Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Human Rib Cage
Uploaded by
AmerOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Human Rib Cage
Uploaded by
AmerCopyright:
Available Formats
Human rib cage
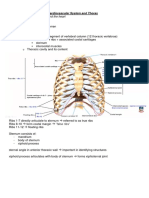
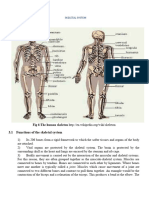
The human rib cage, also known as the thoracic cage, is a bony and cartilaginous structure which surrounds the thoracic cavity and supports the pectoral girdle, forming a core portion of the human skeleton. A typical human rib cage consists of 24 ribs, the sternum (with Xiphoid process , costal cartilages, and the !2 thoracic vertebrae. "t, along with the skin and associated fascia and muscles, makes up the thoracic wall and provides attachments for the muscles of the neck, thora#, upper abdomen, and back.
Thorcic cage
$ideview of heart and ribs
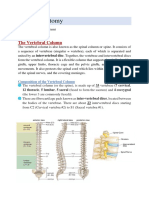
Ribs The ribs are elastic arches of bone, which form a large part of the thoracic skeleton. They are twelve in number on either side% but this number may be increased by the development of a cervical or lumbar rib, or may be diminished to eleven. All ribs attach posteriorly to the thoracic vertebrae and curve inferiorly toward the anterior body surface. The superior seven rib pairs attach directly to the sternum. These are true or vertebrosternal ribs. The remaining five pairs of ribs are called false ribs because they either attach indirectly to the sternum or entirely lack a sternal attachment. &ib pairs '(!) attach to the sternum indirectly. The ribs increase in length from pair ! to pair *, then decrease in length from pair ' to pair !2. +#cept for the first rib, which lies deep to the clavicle, the ribs are easily felt in people of normal weight.
A typical rib, rib 6.
The ribs consist of highly vascular cancellous tissue, enclosed in a thin layer of compact bone. A typical rib is a bowed flat bone. The bulk of a rib is simply called the shaft. "ts superior border is smooth, but its inferior border is sharp and thin and has a costal groove on its inner face that lodges the intercostal nerves and blood vessels. "n addition to the shaft, each rib has a head, neck, and tubercle.
X,ray image of ribs
The neck is the flattened portion which e#tends lateralward from the head% it is about 2.- cm. long, and is placed in front of the transverse process of the lower of the two vertebr. with which the head articulates. "ts anterior surface is flat and smooth, itsposterior rough for the attachment of the ligament of the neck. The body or shaft is thin and flat, with two surfaces, an e#ternal and an internal% and two borders, a superior and an inferior. The external surface is conve#, smooth. Internal surface is concave, smooth, directed a little upward.
First Rib./The first rib is the most curved and usually the shortest of all the ribs.
0irst rib
Second Rib./The second rib is much longer than the first, but has a very similar curvature.
$econd rib
Reference
http122en.wikipedia.org2wiki2&ib http122en.wikipedia.org2wiki23uman4rib4cage http122education.yahoo.com2reference2gray2sub5ects2sub5ect22' 3uman Anatomy 6 7hysiology (8inth +dition +laine 8. 9arieb, :at5a 3oehn
You might also like
- Thoracic Wall: by Professor NzarubaraDocument76 pagesThoracic Wall: by Professor NzarubaraEsdras DountioNo ratings yet
- ثوراكس نظري كاملDocument112 pagesثوراكس نظري كاملyousif.algarahNo ratings yet
- 03 Bones Thorax HandoutDocument3 pages03 Bones Thorax HandoutÇağlaNo ratings yet
- Spaces.: TH TH TH THDocument4 pagesSpaces.: TH TH TH THbarbacumlaudeNo ratings yet
- Thoracic WallDocument46 pagesThoracic WallJavin BissoondyalNo ratings yet
- المحاضرة العاشرة مادة التشريح العام - المرحلة الاولى طب اسنانDocument9 pagesالمحاضرة العاشرة مادة التشريح العام - المرحلة الاولى طب اسنانAbdullah TheNo ratings yet
- Orientation of Thoracic Wall.Document54 pagesOrientation of Thoracic Wall.Shimmering MoonNo ratings yet
- The Chest: Chest Wall, Pulmonary, and Cardiovascular Systems The BreastsDocument2 pagesThe Chest: Chest Wall, Pulmonary, and Cardiovascular Systems The BreastsAn NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Tables - Bones of The Thorax: Bone Structure Description Notes RibDocument3 pagesAnatomy Tables - Bones of The Thorax: Bone Structure Description Notes Ribyachiru121No ratings yet
