Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Yearly Scheme of Work Science Six 2011
Uploaded by
Syahida IslamOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Yearly Scheme of Work Science Six 2011
Uploaded by
Syahida IslamCopyright:
Available Formats
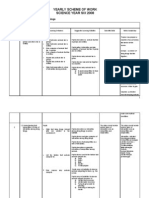
YEARLY SCHEME OF WORK SCIENCE YEAR SIX 2011
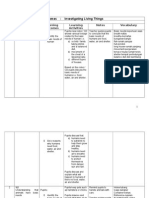
THEME: A. Investigating Living Things
Learning Area: Weeks/ Dates 3.1.11 14.1.11 Learning Objectives Pupils 1.1 Understanding that some animals live in groups and others live in solitary State that some animals live in groups . State that some animals live in solitary Give examples of animals that live in groups Give example of animals that live in solitary. Explain why animals live in groups. Explain why animals live in solitary State that cooperation is a form of interaction among animals. Pupils view video on animals that live in groups and solitary Pupils gather information and give examples of animals that live in group and in solitary Pupils discuss why animals live in group. Pupils observe how ants live together in a vivarium. Pupils discuss why animals live in solitary. a) to avoid competition for food Groups a number of living things that live together. Solitary existing alone/ not social or colonial Cooperation work jointly Competitioninteraction between species or 1 Learning Outcomes Suggested Learning Activities Scientific Skills Notes/ vocabulary
b) to avoid competition for space
organisms which share a limited environmental resource./ strive to gain
17.1.11 28.1.11
1.2 Understanding that competition is a form of interaction among living things.
Pupils
Pupils view video on interaction among living State that living things interact things in various habitats. with one another in the Pupils discuss and give environment. examples of interaction among living things. Pupils discuss that competition is a form of interaction. Pupils view video or computer simulation of competition among animals.
The video should include various types of interaction such as competition and cooperation.
The video should include various types of interaction such as competition and cooperation.
List the factors that animals Pupils discuss and list the factors that animals compete for. compete for. a) Food b) Water c) Mate d) Shelter e) Territory/space
Interaction interaksi breedingpembiakan Competitionpersaingan Limited resources sumber terhad Territory-wilayah Mate-pasangan Defendmempertahankan Space-ruang Shelter-tempat perlindungan
Give reasons why animals Pupils carry out activities to observe animals competing compete. for food, e.g . fish or bird. Pupils carry out activities to observe animals compete because of : a) Limited food resources b) Limited water resources c) Trying to get a mate for breeding d) Defending or looking for shelter
31.1.11 11.2.11
Pupils List factors that plant compete for
Pupils view a video or pictures of plants in the forest. Based on the video or pictures pupils discuss why plants in the forest have different height. Pupils carry out activities to observe competition among plants. Pupils discuss that plants compete for :a) sunlight b) water c) space d) nutrient.
These activities can be prepared earlier because they may take some time to show results.
Suggestion: a) Green beans b) maize
Give reasons why plants compete with each other.
Pupils discuss and conclude that plants complete because of: a) limited sunlight that can reach them b) limited water resources c) limited space d) limited nutrient Pupils view video or pictures of animals that are extinct, e.g dinosaurs. Pupils view video or pictures of endangered animals and plants , e.g tiger, turtle, orang utan, panda, rhinoceros and rafflesia and pitcher plant. Pupils discuss and conclude that certain animals and plants are facing the threat of extinction because of human activities such as illegal or excessive : a) logging b) hunting c) development Discuss ways to prevent animals and plants from extinction , e.g. Rafflesia-bunga pakma Hornbill-burung enggang Conservationpemuliharaan Protectionperlindungan Endangeredterancam Extinct-pupus Excessiveberleluasa Threat-ancama Loggingpembalakan Consumemenggunakan Enforcementpenguatkuasaan .
