Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Development: Land Use
Uploaded by
Yane Rojas ZevallosOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Development: Land Use
Uploaded by
Yane Rojas ZevallosCopyright:
Available Formats
Development
Land use
Green development, a concept that includes consideration of
community-wide or regional environmental implications
Science and technology
Artificial development, an area of computer science and
engineering
Development (differential geometry), the process of rolling one
surface over another
Development (journal), an academic journal in developmental
biology
Development (topology), a countable collection of open
coverings
Developmental biology, the study of the process by which
organisms grow and develop
Drug development, the entire process of bringing a new drug or
device to the market
Embryogenesis, or development, the process by which the embryo
is formed
Energy development, the effort to provide sufficient primary
energy sources
Human development (biology), the process of growing to maturity
o Prenatal development, the process in which a human
embryo or fetus gestates during pregnancy
o Child development, the biological, psychological, and
emotional changes that occur in human beings between
birth and the end of adolescence
o Youth development, the process through which adolescents
acquire the cognitive, social, and emotional skills and
abilities required to navigate life
Neural development, the processes that generate, shape, and
reshape the nervous system
Photographic development, chemical means by which exposed
photographic film or paper is processed to produce a visible
image
New product development, the complete process of bringing a
new product to market
Research and development, work aiming to increase knowledge
Software development, the development of a software product
Tooth development or odontogenesis
Web development, work involved in developing a web site
Social science
Development studies, social science which addresses issues of
concern to developing countries
Development geography, geography with reference to the
standard of living and quality of life of human inhabitants
Developmental psychology, the scientific study of systematic
psychological, emotional, and perception changes over life spans
Community development, the practices and academic disciplines
to improve various aspects of local communities
Sociocultural evolution, how cultures and societies have changed
over time
Economic development, the economic aspect of social change
Human development (humanity), an international and economic
development paradigm
Human development theory, a theory that merges older ideas
from ecological economics, sustainable development, welfare
economics, and feminist economics
Rural development, actions and initiatives taken to improve the
standard of living in non-Urban neighborhoods, countryside, and
remote villages
Social development, processes of change in societies
Sustainable development, a pattern of resources use, that aims to
meet human needs while preserving the environment
International and regional
Regional development, the provision of aid and other assistance
to regions which are less economically developed
o Multilateral development bank
o European Development Fund, an instrument for European
Community aid
o Development aid, the provision of assistance to developing
countries
Economic development, the sustained, concerted effort of
policymakers and community to promote the standard of living
and economic health in a specific area
Human Development Index, used to rank countries by level of
"human development"
International development, the development of greater quality of
life for humans
Business and professional
Business development, a process of growing a business
Career development, which has several meanings
Corporate development, a position in a business
Development & Commerce Bank (now called RHB Bank)
Fundraising, soliciting voluntary contributions to an organization or
prospective organization
Training and development, organizational activity aimed at
bettering the performance of individuals and groups in
organizational settings
Leadership development, activities that enhances the quality of
leadership within an individual or organization
New product development, the complete process of bringing a
new product to market
Organization development, a conceptual, organization-wide
effort to increase an organization's effectiveness and viability
Personal development or self-help
Professional development, skills and knowledge attained for both
personal development and career advancement
Culture
Video game development, a creative process of developing a
video game
Development (album), a 2002 nu-metal album by musical group
Nonpoint
Musical development, a compositional process
Other
Characterisation including character development
Develop, term used in Chess
Development of doctrine, a term used by John Henry Newman to
describe Catholic teachings
Development hell, media industry term for when a project is stuck
in development
Development of religion, the various stages in the evolution of any
particular religion or religious system
Driver development program is a program used by racing teams
to develop younger drivers
Components of the "development" phase in film making include
film finance and film budgeting
Environment
Environment may refer to:
Environment (biophysical), the physical and biological factors
