratings yet
- Note DR Ikhwan SaniDocument39 pagesNote DR Ikhwan SaniShutter Man100% (1)
- Surgery OSCE Stations With KeyDocument274 pagesSurgery OSCE Stations With KeyMoazzam AliNo ratings yet
- SutureDocument4 pagesSutureDanica DeeNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Artery DiseaseDocument8 pagesPeripheral Artery DiseasemainehoonaNo ratings yet
- AIIMS Nursing Officer Question Paper With Key 2019-1Document35 pagesAIIMS Nursing Officer Question Paper With Key 2019-1shubham vermaNo ratings yet
- CPR PDFDocument37 pagesCPR PDFArdhi AgustjikNo ratings yet
- Laparoscopic Bilateral Tubal LigationDocument2 pagesLaparoscopic Bilateral Tubal Ligationapi-3712326100% (1)
- ChoreaDocument6 pagesChoreamainehoonaNo ratings yet
- What Is Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) ?: Blood VesselsDocument6 pagesWhat Is Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) ?: Blood VesselsmainehoonaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Features of ParaperesisDocument31 pagesClinical Features of ParaperesismainehoonaNo ratings yet
- Huntington's Disease: Liver Disease Dystonia VomitingDocument5 pagesHuntington's Disease: Liver Disease Dystonia VomitingmainehoonaNo ratings yet
- Risk Factors For DiabetesDocument2 pagesRisk Factors For Diabetesmainehoona100% (1)
- Movement Disorders Include:: and Lower Lip)Document7 pagesMovement Disorders Include:: and Lower Lip)mainehoonaNo ratings yet
- Chocolate-Orange Carrot Cake: IngredientsDocument2 pagesChocolate-Orange Carrot Cake: IngredientsmainehoonaNo ratings yet
- Blood Supply of Long BonesDocument4 pagesBlood Supply of Long BonesmainehoonaNo ratings yet
- POPDocument42 pagesPOPmainehoonaNo ratings yet
- POPDocument42 pagesPOPmainehoonaNo ratings yet
- Turn On Your Favourite Film and Relax in Front of The TV With The Ultimate Caramel Popcorn!Document2 pagesTurn On Your Favourite Film and Relax in Front of The TV With The Ultimate Caramel Popcorn!mainehoonaNo ratings yet
- Shirazi Salad: IngredientsDocument2 pagesShirazi Salad: IngredientsmainehoonaNo ratings yet
- PubertyDocument1 pagePubertymainehoonaNo ratings yet
- Cancer Prevention: 7 Tips To Reduce Your RiskDocument3 pagesCancer Prevention: 7 Tips To Reduce Your RiskmainehoonaNo ratings yet
- The Hidden Issues of MarriageDocument9 pagesThe Hidden Issues of MarriagemainehoonaNo ratings yet
- Medications For Nebulizer Treatment: BronchodilatorsDocument2 pagesMedications For Nebulizer Treatment: BronchodilatorsmainehoonaNo ratings yet
- As You Inspired Others .. You Added Meaning To Our Life, Too Thanks For Being Great Inspirers . Always .Document6 pagesAs You Inspired Others .. You Added Meaning To Our Life, Too Thanks For Being Great Inspirers . Always .mainehoonaNo ratings yet
- Neuro DisordersDocument159 pagesNeuro DisordersQuolette Constante100% (1)
- The European Guideline On Management of Major Bleeding and Coagulopathy Following Trauma Sixth Edition (2023) PDFDocument1 pageThe European Guideline On Management of Major Bleeding and Coagulopathy Following Trauma Sixth Edition (2023) PDFMatheus LiraNo ratings yet
- ENT Batch 2022 Annual Paper-1Document9 pagesENT Batch 2022 Annual Paper-1mudassirahmedNo ratings yet
- Lumbar Laminectomy IntroductionDocument4 pagesLumbar Laminectomy Introduction09194691603No ratings yet
- Presentation For Rotary Club of Dhaka BurigangaDocument44 pagesPresentation For Rotary Club of Dhaka Burigangaprince323No ratings yet
- 010 - Hand FlapsDocument20 pages010 - Hand FlapsJayNo ratings yet
- New Deadline For Submission of AbstractsDocument2 pagesNew Deadline For Submission of AbstractsmanognaaaaNo ratings yet
- Comparative Study of PFNA Vs PFNA 2 in Unstable inDocument4 pagesComparative Study of PFNA Vs PFNA 2 in Unstable inzubayetarkoNo ratings yet
- Mod9Week3 - PA 3306 - Sept 5&6Document22 pagesMod9Week3 - PA 3306 - Sept 5&6komal sheikhNo ratings yet
- Reviewer - CamcaDocument11 pagesReviewer - CamcaLouise Andrea OdulioNo ratings yet
- Pleural EffusionDocument72 pagesPleural Effusionmaeliszxc kimNo ratings yet
- Neurointensive CareDocument21 pagesNeurointensive CareNancy IratiNo ratings yet
- 13 - Daftar Pustaka NewDocument3 pages13 - Daftar Pustaka NewalfianiNo ratings yet
- Journal of Pediatric Surgery: Ibrahim UygunDocument4 pagesJournal of Pediatric Surgery: Ibrahim UygunNur Ainatun NadrahNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal System DisordersDocument112 pagesGastrointestinal System DisordersTaate MohammedNo ratings yet
- Robot-Assisted Radical Cystectomy and Urinary Diversion in Female Patients Technique With Preservation of The Uterus and VaginaDocument8 pagesRobot-Assisted Radical Cystectomy and Urinary Diversion in Female Patients Technique With Preservation of The Uterus and Vagina肖楚天No ratings yet
- 15 Physio OB - Normal LaborDocument8 pages15 Physio OB - Normal LabormaqmmNo ratings yet
- Evolution in Techniques For Endsocopic Brow Lift With Deep Temporal Fixation Only and Lower Blepharoplasty-Transconjunctival Fat RepositioningDocument16 pagesEvolution in Techniques For Endsocopic Brow Lift With Deep Temporal Fixation Only and Lower Blepharoplasty-Transconjunctival Fat RepositioningBFF BotoxNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Wall - HoDocument71 pagesAbdominal Wall - HoMekuriya BeregaNo ratings yet
- 1411-Article Text-2128-1-10-20190318Document65 pages1411-Article Text-2128-1-10-20190318sagaNo ratings yet
- Knee Cartilage and MeniscalDocument4 pagesKnee Cartilage and MeniscalKapil LakhwaraNo ratings yet
- Past Paper - 221208 - 003047Document96 pagesPast Paper - 221208 - 003047Ashraf ShalbiNo ratings yet