Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter1 Fundamentals of Microwave Engineering
Uploaded by
tranhieu_hcmutOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter1 Fundamentals of Microwave Engineering
Uploaded by
tranhieu_hcmutCopyright:
Available Formats
MICROWAVE INTERGRATED CIRCUITS
Huynh Phu Minh Cuong, PhD
hpmcuong@hcmut.edu.vn
Department of Telecommunications Faculty of Electrical and Electronics Engineering Ho Chi Minh city University of Technology
Dr. Cuong HuynhTelecommunications DepartmentHCMUT 1
MICROWAVE INTERGRATED CIRCUITS
Instructor: Cuong Huynh (PhD) Office: 112 B3 , HCMUT Office Hours: Friday 2:00-4:00 PM E-mail: hpmcuong@hcmut.edu.vn Textbook: [1] David M. Pozar, Microwave Engineering, John Wiley & Sons, Inc, 4th ed., 2012. References: [2] Gonzalez, Microwave Transistor Amplifiers, Prentice Hall, 2nd ed. 1997 [3] I.D. Robertson, S. Lucyszyn, RFIC and MMIC Design and Technology, The Institution of Electrical Engineers, London, 2001 [4] V nh Thnh, Mch Siu Cao Tn, NXB HQG, 2006 [5] V nh Thnh, K Thut Siu Cao Tn, NXB HQG, 2004.
Dr. Cuong HuynhTelecommunications DepartmentHCMUT
MICROWAVE INTERGRATED CIRCUITS
Learning outcomes
Understand effects of noise and nonlinearity distortion on microwave systems and system parameters such as noise figure, input/output referred noise, 1-dB compression point and third-order intercept point. Analyze various microwave transceiver architectures and design system parameters for microwave transceivers. Analyze, design, fabricate and measure microwave passive components such as power divider/combiner, directional coupler, hybrid coupler, circulator and T/R switch. Analyze, design, fabricate and measure microwave filters using distributed elements. Analyze, design, fabricate and measure microwave amplifiers including low noise amplifier, broadband amplifier and power amplifier. Analyze, design, fabricate and measure microwave mixers and oscillators. Use microwave simulation soft-wares such as ADS, Cadence and SDH, and equipments such as network analyzer, spectrum analyzer, synthesizer and noise figure analyzer.
Dr. Cuong HuynhTelecommunications DepartmentHCMUT
MICROWAVE INTERGRATED CIRCUITS
Grading
Homework 20% You are encouraged to work together with your classmates on the homework. HW can be turned in via Email. No late homework will be graded
Final Project 30%
Report and PowerPoint presentation are required Final Exams 50% Closed book One single-sided A4 of notes is allowed
4
Dr. Cuong HuynhTelecommunications DepartmentHCMUT
MICROWAVE INTERGRATED CIRCUITS
Outline
Chapter 1: Fundamentals of Microwave Engineering Chapter 2: System Parameters and Transceiver Architectures Chapter 3: Power Dividers and Directional Couplers Chapter 4: Microwave Amplifier Chapter 5: Oscillators and Mixers Chapter 6: Microwave Filters
Dr. Cuong HuynhTelecommunications DepartmentHCMUT
MICROWAVE INTERGRATED CIRCUITS
Chapter 1
Fundamentals of Microwave Engineering
Huynh Phu Minh Cuong
hpmcuong@hcmut.edu.vn Department of Telecommunications Faculty of Electrical and Electronics Engineering Ho Chi Minh city University of Technology
Dr. Cuong HuynhTelecommunications DepartmentHCMUT 6
Introduction
and emerging applications !
Integrated Circuits (IC)
Is the key driver behind the scene !
