Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Four basic business activities revenue cycle
Uploaded by
faudOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Four basic business activities revenue cycle
Uploaded by
faudCopyright:
Available Formats
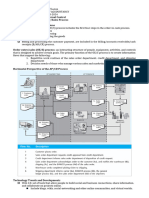
Four basic business activities are performed in the revenue cycle: I. II. III. IV.
Sales order entry Shipping Billing Cash collection
SALES ORDER ENTRY Sales order entry is performed by the sales order department. The sales order department typically reports to the VP of Marketing. Steps in the process include: I. Taking the customers order
Many different ways can use such as phone, store, mail, web and so on. Optical scanners can convert hardcopy to electronic data or customers enter data. Choice boards allow customers to customize products to their needs (e.g., Dell). Using EDI (EDINT) for orders or to allow vendors to manage inventory (vendor managed inventory (VMI).Software can be used to optimize selling prices. II. Checking and approving customer credit.
Most business-to-business sales are made on credit. Credit sales should be approved before they are processed. Each customer will have a credit limit. Credit limit is the maximum allowable account balance for each customer based on the customers past credit history and ability to pay. III. Checking inventory availability
The next step is to determine if there is sufficient inventory available to fill the order. When there are not sufficient items on hand to fill the customers order, a back order is created. Once the item(s) become available, a picking ticket is created. The picking ticket authorizes the inventory control function to release merchandise to the shipping department. The accuracy of inventory records is important because customer may become justifiably upset when unexpected delays occur in filling their orders. IV. Responding to Customer Inquiries
Customer services is so important that many companies use special software packages, called Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems, to support this vital process. The goal of customer relationship management is to retain customers. This is important because a general
marketing rule of thumb is that it costs at least five times as much to attract and make a sale to a new customer as it does to make a repeat sale to an existing customer.
SHIPPING The second basic activity in the revenue cycle is filling customer orders and shipping the desired merchandise. Shipping consists of the following two steps: I. Picking and packing the order The picking ticket printed by sales order entry triggers the pick and pack process. Some of the investments companies have an automated warehouse system which includes computers, bar-code scanners, and conveyer belts and communications technology. Some warehouses have no peopleuse robots. Radio-Frequency Identification (RFID) is replacing bar codes. The RFID tag eliminates the need to align items with scanners; instead, the tags can be read as the inventory moves throughout the warehouse II. Shipping the order The shipping department compares the physical count of inventory with the quantities indicated on the picking ticket and with the quantities indicated on the copy of the sales order that was sent directly to shipping from sales order entry. The packing slip lists the quantity and description of each item included in the shipment. The bill of lading is a legal contract that defines responsibility for the goods in transit. If the customer is to pay the shipping charges, the copy of the bill of lading may serve as a freight bill, to indicate the amount the customer should pay to the carrier. Another important decision concerns the location of distribution centers. RFID systems can provide real-time information on shipping status and thus provide additional value to customers. BILLING Involves two separate but related tasks: I. II. Invoicing: The document created in the billing process is the sales invoice, which notifies customers of the amount to be paid and where to send payment. Updating A/R: The accounts receivable function uses the information on the invoice to debit the customers accounts for credit purchases and credit the customers accounts when payment is received.
Under the open-invoice method, customers normally pay according to each invoice. The customer is asked to return a copy of the invoice when mailing in their payment. This return copy is referred to as the remittance advice. Under the balance-forward method, customers
typically pay according to the amount shown on a monthly statement. A monthly statement lists all transactions, including both sales and payments.
CASH COLLECTION The final step in the revenue cycle is cash collections. The cashier handles customer remittances and deposits them in the bank. A remittance list provides the names and amounts of all customer remittances, and sends it to accounts receivable. Imaging technology can be used to improve the efficiency of processing customer payments. A lockbox is a postal address to which customers send their remittances. The participating bank picks up the checks from the post office box and deposits them to the companys account. Under an electronic lockbox arrangement, the bank electronically sends the company information about the customer account number and the amount remitted as soon as it receives and scans those checks. With electronic funds transfer (EFT), customers send their remittances electronically to the companys bank and thus eliminate the delay associated with the time the remittance is in the mail system. EFT is usually accomplished through the banking systems Automated Clearing House (ACH) network.