14.2.11 25.2.11
1.3 Understanding the responsibility of human beings in protecting endangered species.
Pupils give examples of extinct animal. Give examples of endangered animals Give examples of endangered plant Explain why certain animals or plants are facing the threat of extinction Suggest ways to prevent animals and plants from extinction.
a) campaign against excessive logging b) educating the public about the importance of protecting and conserving animals and plants c) avoid consuming or buying products made from endangered species d) enforcing the law 28.2.11 11.3.11 1.4 Knowing the impact of human activities on environment Pupils Give examples of environmental destruction caused by humans. Explain how human activities cause environmental destruction Predict what will happen to the Earth if human activities that caused environmental destructions are not controlled. Pupils view video or see pictures of environmental destructions caused by human activities ,e.g a) erosion b) landslide c) flash-flood d) water pollution e) air pollution Pupils view a video and discuss human activities that cause human activities that cause destruction to the environment, e.g. a) illegal and excessive logging b) illegal and excessive hunting c) improper management of development Balance of naturekeseimbangan alam Illegal loggingpembalakan haram Landslide-tanah runtuh Flash-flood-banjir kilat Pollutionpencemaran Erosion-hakisan Disaster-bencana Destructionkemusnahan
Pupil discuss what will happen to the Earth if human activities that caused environmental destructions are not controlled Pupils prepare a scrap bookon environmental destructions are not controlled Pupils prepare a scrap book on environmental destruction caused by human activities and steps taken the reduce its effects. Learning Area: Weeks/ Dates 21.3.11 25.3.11 Learning Objectives 1.1 Understanding that push and pull are forces Learning Outcomes Pupils State that push and pull are forces State that force cannot be seen but its effect can be observed. Suggested Learning Activities Pupils push and pull each others palms to feel the effect of forces. Pupils discuss and conclude that push and pull are forces Based on the above activity pupils discuss and conclude that a force cannot be seen 6 Scientific Skills Notes/ vocabulary Pull-tarikan Push-tolakan Force-daya palm-tapak tangan
but its effect can be observed 28.3.11 1.4.11 1.2 Understanding the effects of a force Pupils State that a force can move a stationary object State that a force can change the motion of an object State that a force can change the shape of an object Pupils carry out activities and discuss the effects of pushing a) a stationary ball b) a moving ball Pupils press , twist or squeeze objects such as plasticine, sponge and spring Pupils observe and discuss the effect of forces Pupils discuss and conclude that a force can : a) move the stationary object b) stop a moving car c) change the direction of a moving object d) make an object move faster or slower e) change the shape of an object 4.4.11 22.4.11 Pupils State that fiction is a type of force Describe the effect of Friction-geseran Aerodynamicaerodinamik Opposebertentangan 7 Speed-kelajuan Stationary-pegun Moving-bergerak Twist-pulas Press-tekan
Pupils observe an object such as book or a coin sliding on a surface
friction Describe ways to reduce friction Describe ways to increase friction State the advantages of friction State the disadvantages of friction Conclude that friction occurs when two surfaces are in contact Design a fair test to find out how different types of surfaces affect
Pupils discuss that friction slows down a moving object an conclude that friction is a force Pupils carry out activities that involve friction , e.g: a) open the lid of a jar with dry hands b) open the lid of a jar with oily hands Pupils discuss and conclude that it is easier to open the lid of jar with dry hands because of greater friction Pupils carry out activities that ivolve friction,e.g.: a) rubbing their palms b) pulling a heavy object c) rubbing an eraser against the surface Based on the above activities pupils explain the effects of friction: a) their palms become warmer because friction produce heat, b) it is difficult to move the object because friction opposes motion,
Effect-kesan Reducekurangkan Increasemenambahkan Surfaces in contactpermukaan yang bersentuhan
the distance a trolley moves by deciding what to keep change, what to keep the same and what to measure.
