GTP: Group Transfer Polymerization
Eric Silver CH392N Thursday March 12, 2009
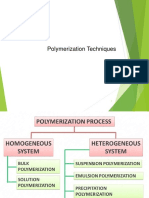
�Brief Overview
Discovery of Method Synthetic Routes Mechanisms: Then and Now Applications Pros and Cons
(Dr. Owen Webster)
http://perceco2.chem.upenn.edu/~percec/member.html
�Discovery of GTP
Webster et al at DuPonts Central R&D Needed a method for controlled living polymerizations of acrylates and methacrylates Name suggested by Trost Aiming for methods of synthesizing pigment dispersing agents and rheology control Printer Inks
Webster, O.W. Adv. Polym. Sci. 2004, 167, 1-34. http://www.mbacasestudysolutions.com/images/Dupont.gif http://www.stanford.edu/group/bmtrost/bmt.html
�Desired Characteristics
Workable Temp. range (50-80C) Can synthesize blocks Cheap production ($5>/lb.) Good PDIs and MWs (~20,000 Da) Nontoxic, colorless, no bad odors, etc.
Webster, O.W. Adv. Polym. Sci. 2004, 167, 1-34.
�Synthetic Routes
Always start with conjugate addition of silyl ketene acetal initiators Monomer: Methacrylates, Acrylates, Ketones, Nitriles, Carboxamides Catalysts: Two choices O CH3 -Nucleophilic Anions O -Lewis Acids
Si
Webster, O.W.; Hertler, W.R.; Sogah, D.Y.; Farnham, W.B.; RajanBabu, T.V. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1983, 105, 5706-5708
�Synthesis: Catalysts
Nucleophilic Anions tried by Webster: KHF2 TASHF2 = Tris(dimethylamino)-sulfonium F H H3C CH3 Bu4NF N F TASCN H3C N S N CH3 Me F Me CH3 CH3 Si O Me Si Me Et4NCN O Me Me F O Me O Me TASN3
Sogah, D.Y.; Hertler, W.R.; Webster, O.W.; Cohen, G.M. Macromolecules, 1987, 20, 1473-1488.
�Synthesis: Catalysts
Nucleophilic Anions tried by Webster: KHF2 TASHF2 = Tris(dimethylamino)-sulfonium F H H3C CH3 Bu4NF N F TASCN H3C N S N CH3 Me F Me CH3 CH3 Si O Me Si Me Et4NCN O Me Me F O Me O Me TASN3
Sogah, D.Y.; Hertler, W.R.; Webster, O.W.; Cohen, G.M. Macromolecules, 1987, 20, 1473-1488.
�Synthesis: Catalyst
Later Variations: Bu4NPhCO2HO2CPh = TBA Bibenzoate Bis(triphenylphosphoranylidene)ammonium O bifluoride
F H F P N P
O K O
O O O
Potassium 18-crown-6
Dicker, I.B.; Cohen, G.M.; Farnham, W.B.; Hertler, W.R.; Laganis, E.D.; Sogah, D.Y. Macromolecules, 1990, 23, 4034. Martin, D.T.; Bywater, S. Makromol. Chem. 1993, 193, 1011. Miller, J.; Jenkins, A.D.; Tsartolia, E.; Watson, D.R.M.; Stejskal, J.; Kratochvil, P. Polym. Bull. 1988, 20, 247.
�Synthesis: Catalyst
Lewis Acids tried by Webster: ZnBr2 ZnI2 Al Al O ZnCl2 (i-Bu2Al)2O i-Bu2AlCl Et2AlCl
Zn Cl O O CH3
Sogah, D.Y.; Hertler, W.R.; Webster, O.W.; Cohen, G.M. Macromolecules, 1987, 20, 1473-1488.
�Synthesis: Catalyst
Lewis Acids tried by Webster: ZnBr2 ZnI2 Al Al O ZnCl2 (i-Bu2Al)2O Low Temps. i-Bu2AlCl Et2AlCl
Zn Cl O O CH3
Sogah, D.Y.; Hertler, W.R.; Webster, O.W.; Cohen, G.M. Macromolecules, 1987, 20, 1473-1488.
�Mechanisms: Associative
Webster, O.W. Adv. Polym. Sci. 2004, 167, 1-34.
�Mechanisms: Associative
Webster, O.W. Adv. Polym. Sci. 2004, 167, 1-34.
�Mechanisms: Dissociative
O O Me O O Me
Webster, O.W. Adv. Polym. Sci. 2004, 167, 1-34.
�Elucidating the Mechanism
Quirk used bare enolate to both catalyze and initiate polymerization
Quirk, R.P.; Kim J-S. J. Phys. Org. Chem. 1995, 8, 242.
�Elucidating the Mechanism
Persisting paradox: too much catalyst retards the polymerization Initiator actually DESTROYS catalyst in absence of monomer Induction Period
Sitz, H-D; Bandermann, F. (1987) Group Transfer of methyl methacrylate with basic catalysts In: Fontanille M, Guyot M (eds) Recent advances in mechanistic aspects of polymerization. Reidel, p 41
�Any Evidence for Associative Mechanism?
Yes! Excellent Double-Label Experiment by Farnham and Sogah
Sogah, D.Y.; Farnham, W.B. Polym. Prepr. Am. Chem. Soc. Div. Polym. Chem. 1986, 27, 167.
�GTP: The Truth
So, actually an anionic living polymerization Anionic initiators for MMA can act as catalysts for GTP Caveat: Back-biting not an issue with this anionic living polymerization
�From Back-Biting to Chain Transfer
Webster, O.W. Adv. Polym. Sci. 2004, 167, 1-34.
�Applications
Pigment Dispersant Emulsion Stabilizers AB block co-polymer A = Hydrophilic Block B = Hydrophobic Block
H2O H2O
H2O H2O
Spinelli, H.J. Prog. Org. Coat. 1996, 27, 255-260.
�Pros and Cons
Advantages 1. Good for making blocks of acrylates and methacrylates 2. Can be done at RT and elevated T 3. Excellent architectural control (stars, blocks, etc.) 4. Low PDIs (can get down to 1.03!) 5. No metallic or halide impurities left over 6. No bad odors! Disadvantages 1. Cannot be done in presence of water 2. Initiator still costly 3. Cannot use monomers with acidic or active hydrogen functional groups
�Conclusion
Relatively new living polymerization technique Full of potential, still room for improvement Best method around for block polymers of methacrylate derivatives
�Questions???