You might also like
- Purchasing, Inventory, and Cash Disbursements: Common Frauds and Internal ControlsFrom EverandPurchasing, Inventory, and Cash Disbursements: Common Frauds and Internal ControlsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Module - Revenue CycleDocument8 pagesModule - Revenue CycleGANNLAUREN SIMANGANNo ratings yet
- Textbook of Urgent Care Management: Chapter 13, Financial ManagementFrom EverandTextbook of Urgent Care Management: Chapter 13, Financial ManagementNo ratings yet
- The Revenue Cycle Is A Recurring Set of Business Activities and RelatedDocument6 pagesThe Revenue Cycle Is A Recurring Set of Business Activities and RelatedJna AlyssaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document4 pagesAssignment 1Perbz07No ratings yet
- Payment Collection for Small Business: QuickStudy Laminated Reference Guide to Customer Payment OptionsFrom EverandPayment Collection for Small Business: QuickStudy Laminated Reference Guide to Customer Payment OptionsNo ratings yet
- ESTER SABATINI - ISIC The Revenue CycleDocument13 pagesESTER SABATINI - ISIC The Revenue CycleESTERSABATININo ratings yet
- Revenue Cycle Business ActivitiesDocument4 pagesRevenue Cycle Business ActivitiesWalter Arcangel50% (4)
- Tracking Revenue from Order to CashDocument3 pagesTracking Revenue from Order to CashMikNo ratings yet
- Revenue Cycle: Sales To Cash CollectionsDocument37 pagesRevenue Cycle: Sales To Cash Collectionsrsh765No ratings yet
- The Revenue Cycle: Sales To Cash Collections: 1 FOSTER School of Business Acctg.320Document37 pagesThe Revenue Cycle: Sales To Cash Collections: 1 FOSTER School of Business Acctg.320David MesaNo ratings yet
- Rais12 IM CH12Document15 pagesRais12 IM CH12Alan OsorioNo ratings yet
- The Revenue Cycle: Sales To Cash Collections: FOSTER School of Business Acctg.320Document37 pagesThe Revenue Cycle: Sales To Cash Collections: FOSTER School of Business Acctg.320Shaina Shanee CuevasNo ratings yet
- Review Questions on Revenue CycleDocument2 pagesReview Questions on Revenue CycleBeny MoldogoNo ratings yet
- Revenue Cycle Activities & Business ProcessesDocument6 pagesRevenue Cycle Activities & Business ProcessesJanica GaynorNo ratings yet
- Share CHAPTER 4 ICT14 Mary Ann DomincelDocument4 pagesShare CHAPTER 4 ICT14 Mary Ann DomincelMA ValdezNo ratings yet
- AIS Chapters 4 5Document3 pagesAIS Chapters 4 5Matthew Brian TajanlangitNo ratings yet
- Point-Of-Sale (POS) SystemDocument17 pagesPoint-Of-Sale (POS) SystemBalestramon100% (2)
- Rais12 SM CH12Document46 pagesRais12 SM CH12Chris Search100% (1)
- POS advantages for businessesDocument9 pagesPOS advantages for businessesTrisha Lorraine RodriguezNo ratings yet
- OESALES ProcessDocument7 pagesOESALES ProcessJeon SeokjinNo ratings yet
- Revenue Cycle Activities ExplainedDocument6 pagesRevenue Cycle Activities ExplainedSamonte JemimahNo ratings yet
- Revenue CycleDocument46 pagesRevenue CycleChrisNo ratings yet
- 13.10 Last Year The Diamond Manufacturing Company Purchased Over $10 Million Worth ofDocument7 pages13.10 Last Year The Diamond Manufacturing Company Purchased Over $10 Million Worth ofJara TakuzawaNo ratings yet
- E Commerce Unit IIDocument17 pagesE Commerce Unit IIRam KumarNo ratings yet
- Script COMACDocument3 pagesScript COMACRany Meldrenz FloresNo ratings yet
- Auditing Revenue CycleDocument63 pagesAuditing Revenue CycleJohn Lexter MacalberNo ratings yet
- Segregation of Duties and Controls in Revenue CycleDocument3 pagesSegregation of Duties and Controls in Revenue CycleMarcellana ArianeNo ratings yet
- Document 2Document5 pagesDocument 2Hashib ArmanNo ratings yet
- The Revenue Cycle: Sales and Cash CollectionsDocument46 pagesThe Revenue Cycle: Sales and Cash CollectionsgoeswidsNo ratings yet
- IT Audit 4ed SM Ch9Document62 pagesIT Audit 4ed SM Ch9randomlungs121223No ratings yet
- Revenue Cycle Self-TestDocument10 pagesRevenue Cycle Self-TestPeachyNo ratings yet
- IT Audit 4ed SM Ch9Document62 pagesIT Audit 4ed SM Ch9randomlungs121223No ratings yet
- AIS Chapter FourDocument14 pagesAIS Chapter FourNaod MekonnenNo ratings yet
- Upload: ClientDocument13 pagesUpload: ClientTanishaSinghNo ratings yet