c) the eraser becomes smaller because friction causes wear and tear. Pupils discuss and compare the effects of friction in everyday life Pupils compare the effects of friction by rubbing their palms Pupils compare the effects of friction by rubbing their palms Pupils discuss and conclude that oil reduces friction Pupils suggest various ways to reduce friction. Pupils carry out activities to test their suggestions Pupils gather information on the advantages and disadvantages of friction in everyday life Pupils discuss various situations where friction occurs and conclude 9
that friction is produced when surfaces are in contact with one another Pupils plan and carry out an experient to investigate how different types of surfaces affects the distance a trolley moves. 25.4.11 6.5.11 Pupils s State that an object which moves faster travels a long distance in a given time State that an object which move faster takes a shorter time to travel a given distance State what speed is Solve problems using the formula Pupils carry out activities to : a) compare the distances traveled ina given time by two moving objects, b) compare the time taken by two moving objects to travel a given distance . Pupils discuss and conclude that : a) an object which moves faster travels a longer distance in a given time b) an object which moves faster takes a shorter to travel a given distance
10
Pupils conclude that : a) speed is a measurement of how fast an object moves b) speed can be calculated by using the formula speed=distance/ time Pupils solve problems using the formula Learning Area: Weeks/ Dates 9.5.11 20.5.11 Learning Objectives Learning Outcomes Pupils Describe what spoilt food is Identify characteristics of spoilt food State that microorganisms can spoilt food State the conditions for microorganisms to grow. Suggested Learning Activities Pupils obesrve samples of spoilt food Pupils discuss and conclude that spoilt food is unsafe to eat. Pupils conclude that spoilt food has one or more of the following characteristics: a) unpleasant smell b) unpleasant taste c) changed colour d) changed texture e) mouldy Scientific Skills Notes/ vocabulary Notes : Food used in the activity should not be tasted. Medium-keadaan
11
Pupils carry out an activity to observe that food turns bad by leaving a slice of bread in the open for a few days. Pupils discuss and conclude that microorganisms can spoil food Pupils gather information and conclude that microorganisms need certain conditions to grow. a) air b) water c) nutrient d) suitable temperature e) suitable acidity 23.5.11 1.7.11 Pupils Describe ways to preserve food Give examples of food for each type of food preservation Give reasons why each way of food preservation is used State what food preservation is Design and carry out a project to preserve a given food Pupils find information about ways to preserve food and examples of food for each type of preservation, i.e: a) drying b) boiling c) coolig d) vacuum packing e) ickling f) freezing g) bottling/canning h) pasteursiing i) salting j) smoking k) waxing Dryingpengeringan Picklingpenjerukan Heatingpemanasa Vacuum packingpembungkusan vakum Coolingpendinginan Freezingpenyejukbekuan Bottlingpembotolan Canning12
Pupils discuss and explain why the above ways are used to preserve food. Pupils view a video or visit food factory to observe how food is processed and preserved. Pupils discuss that food preservation is a process of slowing down the food from becoming bad Pupils carry out a project on food preserve a given food
pengetinan Smokingpengasapan Saltingpengasinan
Food given can be a) tapioca b) banana c) egg d) mango e) chilli
4.7.11 8.7.11
1.3 Realising the importance of preserving food
Pupils Give reasons why we need to preserve food
Pupils discuss and give reasons why we need to preserve food. a) the food will last longer b) the food is easy to store c) to reduce wastage of food Pupils observe various waste in a rubbish bin, e.g plastic, glass, chemical waste, organic waste, and metal Harmful effectskesan buruk Waste disposalpembuangan bahan buangan 13
11.7.11 29.7.11
Pupils 2.1 Understanding the effects of improper disposal Identify types of waste in the environment.
of waste on the environment
Identify sources of waste State the improper ways of waste disposal Desribe the harmful effects of improper waste disposal Describe how waste is disposed in a local area Suggest ways to improve waste disposal
Pupils view video on various waste from factories, food stalls and market. Pupils gather information on: a) source of waste b) various wastes of waste disposal Pupils discuss and classify the proper and improper ways of waste disposal Pupils discuss the harmful effects of improper waste disposal: a) air pollution b) water pollution c) sickness and diseases d) acid rain e) flash-flood Pupils gather information on how waste in alocal area is disposed.