along with their chemical interactions that affect an organism
Environment (systems), the surroundings of a physical system that
may interact with the system by exchanging mass, energy, or
other properties
Environments (series), a series of LPs, cassettes and CDs depicting
natural sounds
It may also refer to:
Built environment, constructed surroundings that provide the
setting for human activity, ranging from the large-scale civic
surroundings to the personal places
Knowledge environment, social practices, technological and
physical arrangements intended to facilitate collaborative
knowledge building, decision making, inference or discovery
Natural environment, all living and non-living things
Social environment, the culture that an individual lives in, and the
people and institutions with whom they interact
Physical environment, in ecology
In computing:
Desktop environment, in computing, the graphical user interface
to the computer
Environment variables, the dynamic set of variables defined in a
process
Integrated development environment, a type of computer
software that assists computer programmers in developing
software
Runtime environment, a virtual machine state which provides
software services for processes or programs while a computer is
running
Environmental may refer to:
Environmental art
Environmental determinism
Environmental epidemiology
Environmental health
Environmental movement
Environmental policy
Environmental psychology
Environmental quality
Environmental science, the study of the interactions among the
physical, chemical and biological components of the environment
Other
Environment (film), a 1917 silent film
See also
Ambient (disambiguation)
Category:Environment, for articles relating to the effect of human
activity on the environment
Ecology, a sub-discipline of biology often confused with the
environment in general
Environmentalism, a concern with the preservation of the
environment
Epidemiology
List of environmental issues
Natural landscape
All pages beginning with "Environment"
Protection
Film
Protection (film), 2001 film directed by John Flynn
Music
Protection (album), by Massive Attack
o "Protection" (Massive Attack song)
"Protection" (Donna Summer song)
"Protection", a song by Krokus from To You All
"Protection", a song by Graham Parker from Squeezing Out Sparks
Places
Protection, Kansas
Protection, New York
Safety and technology
Consumer protection
Dust#Control of dust resistance on surfaces
Environmental protection
Executive protection, security measures taken to ensure the safety of important
persons
Fireproofing
Power system protection
Protection (climbing)
Protection (poker)
Protection animals, such as guard dogs
Protection mechanism (computer science)
Protection racket
Protectionism in economic policy
Public health
o Infection control
o Personal protective equipment
o Sexual protection, e.g. condoms
Rustproof
Thermal conductivity#Resistance
Toughness
Waterproofing
See also
Preservation (disambiguation)
Preserve (disambiguation)
Safety
Security
Coating
A coating is a covering that is applied to the surface of an object, usually referred to as
the substrate. The purpose of applying the coating may be decorative, functional, or
both. The coating itself may be an all-over coating, completely covering the substrate,
or it may only cover parts of the substrate. An example of all of these types of coating is
a product label on many drinks bottles- one side has an all-over functional coating (the
adhesive) and the other side has one or more decorative coatings in an appropriate
pattern (the printing) to form the words and images.
Paints and lacquers are coatings that mostly have dual uses of protecting the substrate
and being decorative, although some artists paints are only for decoration, and the paint
on large industrial pipes is presumably only for the function of preventing corrosion.
Functional coatings may be applied to change the surface properties of the substrate,
such as adhesion, wetability, corrosion resistance, or wear resistance. In other cases, e.g.
semiconductor device fabrication (where the substrate is a wafer), the coating adds a
completely new property such as a magnetic response or electrical conductivity and
forms an essential part of the finished product.
A major consideration for most coating processes is that the coating is to be applied at a
controlled thickness, and a number of different processes are in use to achieve this
control, ranging from a simple brush for painting a wall, to some very expensive
machinery applying coatings in the electronics industry. A further consideration for
'non-all-over' coatings is that control is needed as to where the coating is to be applied.
A number of these non-all-over coating processes are printing processes.
Many industrial coating processes involve the application of a thin film of functional
material to a substrate, such as paper, fabric, film, foil, or sheet stock. If the substrate
starts and ends the process wound up in a roll, the process may be termed "roll-to-roll"
or "web-based" coating. A roll of substrate, when wound through the coating machine,
is typically called a web.
Coatings may be applied as liquids, gases or solids.
System
A system is a set of interacting or interdependent components forming an integrated
whole
[1]
or a set of elements (often called 'components' ) and relationships which are
different from relationships of the set or its elements to other elements or sets.