Dr. Cuong HuynhTelecommunications DepartmentHCMUT
Introduction
Dr. Cuong HuynhTelecommunications DepartmentHCMUT
Introduction
Dr. Cuong HuynhTelecommunications DepartmentHCMUT
Introduction
Dr. Cuong HuynhTelecommunications DepartmentHCMUT
Introduction
Dr. Cuong HuynhTelecommunications DepartmentHCMUT
Introduction
Dr. Cuong HuynhTelecommunications DepartmentHCMUT
Introduction
Dr. Cuong HuynhTelecommunications DepartmentHCMUT
13
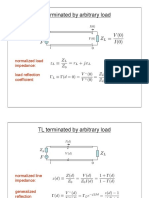
1.1 Fundamentals of microwave engineering
Transmission lines
V ( x) V .e . x V .e . x
V .l V .l I (l ) e e Z0 Z0
1 ( x ) Z ( x) Z0 1 ( x )
( l )
Z L Z0 Z L Z0
2 d
( x) (l ).e
Z L j.R0 .tg ( d ) Z ( x ) R0 R0 j.Z L .tg ( d )
1 1
VSWR
14
Dr. Cuong HuynhTelecommunications DepartmentHCMUT
1.1 Fundamentals of microwave engineering
Smith chart
Dr. Cuong HuynhTelecommunications DepartmentHCMUT
15
1.1 Fundamentals of microwave engineering
Impedance Matching
Using lump elements Using transmission line ADS Smith chart tool
Dr. Cuong HuynhTelecommunications DepartmentHCMUT
16
1.1 Fundamentals of microwave engineering
Scattering Parameters
At microwave regime: S-parameters matrix, defined in terms of traveling waves, is used instead. The scattering matrix represents the relation between the voltage incident waves on the ports to voltage reflected wave from the ports. S-parameters are measured with matched loads rather than open- or short-circuits. At microwave frequencies, matched loads are relatively easy to realize. S-parameters are measured using Vector Network Analyzer (VNA).
Dr. Cuong HuynhTelecommunications DepartmentHCMUT 17
S-Parametter Definition
V+n is the incident voltage wave on port n
V n is the reflected voltage wave from port n.
The scattering matrix, or [S] matrix, is defined in relation to these incident and reflected voltage waves.
Dr. Cuong HuynhTelecommunications DepartmentHCMUT
S-Parametter Definition
Dr. Cuong HuynhTelecommunications DepartmentHCMUT
Dr. Cuong HuynhTelecommunications DepartmentHCMUT
Dr. Cuong HuynhTelecommunications DepartmentHCMUT
Example: Find [S]
Dr. Cuong HuynhTelecommunications DepartmentHCMUT
1.2 Technology and device for microwave integrated circuits
Target: smaller size, lighter weight, lower power requirements, lower cost, and increased complexity. Microwave integrated circuits (MICs) Technology replace bulky and expensive waveguide and coaxial components with small and inexpensive planar components. MIC technology has advanced to the point where complete microwave subsystems, such as receiver front ends and radar transmit/receive modules, can be integrated on a chip that is only a few square millimeters in size.
Hybrid MICs MIC MMIC/RFIC
Hybrid Microwave Integrated Circuits Monolithic Microwave Integrated Circuits Radio Frequency Integrated Circuits
Dr. Cuong HuynhTelecommunications DepartmentHCMUT 23
1.2 Technology and device for microwave integrated circuits
Hybrid MICs
MMIC/RFIC
Dr. Cuong HuynhTelecommunications DepartmentHCMUT
24
1.2 Technology and device for microwave integrated circuits
Technology
CMOS
The metaloxidesemiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) was first patented by Julius Edgar Lilienfeld in 1925, well before the invention of BJT. Due to the fabrication limitation, MOSFET has not been used until the early years of 1960s. CMOS (Complementary MOS p- and n-type device) was patented by Frank Wanlass in 1967, initiating a revolution in the semiconductor industry. CMOS initially dominates in the digital circuit/systems while others for analog. Why CMOS now ? Low cost, high integration and solution for SOC.