Pupils discuss and suggest ways to improe waste disposal in a local area. 14
Pupils visit a waste managemet cetre or listen to a to gather information onhow waste is treated. 2.8.11 26.8.11 2.2 Understanding that some waste can decay. Pupils State that certain waste can decay Give examples of waste that can decay Give examples of waste that do not decay State that microorganisms can cause waste materials to decay State the advantages of waste decaying State the disadvantages of waste decaying Predict what will happen to human and the environment if waste do not decay Describe how waste is disposed in a local area. Suggest ways to improve waste disposal. Pupils view videos and time-lapse clippings about waste that decay and waste that do not decay Pupils separate waste in a rubbish bin accordingn to the categories such as vegetables, paper, glass, plastic and wood. Put each type into separate thick plastic bags. Place these bags in the open and observe the changes over a period of time. Pupils discuss and give examples of waste that : a) decay b) do not decay Pupils discuss and conclude a) some microorganisms caused waste to decay
15
b) during the decaying process nutrients are returned to the soil, in this way they ca be used again Pupils gather information and discuss the advantages and disadvantages of decay of waste. Pupils discuss and predict what will happen to a human and the environment if waste do not decay. Learning Area: Weeks/ Dates 5.9.11 15.9.11 Learning Objectives 1.1 Understanding the eclipse of the moon Learning Outcomes Pupils State that eclipse of the moon is State the position of the Moon, the Earth ad the Sun during the eclipse of the moon Explain why eclipse of the Moon occurs Suggested Learning Activities Pupil use models to simulate the movement of the Earth, the Moon and the Sun Pupils view video or computer simulation about partial and total eclipse of the moon Scientific Skills Notes/ vocabulary Eclipse-gerhana Positionkedudukan Partial eclipsegerhana separa Total eclipse gerhana penuh
16
Pupils discuss and conclude that eclipse of the moon occurs because : a) the Earth is between the Moon and the Sun, and b) the Earth , the Moon and the Su are positioned in a straight line Pupils draw diagrams to show the position of the Moon , The Earth and the Sun during the eclipse of the Moon 19.9.11 30.9.11 1.2 Understanding the eclipse of the sun Pupils State what eclipse of the sun is State the position of the Moon, the Earth and the Sun during the eclipse of the sun Predict the scenario on the Earth dring te eclipse f the sun Pupils use models to stimulate the movement of the Earth , the Moon and the Sun Pupils discuss that the eclipse of the sun occurs during daytime Pupils discuss and conclude that eclipse of the sun occurs because: a) the Moon is between the Earth and the Su b) the Earth, the Moon and the Sun are positioned in a straight line 17
Pupils draw diagrams to show the position of the Moon, the Earth and the Sun during the eclipse of the sun Pupils discuss and predict the scenario on the Earth during the eclipse of the Sun Learning Area: Weeks/ Dates 3.10.11 14.10.11 Learning Objectives 1.2 Understanding simple machine Learning Outcomes Pupils Explain what simple machine is State types of simple machines Give an example for each type of simple machine Suggested Learning Activities Pupils try to remove the lid of a tin using a) bare hands b) spoon Pupils compare the difficulty to complete the task and discuss the function of the tool Pupils discuss that a simple machine is a device that allows us to use less force to make work easier or faster Scientific Skills Notes/ vocabulary lid-penutup wheel and axleroda dan gandar lever-tuas wedge-baji pulley-takal gear-gear inclined planesatah condong screw-skru
18
Pupils examine and manipulate the following simple machine a) b) c) d) e) f) g) wheel and axle lever wedge puller gear inclined plane screw
Pupils discuss that types of simplae machines Pupils walk around the school compound and identify various type of simple machine 17.10.11 4.11.11 1.2 Analysing a complex machine Pupils Identify simple machines in a complex machine Conclude that a complex machine is made up of more than one simple machine Give examples of complex machines Pupils identify the simple machines in a bicycle or a wheel barrow Pupils discuss and conclude that a complex machine is a machine made up of more than one simple machine Pupils prepare scrap books on examples of complex machines Wheel barrowkereta sorong
19
8.11.11 18.11.11
Pupils Predict how life is without machines Explain how machines can make our lives easier Design a machine to solve a problem
Pupils carry out simulation to find out how life would be without machines Pupils discuss and predict how ife would be without machines. Pupils discuss ad explain how machines make our lives easier Pupils identify a problem and design a machine to solve the problem.