[citation
needed]
Fields that study the general properties of systems include systems science, systems
theory, systems engineering, cybernetics, dynamical systems, thermodynamics, and
complex systems. They investigate the abstract properties of systems' matter and
organization, looking for concepts and principles that are independent of domain,
substance, type, or temporal scale.
[citation needed]
Some systems share common characteristics, including:
[citation needed]
A system has structure, it contains parts (or components) that are directly or indirectly
related to each other;
A system has behavior, it contains processes that transform inputs into outputs
(material, energy or data);
A system has interconnectivity: the parts and processes are connected by structural
and/or behavioral relationships.
A system's structure and behavior may be decomposed via subsystems and sub-
processes to elementary parts and process steps.
The term system may also refer to a set of rules that governs structure and/or behavior.
Alternatively, and usually in the context of complex social systems, the term institution
is used to describe the set of rules that govern structure and/or behavior.
System concepts
Environment and boundaries
Systems theory views the world as a complex system of interconnected parts. We
scope a system by defining its boundary; this means choosing which entities are inside
the system and which are outside part of the environment. We then make simplified
representations (models) of the system in order to understand it and to predict or
impact its future behavior. These models may define the structure and/or the behavior
of the system.
Natural and human-made systems
There are natural and human-made (designed) systems. Natural systems may not have
an apparent objective but their outputs can be interpreted as purposes. Human-made
systems are made with purposes that are achieved by the delivery of outputs. Their
parts must be related; they must be designed to work as a coherent entity else
they would be two or more distinct systems.
Theoretical framework
An open system exchanges matter and energy with its surroundings. Most systems are
open systems; like a car, coffeemaker, or computer. A closed system exchanges
energy, but not matter, with its environment; like Earth or the project Biosphere2 or 3.
An isolated system exchanges neither matter nor energy with its environment. A
theoretical example of such system is the Universe.
Process and transformation process
A system can also be viewed as a bounded transformation process, that is, a process or
collection of processes that transforms inputs into outputs. Inputs are consumed;
outputs are produced. The concept of input and output here is very broad. E.g., an
output of a passenger ship is the movement of people from departure to destination.
Subsystem
A subsystem is a set of elements, which is a system itself, and a component of a larger
system.
System model
A system comprises multiple views. For the man-made systems it may be such views as
planning, requirement (analysis), design, implementation, deployment, structure,
behavior, input data, and output data views. A system model is required to describe
and represent all these multiple views.
System architecture
A system architecture, using one single integrated model for the description of
multiple views such as planning, requirement (analysis), design, implementation,
deployment, structure, behavior, input data, and output data views, is a kind of system
model.
Elements of a system
Following are considered as the elements of a system in terms of Information systems:
1. Inputs and outputs
2. Processor
3. Control
4. Environment/surroundings
5. Feedback
6. Boundaries and interface
7. Relationships
You might also like
- DevelopmentDocument2 pagesDevelopmentgian reyesNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Environmental Philosophy SFES 1214: Week 10 Sustainable DevelopmentDocument32 pagesIntroduction To Environmental Philosophy SFES 1214: Week 10 Sustainable Developmentmroslang69No ratings yet