Dr. Cuong HuynhTelecommunications DepartmentHCMUT 25
1.2 Technology and device for microwave integrated circuits
CMOS Technology
CMOS Transistors Interconnect Diodes Resistors Capacitors Inductors Bipolar Transistors
26
Dr. Cuong HuynhTelecommunications DepartmentHCMUT
1.2 Technology and device for microwave integrated circuits
CMOS Technology
Intel 45 nm CMOS Process
Dr. Cuong HuynhTelecommunications DepartmentHCMUT
27
1.2 Technology and device for microwave integrated circuits
Microwave Devices
DIODES BIPOLAR JUNCTION TRANSISTORS FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTORS Capacitor Inductor
Dr. Cuong HuynhTelecommunications DepartmentHCMUT
28
1.2 Technology and device for microwave integrated circuits
Microwave devices
Dr. Cuong HuynhTelecommunications DepartmentHCMUT
29
1.2 Technology and device for microwave integrated circuits
NMOS Transistor
Dr. Cuong HuynhTelecommunications DepartmentHCMUT
30
1.2 Technology and device for microwave integrated circuits
PMOS Transistor
Dr. Cuong HuynhTelecommunications DepartmentHCMUT
31
1.2 Technology and device for microwave integrated circuits
Interconnect
Dr. Cuong HuynhTelecommunications DepartmentHCMUT
32
1.2 Technology and device for microwave integrated circuits
Diode
Dr. Cuong HuynhTelecommunications DepartmentHCMUT
33
1.2 Technology and device for microwave integrated circuits
Resistor
Dr. Cuong HuynhTelecommunications DepartmentHCMUT
34
1.2 Technology and device for microwave integrated circuits
Capacitor
Dr. Cuong HuynhTelecommunications DepartmentHCMUT
35
1.2 Technology and device for microwave integrated circuits
Inductor
Dr. Cuong HuynhTelecommunications DepartmentHCMUT
36
1.3 Microwave simulation tools
Circuit Simulator: EM simulator:
ADS, Cadence Momentum, HFSS,IE3D, CST, SONET
Dr. Cuong HuynhTelecommunications DepartmentHCMUT
37
You might also like
- Done Final-Inc-McrowaveDocument134 pagesDone Final-Inc-McrowaveAnn Manelle MagsinoNo ratings yet
- SUBIN K M Freespace Laser CommunicationsDocument31 pagesSUBIN K M Freespace Laser Communicationsapi-3827000100% (3)
- Ceragon - Case Study - Evolution Long Haul - Links Over WaterDocument4 pagesCeragon - Case Study - Evolution Long Haul - Links Over WaterDaud SuleimanNo ratings yet
- Intelsat Transmission Plan Form: Customer and Capacity EngineeringDocument6 pagesIntelsat Transmission Plan Form: Customer and Capacity EngineeringMahamoud HamoudNo ratings yet
- Generic Proses & Performance SDHDocument115 pagesGeneric Proses & Performance SDHHardy YoelNo ratings yet
- Overview de Produtos SIAEDocument9 pagesOverview de Produtos SIAEThiago Andrade RangelNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Communication System: K. Seetharamaraju (134103062)Document31 pagesAircraft Communication System: K. Seetharamaraju (134103062)JOELNo ratings yet
- LBA CH11 85cm Uplink 2mbpsDocument3 pagesLBA CH11 85cm Uplink 2mbpsAhmadHambaliNo ratings yet
- People Also Ask: C++ Tutorial For Beginners - Full CourseDocument1 pagePeople Also Ask: C++ Tutorial For Beginners - Full Course10A2 Do TungLamNo ratings yet
- A Survey On Digital Modulation Techniques For Software Defined Radio ApplicationsDocument8 pagesA Survey On Digital Modulation Techniques For Software Defined Radio Applicationssreekanthreddy peramNo ratings yet