20
You might also like
- Key Questions in Applied Ecology and Conservation: A Study and Revision GuideFrom EverandKey Questions in Applied Ecology and Conservation: A Study and Revision GuideNo ratings yet
- Yearly Scheme of Work Science Six 2008Document13 pagesYearly Scheme of Work Science Six 2008ff_fadzli275No ratings yet
- Yearly Scheme of Work Science Six 2008Document12 pagesYearly Scheme of Work Science Six 2008Wan Shahlan FatimahNo ratings yet
- Yearly Plan Year6 2012Document21 pagesYearly Plan Year6 2012Hasliza HasNo ratings yet
- Science Yearly Plan Year 6Document16 pagesScience Yearly Plan Year 6shaharinsulongNo ratings yet
- Sekolah Rendah Agama Integrasi: Tengku Ampuan Fatimah, Batu BelahDocument23 pagesSekolah Rendah Agama Integrasi: Tengku Ampuan Fatimah, Batu BelahMohd HafizanNo ratings yet
- Yearly Scheme of Work Yr6 (New)Document17 pagesYearly Scheme of Work Yr6 (New)HairulIzhamIshakNo ratings yet
- Science Yearly Plan: Year 6 2013Document14 pagesScience Yearly Plan: Year 6 2013Rajesware GovindasamyNo ratings yet
- ScienceYearlyPlanYear 6 UPDATED 2013Document16 pagesScienceYearlyPlanYear 6 UPDATED 2013Raja Letchemy Bisbanathan MalarNo ratings yet
- Science Yearly Plan Year 6: Investigating Living ThingsDocument16 pagesScience Yearly Plan Year 6: Investigating Living ThingsGunamathyGanesanNo ratings yet
- Rancangan Tahunan Sains t6Document17 pagesRancangan Tahunan Sains t6ramlybmsNo ratings yet
- Yearly Plan Y6 SC 2014Document27 pagesYearly Plan Y6 SC 2014selvadz00No ratings yet
- Teaching Con 6Document16 pagesTeaching Con 6alyasserbinmdisa82No ratings yet
- Kecukupan Latihan YEAR 6Document23 pagesKecukupan Latihan YEAR 6Asnal KamalNo ratings yet
- Science Year 6 2012Document12 pagesScience Year 6 2012Hirdawati Abdul HamidNo ratings yet
- RPT Sains Tahun 6Document12 pagesRPT Sains Tahun 6Iroet MarteniNo ratings yet
- Yearly Plan Science Year 6Document15 pagesYearly Plan Science Year 6Diana LopezNo ratings yet
- Year 5 Science Sceme of WorkDocument30 pagesYear 5 Science Sceme of WorkJc JoliatiNo ratings yet
- GradeDocument5 pagesGradeapi-273334698No ratings yet
- 1.interaction Among Living ThingsDocument4 pages1.interaction Among Living ThingsRain KipliNo ratings yet
- SN SN SNDocument23 pagesSN SN SNmaya_niranjNo ratings yet
- Suggested Yearly Plan / Please Change or Edit Based On Your School CalendarDocument16 pagesSuggested Yearly Plan / Please Change or Edit Based On Your School CalendarMuhamad Hamadi IthninNo ratings yet
- Yearly Plan Science Yr 6Document18 pagesYearly Plan Science Yr 6Joe SabriNo ratings yet
- Week Learning Objectives Suggested Learning Activities Learning Outcomes Notes VocabularyDocument27 pagesWeek Learning Objectives Suggested Learning Activities Learning Outcomes Notes VocabularyThamil ArasiNo ratings yet
- Rancangan Mengajar Tahunan 2012 YEAR 4Document20 pagesRancangan Mengajar Tahunan 2012 YEAR 4Dilla FadillahNo ratings yet
- Unit Plan OverviewDocument5 pagesUnit Plan Overviewapi-354338223No ratings yet
- RPT Science Year 5 SJKT Ladang GulaDocument29 pagesRPT Science Year 5 SJKT Ladang Gulavargan_ramoNo ratings yet
