Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pulse Width Modulation
Uploaded by
Munira ZulkefliCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pulse Width Modulation
Uploaded by
Munira ZulkefliCopyright:
Available Formats
Report 1 Pulse Width Modulation (PWM)
Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) is the way of controlling the output voltage without any disturbance for the use of ac motor control. The output voltage is from the fixed voltage supply. The advantage of having a PWM is that its uncontrolled rectifier can give a siries of constant dc voltage. This PWM control method can be used in a constant torque area for example in machinery equipments, textile industry, printing and paper manufacturing.
3-Phase Synchronous PWM Controller IC Provides an Integrated Solution for Intel VRM 9.0 Design Guidelines
Table 1 - Summary of the VRM 9.0 output requirements (Source: Intel VRM9.0 DC-DC converter design guidelines.
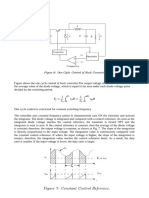
By referring to waveform above, the carrier triangle waveform is the result of a high frequency, which is normally between 1.5 2.5kHz. With a low harmonic and small torque pulse enable a wide range of speed control from 0 rpm to machines full torque. This triangle waveform is then being compared with the sinousoidal waveform. And each crossover point will determine the transistors turn OFF.
PWM is ac motor control method through frequencies alteration. If a low output frequency is desired, then a low output voltage is needed. By chopping the voltage, the mark-space ratio is altered in order to achieve the desired voltage value.
And if a high frequency is desired thus a high output voltage is needed. The chopper is allowed to flow in current for a much longer time. This will then gives out a higher fundamental output component compared during the low frequency output.
And if that frequency is let to be increased, the ON period will be much longer causing the separated waveform united in becoming one as shown in the figure above. Any increment after that will not affect the output voltage.
And if the given frequency is out of range, then an output shown above will be produced. The shape of the waveform will not be change and is named quasi-square.
You might also like
- SPWM V/HZ InverterDocument51 pagesSPWM V/HZ InverterLabi BajracharyaNo ratings yet
- Pulse-Width Modulation PDFDocument8 pagesPulse-Width Modulation PDFSindhuja ThogaruNo ratings yet
- PWM To DC Voltage Conversion: Kyle Burgess 4/3/2015Document8 pagesPWM To DC Voltage Conversion: Kyle Burgess 4/3/2015NaranLoganNo ratings yet
- Camille Ri 99Document5 pagesCamille Ri 99tip31No ratings yet
- PWM InverterDocument2 pagesPWM InverterMandavi Nagar KotasthaneNo ratings yet
- AC Motor Control with 20 kHz PWM InvertersDocument91 pagesAC Motor Control with 20 kHz PWM InvertersElvins AguilarNo ratings yet
- Selective Harmonic Elimination by Programmable Pulse Width Modulation in InvertersDocument6 pagesSelective Harmonic Elimination by Programmable Pulse Width Modulation in InvertersseventhsensegroupNo ratings yet
- PWM Outputs Enhance Sensor Signal ConditionersDocument5 pagesPWM Outputs Enhance Sensor Signal Conditionersshabir faridiNo ratings yet
- Pim Control Method of Multiple Inverters: MaclevDocument6 pagesPim Control Method of Multiple Inverters: Maclevalpe_huandvNo ratings yet
- Open Loop Control of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Using SVMDocument5 pagesOpen Loop Control of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Using SVMVipin_am100% (1)