- Satellite SystemsDocument30 pagesSatellite SystemsHaris SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- IT Project Study Guide by DCH PDFDocument538 pagesIT Project Study Guide by DCH PDFJens DchNo ratings yet
- Combined Smith Chart: Introduction To RF Circuit DesignDocument1 pageCombined Smith Chart: Introduction To RF Circuit DesignbNo ratings yet
- DVB H MeasurementsDocument28 pagesDVB H MeasurementsStarLink1No ratings yet
- Optical Fiber ThesisDocument79 pagesOptical Fiber ThesisHashmat MohamadNo ratings yet
- Satellite Networking - VL-3Document14 pagesSatellite Networking - VL-3Ghulam ShabbirNo ratings yet
- Introduction To LinuxDocument286 pagesIntroduction To LinuxSCRIBDSNo ratings yet
- DVB-S2 FaqDocument5 pagesDVB-S2 Faqdeb1984No ratings yet
- Dvb-S2 Faqs: White PaperDocument4 pagesDvb-S2 Faqs: White Paperacp2678No ratings yet
- Manual SIAEDocument4 pagesManual SIAEAlexander Brito VillaNo ratings yet
- Inr0225-03 - Guidelines For Network Management Planning of SIAE Radio Equipments - AL Series - 2005Document60 pagesInr0225-03 - Guidelines For Network Management Planning of SIAE Radio Equipments - AL Series - 2005German FloresNo ratings yet
- iQlinkXG Quick Start Guide - v1 - 26 PDFDocument36 pagesiQlinkXG Quick Start Guide - v1 - 26 PDFwoody0100% (2)
- Smith ChartDocument47 pagesSmith ChartEly KpNo ratings yet
- A Survey of DWDM Network1sDocument6 pagesA Survey of DWDM Network1sKarthic ShunmugarajNo ratings yet
- Simulate Multipath Rayleigh Fading Propagation Channel - SimulinkDocument6 pagesSimulate Multipath Rayleigh Fading Propagation Channel - SimulinkAngela FasuyiNo ratings yet
- RF Link BudgetDocument4 pagesRF Link BudgetHabib MohammedNo ratings yet
- Name of Course: E1-E2 CFADocument6 pagesName of Course: E1-E2 CFARavi Shankar KrovvidiNo ratings yet
- Impact of GT, SFD and EIRP On System DesignDocument18 pagesImpact of GT, SFD and EIRP On System DesignExtreme DaysNo ratings yet
- Optical Sattelite Communication SeminarDocument16 pagesOptical Sattelite Communication Seminar18Pa1A0418 Battula RevanthrajNo ratings yet
- Satellite Link DesignDocument34 pagesSatellite Link Designrvanande21No ratings yet
- Naser Parhizgar, Khaled Bahmani Department of Electrical Engineering, Science and Research Branch, Islamic Azad University, Fars, IranDocument21 pagesNaser Parhizgar, Khaled Bahmani Department of Electrical Engineering, Science and Research Branch, Islamic Azad University, Fars, IranSharmaarke MohamedNo ratings yet
- QPSKDocument89 pagesQPSKMuthe Murali100% (1)
- Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) On Cisco Routers: Finding Feature InformationDocument10 pagesMultiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) On Cisco Routers: Finding Feature InformationsrikanthNo ratings yet
- TV TransmitterDocument2 pagesTV TransmitterMonirul IslamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Scattering ParametersDocument48 pagesChapter 3 Scattering Parametersnguyenthanhdan811100% (1)
- Programmable Logic Controller (Mitsubishi)Document26 pagesProgrammable Logic Controller (Mitsubishi)Thương Nguyễn ThanhNo ratings yet
- Satellite Communications in The 5G Era (Shree Krishna Sharma, Symeon Chatzinotas Etc.)Document600 pagesSatellite Communications in The 5G Era (Shree Krishna Sharma, Symeon Chatzinotas Etc.)Max Polik100% (1)
- A Vsat Link Margin Calculation A Turbo-C ProgrammeDocument5 pagesA Vsat Link Margin Calculation A Turbo-C ProgrammeIJIRAE- International Journal of Innovative Research in Advanced EngineeringNo ratings yet