- Working Toward Sustainability: Ethical Decision-Making in a Technological WorldFrom EverandWorking Toward Sustainability: Ethical Decision-Making in a Technological WorldNo ratings yet
- Sustainability Science: Managing Risk and Resilience for Sustainable DevelopmentFrom EverandSustainability Science: Managing Risk and Resilience for Sustainable DevelopmentNo ratings yet
- Toward Sustainable Development: Concepts, Methods, and PolicyFrom EverandToward Sustainable Development: Concepts, Methods, and PolicyJan van der StraatenNo ratings yet
- Industrial Symbiosis for the Circular Economy: Operational Experiences, Best Practices and Obstacles to a Collaborative Business ApproachFrom EverandIndustrial Symbiosis for the Circular Economy: Operational Experiences, Best Practices and Obstacles to a Collaborative Business ApproachRoberta SalomoneNo ratings yet
- Phenomenology of Bioethics: Technoethics and Lived-ExperienceFrom EverandPhenomenology of Bioethics: Technoethics and Lived-ExperienceSusi FerrarelloNo ratings yet
- Ecosystems and Human Well-Being: A Manual for Assessment PractitionersFrom EverandEcosystems and Human Well-Being: A Manual for Assessment PractitionersNo ratings yet
- One Health Meets the Exposome: Human, Wildlife, and Ecosystem HealthFrom EverandOne Health Meets the Exposome: Human, Wildlife, and Ecosystem HealthNo ratings yet
- Nvironment May Refer ToDocument2 pagesNvironment May Refer ToAlekhyaNimmalapudiNo ratings yet
- Environmental Business Ethics: January 1999Document5 pagesEnvironmental Business Ethics: January 1999belbi kimNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity Change and Human Health: From Ecosystem Services to Spread of DiseaseFrom EverandBiodiversity Change and Human Health: From Ecosystem Services to Spread of DiseaseNo ratings yet
- Unit I-FundamentlsDocument19 pagesUnit I-FundamentlsRidhi GuptaNo ratings yet
- Meaning, Origin and Scope of Sustainable DevelopmentDocument21 pagesMeaning, Origin and Scope of Sustainable DevelopmentScheherazade Sandhu100% (6)
- Sustainability Strategies for Industry: The Future Of Corporate PracticeFrom EverandSustainability Strategies for Industry: The Future Of Corporate PracticeNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Development Keynote SpeechDocument26 pagesSustainable Development Keynote Speechdwi retnoNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - IntroductionDocument25 pagesUnit 1 - IntroductionFranz JosephNo ratings yet
- A Website and Implementation of The Proposed Project (E.R.O.T.) Environmental Rescue Organization TeamDocument6 pagesA Website and Implementation of The Proposed Project (E.R.O.T.) Environmental Rescue Organization TeamLance Grecco MagnayeNo ratings yet
- Unit - I Environment, Ecosystems and Biodiversity: Environmental ScienceDocument55 pagesUnit - I Environment, Ecosystems and Biodiversity: Environmental ScienceRohith VKNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Design and Build: Building, Energy, Roads, Bridges, Water and Sewer SystemsFrom EverandSustainable Design and Build: Building, Energy, Roads, Bridges, Water and Sewer SystemsNo ratings yet
- The Objectives of Sustainable Development - Ways To Achieve WelfareDocument6 pagesThe Objectives of Sustainable Development - Ways To Achieve WelfareDaniel HernandezNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1A - Multidisplinary Nature of Environmental Studies-2Document4 pagesUNIT 1A - Multidisplinary Nature of Environmental Studies-2Abinash BoruahNo ratings yet
- Environmental Education in Practice: Concepts and ApplicationsFrom EverandEnvironmental Education in Practice: Concepts and ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Evaluating Sustainable Development in the Built EnvironmentFrom EverandEvaluating Sustainable Development in the Built EnvironmentNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document32 pagesLecture 2aNo ratings yet