- Anatomy of Thoracic WallDocument27 pagesAnatomy of Thoracic WallSamuel Pola Karta Sembiring100% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology of The SpineDocument12 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The SpineKinahZildredBibitNo ratings yet
- Thoracic Wall.Document48 pagesThoracic Wall.Shimmering MoonNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy Assignment 1. DR Onanuga-2021Document7 pagesHuman Anatomy Assignment 1. DR Onanuga-2021AlexanderNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Thoracic Wall & Pleura-DikonversiDocument69 pagesAnatomy of Thoracic Wall & Pleura-DikonversiFira TasyaNo ratings yet
- AnatomyDocument211 pagesAnatomyIshimwe TheotimeNo ratings yet
- Katya Anaphysio NewDocument6 pagesKatya Anaphysio NewKriska Herrero TumamakNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Week 3 NotesDocument32 pagesAnatomy Week 3 NotesBasil AdeelNo ratings yet
- The Thorax and Chest WallDocument15 pagesThe Thorax and Chest WallVIRESH VNo ratings yet
- Ribs FractureDocument7 pagesRibs FracturePraisingson SyiemliehNo ratings yet
- Bones and Joints of ThoraxDocument57 pagesBones and Joints of ThoraxNunmoy HnialumNo ratings yet
- 4.thoracic WallDocument20 pages4.thoracic WallAmrith LordNo ratings yet
- ANATOMY I 20.03.20 I Thoracic CageDocument23 pagesANATOMY I 20.03.20 I Thoracic CageArianna RomanoNo ratings yet
- Vertebral JointDocument5 pagesVertebral Jointاحمد البزورNo ratings yet
- SHIKHA SAGAR Thorax BonesDocument30 pagesSHIKHA SAGAR Thorax BonesShikha SagarNo ratings yet
- Thorax - Anatomy.Document26 pagesThorax - Anatomy.Shimmering MoonNo ratings yet
- Dissector Answers - Deep Back & Spinal CordDocument9 pagesDissector Answers - Deep Back & Spinal CordUloko ChristopherNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The CVS: ThoraxDocument10 pagesAnatomy of The CVS: ThoraxNayerShammaaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Spinal CordDocument4 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Spinal CordAla'a Emerald AguamNo ratings yet
- Vertebra: StructureDocument9 pagesVertebra: StructureayudhyaNo ratings yet
- Share '1579792243522 - Lecture 2Document21 pagesShare '1579792243522 - Lecture 2MOHAMMAD ALSWEITYNo ratings yet
- The Vertebral Column - Thoracic VertebraDocument32 pagesThe Vertebral Column - Thoracic VertebraAbhishek SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-Musculoskeletal SystemDocument113 pagesChapter 1-Musculoskeletal SystemWang Ming YaNo ratings yet
- Week 4Document138 pagesWeek 4Anne nicole P. CasemNo ratings yet
- Anatomy 1 - MSS (Upper Limb)Document127 pagesAnatomy 1 - MSS (Upper Limb)Abdullah As'adNo ratings yet
- GRP 7 - Bones, Ligaments, Muscles of The NeckDocument72 pagesGRP 7 - Bones, Ligaments, Muscles of The NeckGuo YageNo ratings yet
- Hyoid BoneDocument14 pagesHyoid BoneAl-Shuaib Astami SonNo ratings yet
- Thorax MooreDocument8 pagesThorax MooreivanajanealexisNo ratings yet
- Vertebral ColumnDocument64 pagesVertebral ColumnJavin BissoondyalNo ratings yet
- The Thoracic Cage: University Ovidius" of Constanta Faculty of DentistryDocument7 pagesThe Thoracic Cage: University Ovidius" of Constanta Faculty of DentistryAndreeaNo ratings yet
- 02 Appendicular SkeletonDocument40 pages02 Appendicular SkeletonkalyanNo ratings yet
- SKELETALSYSTEMDocument14 pagesSKELETALSYSTEMvaleree heart abejuelaNo ratings yet
- The Thoracic CageDocument35 pagesThe Thoracic Cagehananabodeaf41No ratings yet
- Anatomy Lect of Chest and RibsDocument17 pagesAnatomy Lect of Chest and Ribssanullah123khan.13No ratings yet
- Thorax Part 1Document56 pagesThorax Part 1idrimuha333No ratings yet
- GRDA Intro Bony PelvisDocument5 pagesGRDA Intro Bony PelvisKingNo ratings yet
- Gross Anatomy I OsteologyDocument42 pagesGross Anatomy I OsteologySonia FelixNo ratings yet
- Appendicular SkeletonDocument6 pagesAppendicular SkeletonJohn Snow1No ratings yet
- Biomechanics of The Vertebral ColumnDocument44 pagesBiomechanics of The Vertebral ColumnVijay PradeepNo ratings yet
- Thoracic ESDocument237 pagesThoracic ESAbel Belete100% (1)
- Stelios - Joints and LigamentsDocument16 pagesStelios - Joints and LigamentsAdbhut YadavNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System Anatomy For Other Health ScienceDocument165 pagesRespiratory System Anatomy For Other Health Scienceahmedmustefa773No ratings yet
- Vertebrae and Appendicular ANAPHY AND PHYSIODocument10 pagesVertebrae and Appendicular ANAPHY AND PHYSIOshannenmaehfajanilanNo ratings yet