- DC MotorDocument91 pagesDC MotorSatadal DashNo ratings yet
- DC - AC Converter - DDocument30 pagesDC - AC Converter - Dbishnu prasad muniNo ratings yet
- SPWM With Variable Carrier Synchronization for Multilevel InvertersDocument6 pagesSPWM With Variable Carrier Synchronization for Multilevel InvertersDevendra HoleyNo ratings yet
- Design and Development of 3 Phase PWM inDocument4 pagesDesign and Development of 3 Phase PWM inMarc TcheukabaNo ratings yet
- Chapter No.:-01 Introuuction: Pulse-Width Modulation (PWM), Modulation (PDM)Document63 pagesChapter No.:-01 Introuuction: Pulse-Width Modulation (PWM), Modulation (PDM)Pooja BanNo ratings yet
- IJRET V/Hz control of AC induction motorDocument7 pagesIJRET V/Hz control of AC induction motoredi ediNo ratings yet
- 20.direct Back Emf Detection Method For Sensorless Brushless DC Motor DrivesDocument11 pages20.direct Back Emf Detection Method For Sensorless Brushless DC Motor DrivesSanthosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Etco 2017 GRP 8Document3 pagesEtco 2017 GRP 8RohanNo ratings yet
- PWM and DC Motor ControlDocument9 pagesPWM and DC Motor ControlYimy GarciaNo ratings yet
- PWM Inverters ExplainedDocument25 pagesPWM Inverters Explainedسجاد عباسNo ratings yet
- Low Losses PWM For High Power Press-Pack IGBT InvertersDocument9 pagesLow Losses PWM For High Power Press-Pack IGBT InvertersMohamed BerririNo ratings yet
- Speed Control of DC Motor Using PWM 555 TimerDocument20 pagesSpeed Control of DC Motor Using PWM 555 TimerDEBABRATA DASNo ratings yet
- ID 610C Carver Intro To Motor ControlDocument46 pagesID 610C Carver Intro To Motor Control조용규No ratings yet
- Modulation IndexDocument6 pagesModulation IndexyechuriyasaswiniNo ratings yet
- Variable Frequency Drive Fundamentals ExplainedDocument32 pagesVariable Frequency Drive Fundamentals ExplainedCubix AutomationNo ratings yet
- SVPWM Thesis Prepared by DeekshitDocument81 pagesSVPWM Thesis Prepared by Deekshitchunduri_rambabuNo ratings yet
- Understanding EC1 Analog OutputsDocument10 pagesUnderstanding EC1 Analog OutputsJose Antonio Lopez SanchezNo ratings yet
- DC To Ac ConvertersDocument13 pagesDC To Ac ConvertersVinay RathiNo ratings yet
- Drives Manual Final EeeDocument60 pagesDrives Manual Final EeenandhakumarmeNo ratings yet
- Reduction in Induction Motor Heating Fed by Hipwm-Fmtc TechniqueDocument17 pagesReduction in Induction Motor Heating Fed by Hipwm-Fmtc TechniqueNishath IlyasNo ratings yet
- VSD Operation and ControlsDocument1 pageVSD Operation and ControlsAsanka RodrigoNo ratings yet
- Simulation of PWM Inverter Using MATLABDocument28 pagesSimulation of PWM Inverter Using MATLABnagatejaNo ratings yet
- Islamic University of Technology: EEE 4483 Digital Electronics & Pulse TechniquesDocument11 pagesIslamic University of Technology: EEE 4483 Digital Electronics & Pulse TechniquesMUHAMMAD JAWAD CHOWDHURY, 180041228No ratings yet
- PMSM 2012Document62 pagesPMSM 2012Sreerag Kunnathu Sugathan100% (3)
- VVC ControlDocument14 pagesVVC ControlRyte EchanoNo ratings yet
- SPWMDocument5 pagesSPWMKiran Kumar NallamekalaNo ratings yet
- Digital Signal Processing Project Report: Ihtisham Ul HaqDocument9 pagesDigital Signal Processing Project Report: Ihtisham Ul Haqihtishamul HaqNo ratings yet
- Final ProjectDocument27 pagesFinal ProjectMohit KeshriNo ratings yet
- Single Phase Bridge VSIDocument13 pagesSingle Phase Bridge VSIRajesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Multi Level Inverter DocumentationDocument25 pagesMulti Level Inverter Documentationn anushaNo ratings yet
