Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Final Study PDF
Final Study PDF
Uploaded by
Derek AOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Final Study PDF
Final Study PDF
Uploaded by
Derek ACopyright:
Available Formats
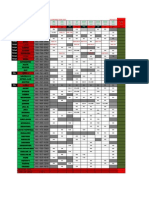
Final&Study&Guide&&
Microbiology&
Ascaris lumbricoides (eggs)- NematodeHELMINTHES
Ascaris lumbricoides - Nematode- Helminthes
Aspergillus Condia- FUNGI
Bacillus
Balantidium coli- Phylum Cilliophora- Protozoa
Candida albicans (budding Yeast) FUNGI
Capsule stain
Clostridium
Endospore
ENTERIC
Enterobius vermicularis - NematodeHELMINTHES
Entamoeba histolytica - Subphylum sarcodinaProtozoa
Fasciola hepatica- Trematodes- HELMINTHES
Flagella
Giardia lamblia- Sarcomastigophora:Subphylum Mastigophora - PROTOZOA
Nisseria
Plasmodium vivax - ApicomplexansPROTOZOA
Penicillium notatum- FUNGI
Schistosoma japonicum -TrematodesHELMINTHES
Schistosoma mansoni (eggs) - TrematodesHELMINTHES
Staph
Strept
Taenia solium- Cestodes- HELMINTHES
TRICHOMONAS vaginalis -Sarcomastigophora PROTOZOA-
Beta-hemolysin breaks down the red blood cells and hemoglobin completely. This leaves a clear zone around the bacterial growth.
Alpha-hemolysin partially breaks down the red blood cells and leaves a greenish color behind
If the organism does not produce hemolysins and does not break down the blood cells, no clearing will occur. This is called -hemolysis (gamma hemolysis).
POSITIVE
NEG
Bacterial Susceptibility test on Blood Agar
Bile esculin agar contains oxgall (bile salts) to inhibit the growth of gram positive organisms other than enterococci and group D streptococci.
(MSA) is a selective and differential medium. The high concentration of salt (7.5%) selects for members of the genus Staphylococcus, since they can tolerate high saline levels. If an organism can ferment mannitol, an acidic byproduct is formed that will cause the phenol red in the agar to turn yellow.
Coagulase&Test&
Urea&Test&
+&
The coagulase test identies whether an organism produces the exoenzyme coagulase, which causes the brin of blood plasma to clot.
=&
9&
differential medium that tests the ability of an organism to produce an exoenzyme, called urease, that hydrolyzes urea to ammonia and carbon dioxide.
selective and differential medium designed to isolate and differentiate selective and differential medium used to isolate fecal coliforms enterics based on their ability to ferment lactose. Bile salts and crystal Green=fermentation+acid Pink= Fermentation little acid violet inhibit the growth of Gram positive organisms
Indole&test&
Glucose&Fermenta@on&
N/R&
Sim Medium used to detect enterics
Methyl&Red&Test&
The Methyl Red test involves adding the pH indicator methyl red to an inoculated tube of MR-VP broth. If the organism uses the mixed acid fermentation pathway and produces stable acidic end-products, the acids will overcome the buffers in the medium and produce an acidic environment in the medium. When methyl red is added, if acidic end products are present, the methyl red will stay red.
SIM&Tubes&
SIM medium is a combination differential medium that tests three different parameters, which are represented by the three letters in the name: Sulfur Reduction Indole Production Motility
used to detect acetoin in a bacterial broth culture. The test is performed by adding alphanaphthol and potassium hydroxide to the Voges-Proskauer broth which has been inoculated with bacteria. A cherry red color indicates a positive result, while a yellow-brown color indicates a negative result.
NO REACTION
POSSITIVE
+ IODINE
Starch agar is a differential medium that tests the ability of an organism to produce certain exoenzymes, A clearing around the bacterial growth indicates that the organism has hydrolyzed starch.
The oxidase test identies organisms that produce the enzyme cytochrome oxidase. If the test organism produces cytochrome oxidase, the oxidase reagent will turn blue or purple within 15 seconds.