- Bones of The Back RegionDocument9 pagesBones of The Back Regionyachiru121No ratings yet
- A Basic UnderstandingDocument6 pagesA Basic Understandingjessica160793No ratings yet
- Pedicles Are Short Projections, From The Superior Part of The Vertebral Body To TheDocument3 pagesPedicles Are Short Projections, From The Superior Part of The Vertebral Body To ThebarbacumlaudeNo ratings yet
- Exp 12 PDFDocument16 pagesExp 12 PDFKath BarcelonaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Hip BoneDocument2 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Hip BoneNkk Aqnd MgdnglNo ratings yet
- Of Fibers That Unite in A: FusiformDocument3 pagesOf Fibers That Unite in A: FusiformAlina Gherman-HaiducNo ratings yet
- 9. المحاضرة التاسعة - مادة التشريح العام - المرحلة الاولىDocument6 pages9. المحاضرة التاسعة - مادة التشريح العام - المرحلة الاولىAbdullah TheNo ratings yet
- Marine-Derived Pharmaceuticals - Challenges and OpportunitiesDocument11 pagesMarine-Derived Pharmaceuticals - Challenges and OpportunitiesElda ErnawatiNo ratings yet
- How To Attune Yourself and Others Into Any Healing SystemDocument36 pagesHow To Attune Yourself and Others Into Any Healing Systemcarmen100% (19)
- Csa Z32 - Testing Guideline and Procedures: PO Box 20020 Red Deer, AB T4N 6X5 Phone: 403.986.2939Document8 pagesCsa Z32 - Testing Guideline and Procedures: PO Box 20020 Red Deer, AB T4N 6X5 Phone: 403.986.2939tim4109No ratings yet
- The - Utics and Control of Sheep and Goat Diseases, An Issue of Veterinary Clinics, Food Animal PracticeDocument262 pagesThe - Utics and Control of Sheep and Goat Diseases, An Issue of Veterinary Clinics, Food Animal PracticeIurydyana Villalobos0% (1)
- CHN Study GuideDocument5 pagesCHN Study GuideAshNo ratings yet
- Demographics: Discharge DocumentationDocument8 pagesDemographics: Discharge Documentationjenny100% (1)
- Sido Muncul Value Chain - Final10112021Document16 pagesSido Muncul Value Chain - Final10112021Hezekiah PardedeNo ratings yet
- Journal B.cereus With PCR 2017Document10 pagesJournal B.cereus With PCR 2017deryl sepradanaNo ratings yet
- Mobicare BrochureDocument4 pagesMobicare Brochuremicrobotica126No ratings yet
- Hospital Requirement-FinalDocument9 pagesHospital Requirement-FinalPrasanna Ramasamy100% (1)
- Research Forms 2Document35 pagesResearch Forms 2api-343437101No ratings yet
- Ace ArsenalDocument11 pagesAce ArsenalJustus WeißeNo ratings yet
- MAHE Prospectus 2018 PDFDocument224 pagesMAHE Prospectus 2018 PDFAnshuttam MishraNo ratings yet
- Interaksi DadahDocument36 pagesInteraksi Dadahnorish7100% (2)
- Surgical Correction Subglottic Stenosis of The Larynx: AnnoldDocument6 pagesSurgical Correction Subglottic Stenosis of The Larynx: Annoldcanndy202No ratings yet
- Clinical Guideline For Management of Gallstones Pathology in AdultsDocument11 pagesClinical Guideline For Management of Gallstones Pathology in AdultsrintyosoNo ratings yet
- Daftar Obat Apotek MutiaraDocument7 pagesDaftar Obat Apotek Mutiarafany hertinNo ratings yet
- Healthy LivingDocument57 pagesHealthy LivingGrover DejucosNo ratings yet
- Incision and Drainage of AbscessesDocument25 pagesIncision and Drainage of Abscessesjaphetnwapi100% (1)
- Basic Offshore Safety Induction and Emergency Training (Bosiet) ScopeDocument31 pagesBasic Offshore Safety Induction and Emergency Training (Bosiet) ScopePalaniraja Rajarathinam67% (6)
- Anatomy & Physiology Unit 1Document29 pagesAnatomy & Physiology Unit 1Priyanjali SainiNo ratings yet
- Ownership, Operation, Maintenance, and Inspection of Amusement Rides and DevicesDocument4 pagesOwnership, Operation, Maintenance, and Inspection of Amusement Rides and DevicesMarlon Piarpuito Enriquez0% (1)
- Medical Needs Fatiguing The Descrpit Social CcienceDocument11 pagesMedical Needs Fatiguing The Descrpit Social Ccienceicicle900No ratings yet
- Eac MsdsDocument2 pagesEac Msdsteguh30No ratings yet
- Ancondroplasia DwarfismDocument10 pagesAncondroplasia DwarfismjordandeanNo ratings yet
- Act 1 Urinary SystemDocument20 pagesAct 1 Urinary Systemisabellamarie.castillo.crsNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Case Study Pneumonia EpidemidimiologyDocument4 pagesMicrobiology Case Study Pneumonia EpidemidimiologyArguend0No ratings yet
- Drug AsthmaDocument60 pagesDrug AsthmaReema MitraNo ratings yet
- Clinical ReflectionDocument3 pagesClinical ReflectionNaomi MasudaNo ratings yet
- PostpartumDocument3 pagesPostpartumMuhammad RifaiNo ratings yet