Gas Constant
Uploaded by
Ardhendu SamantaGas Constant
Uploaded by
Ardhendu SamantaUniversal Gas Constant
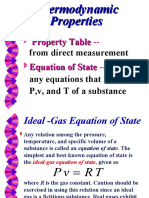
The behaviour of an Ideal gas is described by the following equation, PV = nRT Where, P = Pressure (bar, atmosphere, Pa) V = Gaseous volume (m3, cm3) n = number of gaseous moles (dimensionless) R = Universal gas constant (J/mol.K, lit.atm/mol.K) T = Temperature of the gas (K, 0C) The universal gas constant is also known by alternative names such as Ideal gas constant, molar gas constant or simply, gas constant. The universal gas constant is common for all the gases and the numerical value of this constant depends on the units used to describe the remaining entities in the Ideal gas equation, such as pressure, temperature, and volume. For different combinations of units, numerical values of Universal gas constant are given by following list, Units ( P.V / n.T ) J/K.mol cal/K.mol erg/K.mol lit.kPa/K.mol m3.Pa/K.mol cm3.MPa/K.mol m3.bar/K.mol cm3.atm/K.mol lit.bar/K.mol Value of R 8.314 1.986 8.314X107 8.314 8.314 8.314 8.314X10-5 82.06 8.314X10-2
lit.atm/K.mol lit.mmHg/K.mol lit.torr/K.mol ft.lbf/K.gmol ft.lbf/0R.lb-mol ft3.psi/0R.lb-mol ft3.atm/0R.lb-mol ft3.mmHg/K.lb-mol
0.082 62.364 62.364 6.132 1545.35 10.732 0.730 998.97
Calculation of NM3/hr and SM3/hr gas flow
Sample Problem Statement
What is the NM3/hr (normal cubic meter per hour) and SM3/hr (standard cubic meter per hour) flowrate corresponding to 100m3/hr of nitrogen flowing through a pipe? Operating temperature of nitrogen stream is 800C. Operating pressure at the point of flow measurement is 25 bar. Normal temperature and pressure conditions to be used are T = 250C and P = Atmospheric pressure Standard conditions defined by NIST to be used.
Solution
The calculation of normal and standard gas flowrates (NM3/hr and SM3/hr calculation), first requires the normal and standard conditions to be fixed. Normal temperature and pressure conditions are already defined in the problem statement and standard temperature and pressure conditions defined by NIST are to be used. Normal Temperature TN = 250C = 298.16 K Normal Pressure PN = 101.3 kPa (atmospheric pressure) From a list of standard temperature and pressure conditions defined by various organizations, the standards conditions defined by NIST are noted as, Standard Temperature TS = 00C = 273.16 K Standard Pressure PS = 101.325 kPa
The operating conditions are, Volumetric gas flow V = 100m3/hr Gas temperature T = 800C = 353.16 K Gas pressure P = 25 bar = 2500 kPa Gas volume is directly proportional to temperature and inversely proportional to pressure. Hence, gas flow at normal conditions is calculated as, NM3/hr = V(TN/T)(P/ PN) = 100(298.16/353.16)(2500/101.3) Gas flow = 2083.57 NM3/hr Gas flow at standard conditions is calculated as, SM3/hr = V(TS/T)(P/ PS) = 100(273.16/353.16)(2500/101.325) Gas flow = 1908.4 SM3/hr