- Harmonic DistortionDocument5 pagesHarmonic Distortionnarendra.pathakNo ratings yet
- Speed Control of Three Phase Induction MotorDocument48 pagesSpeed Control of Three Phase Induction MotorChancy Dash100% (3)
- Comparison of Output Current Harmonics of Voltage Source Inverter Used Different PWM Control TechniquesDocument10 pagesComparison of Output Current Harmonics of Voltage Source Inverter Used Different PWM Control TechniquesFitri AhmadNo ratings yet
- Different PWM Modulation Techniques Indexes Performance Evaluation, 1993.Document7 pagesDifferent PWM Modulation Techniques Indexes Performance Evaluation, 1993.Ali H. NumanNo ratings yet
- Design Guideline For Flyback Charger Using FAN302HL/ULDocument20 pagesDesign Guideline For Flyback Charger Using FAN302HL/ULteomondoNo ratings yet
- U-93 Application NOTE A New Integrated Circuit For Current Mode ControlDocument9 pagesU-93 Application NOTE A New Integrated Circuit For Current Mode ControlpramodNo ratings yet
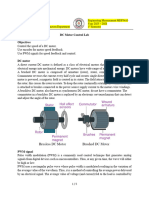
- DC Motor Control LabDocument5 pagesDC Motor Control Labdks697bvhcNo ratings yet
- Intersil - Selecting-A-Pwm-Controller For Narrow On Time Buck ConversionDocument7 pagesIntersil - Selecting-A-Pwm-Controller For Narrow On Time Buck ConversionIvana PrezimeNo ratings yet
- Q02201300137Document8 pagesQ02201300137Vikas PatelNo ratings yet
- JM610 Basic Power Electronics PWM Modulation IntroductionDocument20 pagesJM610 Basic Power Electronics PWM Modulation IntroductionThivaakar RajaratinamNo ratings yet
- Module 4 Part2Document9 pagesModule 4 Part2FreedomNo ratings yet
- AVR With Dead TimeDocument26 pagesAVR With Dead TimegrittinjamesNo ratings yet
- PFM - Pulse Frequency Modulation: Jaydeep ShahDocument3 pagesPFM - Pulse Frequency Modulation: Jaydeep ShahJAYDEEP SHAHNo ratings yet
- Inverter (Electrical) : TypesDocument16 pagesInverter (Electrical) : Typesramkrishna01No ratings yet
- Design of Multi-Level Inverter and Its Application As Statcom To Compensate Voltage Sags Due To FaultsDocument6 pagesDesign of Multi-Level Inverter and Its Application As Statcom To Compensate Voltage Sags Due To FaultsManpreet SinghNo ratings yet
- H09344448 PDFDocument5 pagesH09344448 PDFslimabidNo ratings yet
- Comparison of PWM Techniques and Inverter Performance: Raja Ram Kumar, Sunil Kumar, Alok YadavDocument5 pagesComparison of PWM Techniques and Inverter Performance: Raja Ram Kumar, Sunil Kumar, Alok YadavchaitanyaNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Influence of System Parameters Using Fuse Protection of Regenerative DC DrivesFrom EverandInfluence of System Parameters Using Fuse Protection of Regenerative DC DrivesNo ratings yet
- Bit DefenderDocument1 pageBit DefenderMunira ZulkefliNo ratings yet
- USER Manual V1.0 enDocument19 pagesUSER Manual V1.0 enLogesh WaranNo ratings yet
- APA Guide PDFDocument17 pagesAPA Guide PDFHafizAceNo ratings yet
- Template Assignment EvaluationsDocument4 pagesTemplate Assignment EvaluationsMunira ZulkefliNo ratings yet
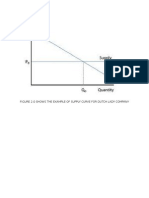
- Figure 2.0 Shows The Example of Supply Curve For Dutch Lady CompanyDocument1 pageFigure 2.0 Shows The Example of Supply Curve For Dutch Lady CompanyMunira ZulkefliNo ratings yet
- ReadmeDocument1 pageReadmeMunira ZulkefliNo ratings yet
- Induction MotorDocument9 pagesInduction MotorMunira ZulkefliNo ratings yet
- ReadmeDocument1 pageReadmeHadi SumantriNo ratings yet
- Higher Algebra - Hall & KnightDocument593 pagesHigher Algebra - Hall & KnightRam Gollamudi100% (2)
- CASCamerasDocument5 pagesCASCameraserynnNo ratings yet