- Yearly Plan For Science Year 4Document26 pagesYearly Plan For Science Year 4Muhammad Azrieen SamsudinNo ratings yet
- Learning Area: Interaction Among Living ThingsDocument1 pageLearning Area: Interaction Among Living ThingshussainihelmiNo ratings yet
- MypplanneradaptationandevolutionDocument5 pagesMypplanneradaptationandevolutionapi-282478282No ratings yet
- Build A Habitat Lesson 1Document3 pagesBuild A Habitat Lesson 1mgizzareNo ratings yet
- Weird & Wild: Teacher Guide Grades 3 - 5 Program DescriptionDocument28 pagesWeird & Wild: Teacher Guide Grades 3 - 5 Program DescriptionBecky BrownNo ratings yet
- Day 2 Lesson PlanDocument7 pagesDay 2 Lesson Planapi-532490346No ratings yet
- Interdisciplinary Project Lesson PlansDocument10 pagesInterdisciplinary Project Lesson Plansapi-251762082No ratings yet
- Unit of WorkDocument24 pagesUnit of Workapi-224046430No ratings yet
- Science Grade 3 4th QuarterDocument11 pagesScience Grade 3 4th QuarterMimi MirabuenoNo ratings yet
- Ross 16te802 Glt1reportDocument9 pagesRoss 16te802 Glt1reportapi-325792607No ratings yet
- Carlos Hilado Memorial State CollegeDocument3 pagesCarlos Hilado Memorial State CollegeJanine Gevero MendozaNo ratings yet
- 4th Grade Animal Adaptations Final VersionDocument78 pages4th Grade Animal Adaptations Final VersionTGNo ratings yet
- S5 LT-II-h-8Document6 pagesS5 LT-II-h-8Kristine Joy PitaNo ratings yet
- Ubd EcologyDocument13 pagesUbd EcologyPaul Michael Vial Boncayo100% (1)
- K5 Science Endorsement GPS Lesson Plan: Title Teacher(s) E-Mail School Lesson Title Grade Level Concepts(s) TargetedDocument4 pagesK5 Science Endorsement GPS Lesson Plan: Title Teacher(s) E-Mail School Lesson Title Grade Level Concepts(s) Targetedapi-371303595No ratings yet
- Lessonplan 4Document5 pagesLessonplan 4api-272727134No ratings yet
- Lesson 5Document13 pagesLesson 5api-280508148No ratings yet
- A Frogs Skin - Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesA Frogs Skin - Lesson Planapi-255425919No ratings yet
- Grade 7 Heart Plant 4th Quarter Session 5 8Document7 pagesGrade 7 Heart Plant 4th Quarter Session 5 8jezilbanayo01No ratings yet
- DLP 4Document2 pagesDLP 4Marlow LowkeyNo ratings yet
- Lessons PlansDocument41 pagesLessons Plansapi-596860967No ratings yet
- Yearly Planner Science Year 4 2006Document51 pagesYearly Planner Science Year 4 2006sulia81No ratings yet
- Lesson 6 IsitlivingcandidateDocument2 pagesLesson 6 Isitlivingcandidateapi-322160452No ratings yet
- Ict 22Document5 pagesIct 22api-250192253No ratings yet
- Lesson 1Document2 pagesLesson 1gnbeccariaNo ratings yet
- Scholastic Two 2Document8 pagesScholastic Two 2api-319615100No ratings yet
- scn400 LPDocument5 pagesscn400 LPapi-282424857No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 1 Water CycleDocument5 pagesLesson Plan 1 Water Cycleapi-624400995No ratings yet
- Science Final Powerpoint Sarah Yunus Tiffany ChenDocument14 pagesScience Final Powerpoint Sarah Yunus Tiffany Chenapi-512625125No ratings yet
- Inquiry Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesInquiry Lesson Planapi-276896817No ratings yet
- Stage 1 Wet and Dry EnvironmentsDocument5 pagesStage 1 Wet and Dry Environmentsapi-184739074100% (1)