- Revenue Cycle - DefinitionDocument4 pagesRevenue Cycle - DefinitionGANNLAUREN SIMANGANNo ratings yet
- Henrico Retail, Inc.Document5 pagesHenrico Retail, Inc.Nguyễn Thị DiễmNo ratings yet
- Oxigen Services India Private LTD.: I. Business BackgroundDocument7 pagesOxigen Services India Private LTD.: I. Business BackgroundChirag MalhotraNo ratings yet
- Henrico Retail Inc.Document3 pagesHenrico Retail Inc.Lê KhoaNo ratings yet
- Revenue CycleDocument20 pagesRevenue CycleBear CooporNo ratings yet
- Download Audit of Sales and Collection Cycle ChapterDocument28 pagesDownload Audit of Sales and Collection Cycle ChapterfitriNo ratings yet
- 2011 Revenue and Cash Receipts Cycle Internal ControlDocument11 pages2011 Revenue and Cash Receipts Cycle Internal ControlTheQUICKbrownFOXNo ratings yet
- Understanding Manual Accounting SystemsDocument13 pagesUnderstanding Manual Accounting SystemsPaul Assie RosarioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document79 pagesChapter 4Clarizza0% (1)
- Acquisition and Payment Cycle Final AnswerDocument2 pagesAcquisition and Payment Cycle Final AnswerPrincess MarceloNo ratings yet
- Review of Literature on Billing, Inventory ManagementDocument14 pagesReview of Literature on Billing, Inventory ManagementHoney Sepala JaposNo ratings yet
- The Revenue CycleDocument68 pagesThe Revenue CycleKino Marinay100% (1)
- 2: Design of Oe/S ProcessDocument4 pages2: Design of Oe/S ProcessksNo ratings yet
- AEB14 SM CH14 v1Document36 pagesAEB14 SM CH14 v1RonLiu35No ratings yet
- Auditing The Revenue CycleDocument2 pagesAuditing The Revenue CycleBella PatriceNo ratings yet
- Aguila, Paulo Timothy - Cis c9Document3 pagesAguila, Paulo Timothy - Cis c9Paulo Timothy AguilaNo ratings yet
- Henrico Retail Sales Audit TrailDocument4 pagesHenrico Retail Sales Audit TrailKim NguyenNo ratings yet
- CHP 4Document26 pagesCHP 4ali alhussainNo ratings yet
- Components+of+E+ 1Document8 pagesComponents+of+E+ 1Mui GaiNo ratings yet
- E-Commerce Introduction Guide for RetailersDocument24 pagesE-Commerce Introduction Guide for RetailersSwathi SwaNo ratings yet
- Rais12 SM CH12Document46 pagesRais12 SM CH12Anton Vitali100% (1)
- UNIT 4 The Revenue Cycle Detailed Report BSA 2 1Document45 pagesUNIT 4 The Revenue Cycle Detailed Report BSA 2 1Harvey AguilarNo ratings yet
- Application Areas of ICTDocument12 pagesApplication Areas of ICTowuor PeterNo ratings yet
- Activity in Module 5 AISDocument9 pagesActivity in Module 5 AISLovely Sheen AbisNo ratings yet
- Wavelet Feature Based Fault Detection and Classification Technique For Transmission Line ProtectionDocument7 pagesWavelet Feature Based Fault Detection and Classification Technique For Transmission Line ProtectionGRD JournalsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Concrete StructuresDocument432 pagesChapter 5 Concrete StructuresrizwanNo ratings yet
- KCP Operation Modes Coordinate SystemsDocument25 pagesKCP Operation Modes Coordinate SystemsNguyễn Duy AnhNo ratings yet
- JD730 Power Sensor JDPM Operating Guide R1.4Document44 pagesJD730 Power Sensor JDPM Operating Guide R1.4mborazNo ratings yet
- Ad 4486Document60 pagesAd 4486Kaya EmanuelNo ratings yet
- Website Process Modelling Gaming WebsiteDocument13 pagesWebsite Process Modelling Gaming Websiteapi-225276867No ratings yet
- Legends of SkyloftDocument30 pagesLegends of SkyloftAnonymous WaLbdWNo ratings yet
- Tablita-Comandos 2.3Document2 pagesTablita-Comandos 2.3hernan_27No ratings yet
- Shell Scripting PreparationDocument23 pagesShell Scripting Preparationnjoy986No ratings yet
- S-AAA-CAB-ACC-LV-S&I (Rev.0-2019)Document10 pagesS-AAA-CAB-ACC-LV-S&I (Rev.0-2019)Wael AlmassriNo ratings yet
- Us Navy Practical Guide Flame Bending PipeDocument102 pagesUs Navy Practical Guide Flame Bending PipeBrian DohertyNo ratings yet
- HMT 113401 Anna UnivDocument4 pagesHMT 113401 Anna Univsathiya_ramNo ratings yet
- FM Approvals News Release 030117Document2 pagesFM Approvals News Release 030117Thuc PhanNo ratings yet
- Zone 13 PDFDocument54 pagesZone 13 PDFSobiya100% (1)
- TerminologyDocument77 pagesTerminologyBianca Emanuela LazarNo ratings yet
- DESMODUR LUT+ MocaDocument2 pagesDESMODUR LUT+ MocaSebastian Ordoñez100% (1)