- Ecological Engineering Design: Restoring and Conserving Ecosystem ServicesFrom EverandEcological Engineering Design: Restoring and Conserving Ecosystem ServicesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Environmental Science - Definition, Scope and Importance Narrative ReportDocument3 pagesChapter 1 - Environmental Science - Definition, Scope and Importance Narrative ReportRenze OreaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - GE 705Document9 pagesChapter 6 - GE 705Ian Alimosa PanesNo ratings yet
- 96-Article Text-539-1-10-20200215 PDFDocument19 pages96-Article Text-539-1-10-20200215 PDFFebrian MaulanaNo ratings yet
- Thesis Topics Environmental EducationDocument9 pagesThesis Topics Environmental Educationjamieramirezdesmoines100% (2)
- Unit I Environmental Studies and Natural Resources Land Forest Water and Energy Problem and SolutionsDocument155 pagesUnit I Environmental Studies and Natural Resources Land Forest Water and Energy Problem and Solutionsssaurabhkumar061No ratings yet
- Philo-Notes: Learn Philosophy Online!Document17 pagesPhilo-Notes: Learn Philosophy Online!Jenny ForcadillaNo ratings yet
- Unit I Introduction To Environmental Studies - Multidicplinary Nature - Scope and Sustainable Development.Document142 pagesUnit I Introduction To Environmental Studies - Multidicplinary Nature - Scope and Sustainable Development.ssaurabhkumar061No ratings yet
- Bridging Scales and Knowledge Systems: Concepts and Applications in Ecosystem AssessmentFrom EverandBridging Scales and Knowledge Systems: Concepts and Applications in Ecosystem AssessmentNo ratings yet
- 07 Chapter1 PDFDocument62 pages07 Chapter1 PDFYadhu Krishna R SNo ratings yet
- Sustainable DevelopmentDocument32 pagesSustainable Developmentaditya pariharNo ratings yet
- HANDBOOK 101: A Guide to Sustainability for the Individual ConsumerFrom EverandHANDBOOK 101: A Guide to Sustainability for the Individual ConsumerNo ratings yet
- Design For Human and Planetary Health PDFDocument10 pagesDesign For Human and Planetary Health PDFIsabella MunizNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Architecture and Building Design (SABD) PDFDocument19 pagesSustainable Architecture and Building Design (SABD) PDFShivachandran Sivanesan67% (3)
- 01 - Green - Chapter 2Document10 pages01 - Green - Chapter 2Dhanraj VenugopalNo ratings yet
- Protecting the Future: Stories of Sustainability from RMIT UniversityFrom EverandProtecting the Future: Stories of Sustainability from RMIT UniversitySarah S. HoldsworthNo ratings yet
- Evaluating Education For Sustainable DevDocument19 pagesEvaluating Education For Sustainable DevLeon RodriguesNo ratings yet
- Biophilic Design: The Theory, Science and Practice of Bringing Buildings to LifeFrom EverandBiophilic Design: The Theory, Science and Practice of Bringing Buildings to LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Unit 1. Introduction To Environmental StudiesDocument13 pagesUnit 1. Introduction To Environmental StudiesKshitijNo ratings yet
- Environment Systems and Decisions Volume 22 Issue 4 2002 (Doi 10.1023 - A - 1020766914456) M. Kassas - Environmental Education - Biodiversity PDFDocument7 pagesEnvironment Systems and Decisions Volume 22 Issue 4 2002 (Doi 10.1023 - A - 1020766914456) M. Kassas - Environmental Education - Biodiversity PDFSyafranNo ratings yet
- 01 Unit I Environmental Studies-A Multidisciplinary SubjectDocument50 pages01 Unit I Environmental Studies-A Multidisciplinary SubjectHarsh SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Respect For Environment and SustainableDocument13 pagesRespect For Environment and Sustainablezakariye ahmedNo ratings yet
- Healthy Environments, Healing Spaces: Practices and Directions in Health, Planning, and DesignFrom EverandHealthy Environments, Healing Spaces: Practices and Directions in Health, Planning, and DesignNo ratings yet
- Unit VDocument80 pagesUnit VMohammed Mian ANo ratings yet
- Introduction To Environmental StudiesDocument11 pagesIntroduction To Environmental StudiesRavi TejaNo ratings yet