Lactose&Fermenta@on&
+&Gas&&&&&&&&&+&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&=&
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5819)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (845)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Training Study GuiedDocument13 pagesTraining Study GuiedDerek A100% (2)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Infection Control ManualDocument206 pagesInfection Control ManualJohnny DeeNo ratings yet
- Buku TARIF PRODIADocument553 pagesBuku TARIF PRODIAAprillia Putrie100% (6)
- Lehi 7-17 FOH SchedDocument1 pageLehi 7-17 FOH SchedDerek ANo ratings yet
- Lehi 7-31FOH SchedDocument1 pageLehi 7-31FOH SchedDerek ANo ratings yet
- Temple LEA Lecture GuideDocument164 pagesTemple LEA Lecture GuideDerek ANo ratings yet
- Lehi 7-17 FOH SchedDocument1 pageLehi 7-17 FOH SchedDerek ANo ratings yet
- Lehi 7-17 FOH SchedDocument1 pageLehi 7-17 FOH SchedDerek ANo ratings yet
- Lehi 6-5 FOH SchedDocument1 pageLehi 6-5 FOH SchedDerek ANo ratings yet
- Lehi 5-29 FOH SchedDocument1 pageLehi 5-29 FOH SchedDerek ANo ratings yet
- Lehi 7-10 FOH SchedDocument1 pageLehi 7-10 FOH SchedDerek ANo ratings yet
- Lehi 5-15 FOH SchedDocument1 pageLehi 5-15 FOH SchedDerek ANo ratings yet
- TUSPM Student HandbookDocument198 pagesTUSPM Student HandbookDerek ANo ratings yet
- Lehi 6-26 FOH SchedDocument1 pageLehi 6-26 FOH SchedDerek ANo ratings yet
- New Student Aid ProcessDocument2 pagesNew Student Aid ProcessDerek ANo ratings yet
- Lehi 5-1 FOH SchedDocument1 pageLehi 5-1 FOH SchedDerek ANo ratings yet
- Derek: TR TR TR TR TR TR TR TR TR TR TR Alex Alicia ALYDocument1 pageDerek: TR TR TR TR TR TR TR TR TR TR TR Alex Alicia ALYDerek ANo ratings yet
- Lehi 12-12 FOH SchedDocument1 pageLehi 12-12 FOH SchedDerek ANo ratings yet
- Christmas ScheduleDocument1 pageChristmas ScheduleDerek ANo ratings yet
- Lehi 11-07 Foh SchedDocument1 pageLehi 11-07 Foh SchedDerek ANo ratings yet
- Lehi 11-21 Foh SchedDocument1 pageLehi 11-21 Foh SchedDerek ANo ratings yet
- Lehi 11-14 Foh SchedDocument1 pageLehi 11-14 Foh SchedDerek ANo ratings yet
- The Four Temperaments in Greek MedicineDocument98 pagesThe Four Temperaments in Greek MedicineCor ScorpiiNo ratings yet
- Hemodialysis Clinic Assessment ToolDocument5 pagesHemodialysis Clinic Assessment ToolAn-Nisa Khoirun UmmiNo ratings yet
- Acute GlomerulonephritisDocument21 pagesAcute Glomerulonephritisbrinda johnNo ratings yet
- Glomerular DiseasesDocument28 pagesGlomerular DiseasesNagaraj Reddy100% (1)
- Lecture 11 - Chemotherapy and AntibioticsDocument2 pagesLecture 11 - Chemotherapy and AntibioticsAngela ChoiNo ratings yet
- Pmls 1 Final Exam Reviewer: Clinical Chemistry ContDocument14 pagesPmls 1 Final Exam Reviewer: Clinical Chemistry ContPlant in a PotNo ratings yet
- McGoldrick - Infection Control Ritual To Science - Based PracticeDocument8 pagesMcGoldrick - Infection Control Ritual To Science - Based PracticeUswaPutriemelelaNo ratings yet
- STI Slides EditedDocument43 pagesSTI Slides Editedokureblessing33No ratings yet
- SummaryDocument47 pagesSummaryDelon van den AkkerNo ratings yet
- Protozoa: Department of Parasitology Medical Faculty, Hasanuddin UniversityDocument21 pagesProtozoa: Department of Parasitology Medical Faculty, Hasanuddin UniversityNurul fatimahNo ratings yet
- Case Protocol UtiDocument4 pagesCase Protocol UtiRommel IrabagonNo ratings yet
- I. Bacterial Transformation: 12.1 Identifying The Substances of GenesDocument2 pagesI. Bacterial Transformation: 12.1 Identifying The Substances of Genesapi-308255098No ratings yet
- Pathophysio 101 To 117qDocument27 pagesPathophysio 101 To 117qRaquel Bencosme0% (1)
- Thesis LagundiDocument10 pagesThesis LagundiPrincess Joy Torrijas Factora100% (10)
- My SeminarDocument52 pagesMy SeminarvinnycoolbuddyNo ratings yet
- Acute Flaccid Paralysis: Dr. Rajakumar Professor Dept of Pediatrics Sssmc&RiDocument18 pagesAcute Flaccid Paralysis: Dr. Rajakumar Professor Dept of Pediatrics Sssmc&RiMaaddyKumarNo ratings yet
- Nursing Case StudyDocument26 pagesNursing Case StudyjoselaureanoNo ratings yet
- The Lymphatic & Immune Systems: Thymus Spleen Lymph Nodes Lymphatic VesselDocument30 pagesThe Lymphatic & Immune Systems: Thymus Spleen Lymph Nodes Lymphatic VesselAubrey SungaNo ratings yet
- Gastroenteritis in Children: Prepared by R. J. C. Manalo, BSN, RN, MNDocument45 pagesGastroenteritis in Children: Prepared by R. J. C. Manalo, BSN, RN, MNHui ChenNo ratings yet
- Pathology and Microbiology-QbDocument3 pagesPathology and Microbiology-QbSolangkilisaravananNo ratings yet
- Project On Malaria 1Document9 pagesProject On Malaria 1Ankur BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Immunology - SyllabusDocument3 pagesImmunology - SyllabusAlaa' Al-AbdulrazzaqNo ratings yet
- NeutrophillsDocument40 pagesNeutrophillsapi-351139461No ratings yet
- Infection Control AssignmentDocument3 pagesInfection Control AssignmentTrfyghu FytghubNo ratings yet
- Exanthematous Viral DiseasesDocument64 pagesExanthematous Viral DiseasesHoc Lim SeeNo ratings yet
- Vestibular DisorderDocument6 pagesVestibular DisorderEcaterina ChiriacNo ratings yet
- MDR-TB An Update by Dr.T.V.Rao MDDocument43 pagesMDR-TB An Update by Dr.T.V.Rao MDtummalapalli venkateswara raoNo ratings yet
- Crimean-Congo Hemorrhagic Fever: TransmissionDocument2 pagesCrimean-Congo Hemorrhagic Fever: TransmissionMoin DilawarNo ratings yet