- Confined Masonry Construction: An Illustrated GuideDocument16 pagesConfined Masonry Construction: An Illustrated GuideDiana Matilda CrișanNo ratings yet
- Low Pressure Switch Technical SpecsDocument10 pagesLow Pressure Switch Technical Specsdcf67myNo ratings yet
- Quectel M10 AT Commands Manual V4.0 PDFDocument248 pagesQuectel M10 AT Commands Manual V4.0 PDFNarendra NarenNo ratings yet
- LESSON PLAN FORMAT GUIDEDocument11 pagesLESSON PLAN FORMAT GUIDERjNo ratings yet
- Mid-Term Sol PDFDocument4 pagesMid-Term Sol PDFcosmaskaNo ratings yet
- DevOps Training in KukatpallyDocument4 pagesDevOps Training in KukatpallyComputech InfoSolutions100% (1)
- The Bio ChipsDocument15 pagesThe Bio ChipsPradeep CheekatlaNo ratings yet
- Identity Management For IBM Cognos 8 With IBM Tivoli Identity Manager Redp4643Document40 pagesIdentity Management For IBM Cognos 8 With IBM Tivoli Identity Manager Redp4643bupbechanhNo ratings yet
- ComNav Vector G2 & G2B CompassDocument2 pagesComNav Vector G2 & G2B CompasstariktunadNo ratings yet
- Machinery Inspection ChecklistDocument4 pagesMachinery Inspection ChecklistCynthia ChuaNo ratings yet
- Visualforce Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesVisualforce Cheat SheetMahendraKumarNo ratings yet
- Moscow's iconic Narkomfin commune houseDocument4 pagesMoscow's iconic Narkomfin commune housebamca123No ratings yet
- Proces Rm002 en PDocument2 pagesProces Rm002 en PFernando_Paez_No ratings yet
- lm2841 Transistor RegulatorDocument27 pageslm2841 Transistor RegulatorAbbas MaghazehiNo ratings yet
- 12 Months to $1 Million: How to Pick a Winning Product, Build a Real Business, and Become a Seven-Figure EntrepreneurFrom Everand12 Months to $1 Million: How to Pick a Winning Product, Build a Real Business, and Become a Seven-Figure EntrepreneurRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- I Will Teach You to Be Rich: No Guilt. No Excuses. No B.S. Just a 6-Week Program That Works (Second Edition)From EverandI Will Teach You to Be Rich: No Guilt. No Excuses. No B.S. Just a 6-Week Program That Works (Second Edition)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (13)
- ChatGPT Side Hustles 2024 - Unlock the Digital Goldmine and Get AI Working for You Fast with More Than 85 Side Hustle Ideas to Boost Passive Income, Create New Cash Flow, and Get Ahead of the CurveFrom EverandChatGPT Side Hustles 2024 - Unlock the Digital Goldmine and Get AI Working for You Fast with More Than 85 Side Hustle Ideas to Boost Passive Income, Create New Cash Flow, and Get Ahead of the CurveNo ratings yet
- The Millionaire Fastlane, 10th Anniversary Edition: Crack the Code to Wealth and Live Rich for a LifetimeFrom EverandThe Millionaire Fastlane, 10th Anniversary Edition: Crack the Code to Wealth and Live Rich for a LifetimeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (87)
- The Science of Prosperity: How to Attract Wealth, Health, and Happiness Through the Power of Your MindFrom EverandThe Science of Prosperity: How to Attract Wealth, Health, and Happiness Through the Power of Your MindRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (231)
- Anything You Want: 40 lessons for a new kind of entrepreneurFrom EverandAnything You Want: 40 lessons for a new kind of entrepreneurRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (46)
- Summary of The Subtle Art of Not Giving A F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good Life by Mark Manson: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary of The Subtle Art of Not Giving A F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good Life by Mark Manson: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (38)
- To Pixar and Beyond: My Unlikely Journey with Steve Jobs to Make Entertainment HistoryFrom EverandTo Pixar and Beyond: My Unlikely Journey with Steve Jobs to Make Entertainment HistoryRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (26)