- W1. CH 01 Sattelite CommunicationDocument78 pagesW1. CH 01 Sattelite CommunicationRamNo ratings yet
- JUNOSDocument32 pagesJUNOSBon Tran HongNo ratings yet
- MQ47856 PDFDocument127 pagesMQ47856 PDFDon DonNo ratings yet
- Wavelength Division MultiplexingDocument7 pagesWavelength Division MultiplexingJorge RzezakNo ratings yet
- Smith Chart IntroductionDocument18 pagesSmith Chart Introductionchakri474No ratings yet
- 15 Basics of Vsat PDFDocument40 pages15 Basics of Vsat PDFtoewin zawNo ratings yet
- Signal Integrity Tips and VNA MeasurementsDocument43 pagesSignal Integrity Tips and VNA MeasurementsF.DzialoNo ratings yet
- Satellite Communication l1Document21 pagesSatellite Communication l1Mehzabin ProvaNo ratings yet
- LinkWay S2 Datasheet 012 WebDocument2 pagesLinkWay S2 Datasheet 012 Webvsharma26No ratings yet
- DVB T2 HandbookDocument25 pagesDVB T2 HandbookarsenaldoNo ratings yet
- Electronic Communication TrainerDocument1 pageElectronic Communication TrainerFandeto Gaming100% (1)
- Applied MechatronicDocument16 pagesApplied MechatronicDuong Van Tu33% (3)
- GTE Lenkurt BookDocument172 pagesGTE Lenkurt Bookdpsguard-buy8922No ratings yet
- Ceragon Training Program 2011 VER 2 Hand OutDocument15 pagesCeragon Training Program 2011 VER 2 Hand Outdrytool100% (1)
- Radio Propagation ModelingDocument24 pagesRadio Propagation Modelingcoolboy_usamaNo ratings yet
- Mobile Computing Deployment and Management: Real World Skills for CompTIA Mobility+ Certification and BeyondFrom EverandMobile Computing Deployment and Management: Real World Skills for CompTIA Mobility+ Certification and BeyondNo ratings yet
- WDM Technologies: Passive Optical ComponentsFrom EverandWDM Technologies: Passive Optical ComponentsAchyut K. DuttaNo ratings yet
- Understanding UMTS Radio Network Modelling, Planning and Automated Optimisation: Theory and PracticeFrom EverandUnderstanding UMTS Radio Network Modelling, Planning and Automated Optimisation: Theory and PracticeMaciej NawrockiNo ratings yet
- Optimizing and Testing WLANs: Proven Techniques for Maximum PerformanceFrom EverandOptimizing and Testing WLANs: Proven Techniques for Maximum PerformanceNo ratings yet
- Thesis Rhee PDFDocument128 pagesThesis Rhee PDFtranhieu_hcmutNo ratings yet
- TTQ 5-3 Attenuation LimitDocument19 pagesTTQ 5-3 Attenuation Limittranhieu_hcmutNo ratings yet
- Optical Communications: Pham Quang ThaiDocument13 pagesOptical Communications: Pham Quang Thaitranhieu_hcmutNo ratings yet
- TTQ 2-4 Type of FibersDocument15 pagesTTQ 2-4 Type of Fiberstranhieu_hcmutNo ratings yet
- TTQ 2-3 Signal DegradationDocument27 pagesTTQ 2-3 Signal Degradationtranhieu_hcmutNo ratings yet
- TTQ 2-2 Light PropagationDocument36 pagesTTQ 2-2 Light Propagationtranhieu_hcmutNo ratings yet
- TTQ 2-1 Geometrical OpticsDocument12 pagesTTQ 2-1 Geometrical Opticstranhieu_hcmutNo ratings yet
- OP03b-Graident Methods PDFDocument22 pagesOP03b-Graident Methods PDFtranhieu_hcmutNo ratings yet
- OP03d Filter DesignDocument23 pagesOP03d Filter Designtranhieu_hcmutNo ratings yet
- Optical Communications: Chapter 1: IntroductionDocument16 pagesOptical Communications: Chapter 1: Introductiontranhieu_hcmutNo ratings yet
- OP03b Graident MethodsDocument22 pagesOP03b Graident Methodstranhieu_hcmutNo ratings yet