- Creating Competitive Advantage: How to be Strategically Ahead in Changing MarketsFrom EverandCreating Competitive Advantage: How to be Strategically Ahead in Changing MarketsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Summary: Who Not How: The Formula to Achieve Bigger Goals Through Accelerating Teamwork by Dan Sullivan & Dr. Benjamin Hardy:From EverandSummary: Who Not How: The Formula to Achieve Bigger Goals Through Accelerating Teamwork by Dan Sullivan & Dr. Benjamin Hardy:Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Summary of Zero to One: Notes on Startups, or How to Build the FutureFrom EverandSummary of Zero to One: Notes on Startups, or How to Build the FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (100)
- The Kingdom Driven Entrepreneur's Guide: Doing Business God's WayFrom EverandThe Kingdom Driven Entrepreneur's Guide: Doing Business God's WayRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (42)
- What Self-Made Millionaires Do That Most People Don't: 52 Ways to Create Your Own SuccessFrom EverandWhat Self-Made Millionaires Do That Most People Don't: 52 Ways to Create Your Own SuccessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (24)
- The Millionaire Fastlane: Crack the Code to Wealth and Live Rich for a LifetimeFrom EverandThe Millionaire Fastlane: Crack the Code to Wealth and Live Rich for a LifetimeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (58)
- SYSTEMology: Create time, reduce errors and scale your profits with proven business systemsFrom EverandSYSTEMology: Create time, reduce errors and scale your profits with proven business systemsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (48)
- Your Next Five Moves: Master the Art of Business StrategyFrom EverandYour Next Five Moves: Master the Art of Business StrategyRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (798)
- Faith Driven Entrepreneur: What It Takes to Step Into Your Purpose and Pursue Your God-Given Call to CreateFrom EverandFaith Driven Entrepreneur: What It Takes to Step Into Your Purpose and Pursue Your God-Given Call to CreateRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (33)
- Transformed: Moving to the Product Operating ModelFrom EverandTransformed: Moving to the Product Operating ModelRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- How to Start a Business: Mastering Small Business, What You Need to Know to Build and Grow It, from Scratch to Launch and How to Deal With LLC Taxes and Accounting (2 in 1)From EverandHow to Start a Business: Mastering Small Business, What You Need to Know to Build and Grow It, from Scratch to Launch and How to Deal With LLC Taxes and Accounting (2 in 1)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (5)
- Without a Doubt: How to Go from Underrated to UnbeatableFrom EverandWithout a Doubt: How to Go from Underrated to UnbeatableRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (23)
- Enough: The Simple Path to Everything You Want -- A Field Guide for Perpetually Exhausted EntrepreneursFrom EverandEnough: The Simple Path to Everything You Want -- A Field Guide for Perpetually Exhausted EntrepreneursRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (24)
- Don't Start a Side Hustle!: Work Less, Earn More, and Live FreeFrom EverandDon't Start a Side Hustle!: Work Less, Earn More, and Live FreeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (30)
- The Master Key System: 28 Parts, Questions and AnswersFrom EverandThe Master Key System: 28 Parts, Questions and AnswersRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (62)
- The E-Myth Revisited: Why Most Small Businesses Don't Work andFrom EverandThe E-Myth Revisited: Why Most Small Businesses Don't Work andRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (709)
- The Science of Positive Focus: Live Seminar: Master Keys for Reaching Your Next LevelFrom EverandThe Science of Positive Focus: Live Seminar: Master Keys for Reaching Your Next LevelRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (51)
- Expert Secrets: The Underground Playbook for Creating a Mass Movement of People Who Will Pay for Your AdviceFrom EverandExpert Secrets: The Underground Playbook for Creating a Mass Movement of People Who Will Pay for Your AdviceRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (363)
- Summary: Choose Your Enemies Wisely: Business Planning for the Audacious Few: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Choose Your Enemies Wisely: Business Planning for the Audacious Few: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)