- Various ToolRoomDocument18 pagesVarious ToolRoomToshang SharmaNo ratings yet
- Preventive Maintenance: Basic Management Development Program EngineeringDocument63 pagesPreventive Maintenance: Basic Management Development Program EngineeringBunga Panjaitan100% (1)
- Product Manual For Electric Immersion Water Heaters ACCORDING TO IS 368:2014Document7 pagesProduct Manual For Electric Immersion Water Heaters ACCORDING TO IS 368:2014Mani DhamodharanNo ratings yet
- Vin LmiDocument8 pagesVin LmiSHEMIM ABDUL AZEEZNo ratings yet
- Carrier 7.5TRDocument2 pagesCarrier 7.5TRbrian mmec2020No ratings yet
- CDA3000Document2 pagesCDA3000Edilson AmilNo ratings yet
- A330-200/300 Air Conditioning SystemDocument196 pagesA330-200/300 Air Conditioning SystemBernard XavierNo ratings yet
- Spesifikasi Ysio X.preeDocument1 pageSpesifikasi Ysio X.preeRadiologi RSUD KilisuciNo ratings yet
- SPI MX66UM2G45G, 1.8V, 2Gb, v1.0 PDFDocument101 pagesSPI MX66UM2G45G, 1.8V, 2Gb, v1.0 PDFErivaldo MateNo ratings yet
- 3RV20414YA10 Datasheet enDocument8 pages3RV20414YA10 Datasheet enhilal serenNo ratings yet
- Brake ControlDocument212 pagesBrake ControllogammicNo ratings yet
- Current-Source DC-DC ConverterDocument53 pagesCurrent-Source DC-DC ConverterpepenitoNo ratings yet
- RFQ Lines 2119139Document5 pagesRFQ Lines 2119139MESHELNo ratings yet
- Clarity Line AmpDocument27 pagesClarity Line AmpPayphone.comNo ratings yet
- W&H - LinaDocument74 pagesW&H - LinaPreciosa SilvaNo ratings yet
- Tower Crane CatalogDocument159 pagesTower Crane CatalogPoorna AbeywardanaNo ratings yet
- Datasheet 350Document2 pagesDatasheet 350Sebastian RentschNo ratings yet
- Scada Control Room: EFS-A1 EFS-B1Document1 pageScada Control Room: EFS-A1 EFS-B1Prem KumarNo ratings yet
- BarriersDocument14 pagesBarriersAbdel BezzariNo ratings yet
- Review Review Review Review M M M M Ssss OHE OHE OHE OHEDocument61 pagesReview Review Review Review M M M M Ssss OHE OHE OHE OHETushar100% (2)
- (4-2) Synchronous GeneratorDocument35 pages(4-2) Synchronous Generatorfarah haniNo ratings yet
- On The Simulation of Three Phase Induction Machine PDFDocument3 pagesOn The Simulation of Three Phase Induction Machine PDFJOHN MINKHANTNo ratings yet
- INIM Catalogo Incendio ENG Rev3.00 MediumRes PDFDocument76 pagesINIM Catalogo Incendio ENG Rev3.00 MediumRes PDFnedzadNo ratings yet
- Champion C-Base - C-Line - C-Pro - C-Advanced - C-Silenced - C-Engine Piston CompressorsDocument12 pagesChampion C-Base - C-Line - C-Pro - C-Advanced - C-Silenced - C-Engine Piston Compressorssergimiravia1No ratings yet
- Preconnectorized "Stubbed" Hardware: Features and BenefitsDocument12 pagesPreconnectorized "Stubbed" Hardware: Features and BenefitsSergio Denis UCNo ratings yet
- VRV IV S Didvs2001 PDFDocument14 pagesVRV IV S Didvs2001 PDFmas zak danielNo ratings yet
- Sungrow ST68KWH-50HV Datasheet PDFDocument2 pagesSungrow ST68KWH-50HV Datasheet PDFNicolás Herrera SapunarNo ratings yet
- Project LeftDocument6 pagesProject Leftseham hejaziNo ratings yet
- Toparts Quotation-Cat Seal Kit-Nss Ci-Cote Dovoire-2017!11!10Document3 pagesToparts Quotation-Cat Seal Kit-Nss Ci-Cote Dovoire-2017!11!10zephyrinNo ratings yet
- High-Speed, High-Side MOSFET Driver With Charge Pump and Overcurrent LimitDocument24 pagesHigh-Speed, High-Side MOSFET Driver With Charge Pump and Overcurrent LimitiyanuNo ratings yet