- Psychophysics As New Priority in Modern Science - Physical Basics of Informational InteractionDocument15 pagesPsychophysics As New Priority in Modern Science - Physical Basics of Informational InteractionBoris PetrovicNo ratings yet
- Approved LaboratoriesDocument22 pagesApproved LaboratoriesPaul CNo ratings yet
- Is A Calorie Really A Calorie - Metabolic Advantage of Low-Carbohydrate DietsDocument6 pagesIs A Calorie Really A Calorie - Metabolic Advantage of Low-Carbohydrate DietsGustavo CastroNo ratings yet
- Muscle Biopsy A Diagnostic Tool in Muscle DiseasesDocument9 pagesMuscle Biopsy A Diagnostic Tool in Muscle DiseasesRosa AquinoNo ratings yet
- Temperament ThesisDocument4 pagesTemperament ThesisBuyCheapPaperOnlineSingapore100% (2)
- Taxonomy of Haematococcus PluvialisDocument2 pagesTaxonomy of Haematococcus PluvialisKomathi BalasupramaniamNo ratings yet
- Jagaroo & Santangelo - Neurophenotypes Advancing Psychiatry and Neuropsychology 2016Document305 pagesJagaroo & Santangelo - Neurophenotypes Advancing Psychiatry and Neuropsychology 2016Jaime Fernández-Aguirrebengoa100% (1)
- 19 - Lipid MetabolismDocument35 pages19 - Lipid MetabolismcheckmateNo ratings yet
- Practice Test 22: Questions 1-10Document7 pagesPractice Test 22: Questions 1-10Несибели НаурызбаеваNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of OPHTHALMOLOGYDocument40 pagesAnatomy of OPHTHALMOLOGYhenok birukNo ratings yet
- Jellyfish Research PaperDocument6 pagesJellyfish Research Papergzrvpcvnd100% (1)
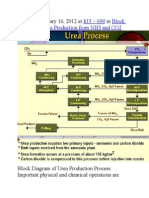
- Published January 16, 2012 at In: 813 × 699 Block Diagram of Urea Production From NH3 and CO2Document9 pagesPublished January 16, 2012 at In: 813 × 699 Block Diagram of Urea Production From NH3 and CO2himanshuchawla654No ratings yet
- Natural Products Chemistry: Indian Institute of Integrative Medicine, JammuDocument2 pagesNatural Products Chemistry: Indian Institute of Integrative Medicine, JammuPratik VaghelaNo ratings yet
- Leveraging Big Data To Transform TargetDocument13 pagesLeveraging Big Data To Transform Targetdeweyev699No ratings yet
- BIOL 3121 - Lecture 13 - 081116Document91 pagesBIOL 3121 - Lecture 13 - 081116Sara HuebnerNo ratings yet
- CAPE Bio Mark SchemeDocument4 pagesCAPE Bio Mark Schemeron97150% (2)
- Jane Goodall BiographyDocument2 pagesJane Goodall BiographyOjas JangalNo ratings yet
- Hamsters - A General DescriptionDocument5 pagesHamsters - A General Descriptiondulce crissNo ratings yet
- CS Audi - Case Study DRAFTDocument21 pagesCS Audi - Case Study DRAFTcahlahNo ratings yet
- The Ethics of Respect For Nature - Paul W. Taylor PDFDocument22 pagesThe Ethics of Respect For Nature - Paul W. Taylor PDFArtur P. CoelhoNo ratings yet
- His To PathologyDocument52 pagesHis To PathologyRathinaKumarNo ratings yet
- Cat ExamDocument25 pagesCat Examlahsivlahsiv684No ratings yet
- XLD Agar - Manufcture by TM MediaDocument3 pagesXLD Agar - Manufcture by TM MediaKunal VermaNo ratings yet
- Test On Gmos GM Foods Cloning b1b2 Grammar Drills Information Gap Activities Reading 96207Document4 pagesTest On Gmos GM Foods Cloning b1b2 Grammar Drills Information Gap Activities Reading 96207Thu Quynh NguyenNo ratings yet
- Clave Genero Dermanura (Otros) PDFDocument520 pagesClave Genero Dermanura (Otros) PDFJuan D Garcia Peluffo100% (1)
- Preparation of Histological SpecimensDocument4 pagesPreparation of Histological SpecimensAqilah HazwaniNo ratings yet
- Phet - Activity 1Document4 pagesPhet - Activity 1api-306913723No ratings yet
- (Springer Series in Wood Science) W. E. Hillis (auth.), John W. Rowe (eds.)-Natural Products of Woody Plants_ Chemicals Extraneous to the Lignocellulosic Cell Wall-Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg (1.pdfDocument1,274 pages(Springer Series in Wood Science) W. E. Hillis (auth.), John W. Rowe (eds.)-Natural Products of Woody Plants_ Chemicals Extraneous to the Lignocellulosic Cell Wall-Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg (1.pdfArmandoNo ratings yet
- Why Do Giraffes Have Long Necks?Document22 pagesWhy Do Giraffes Have Long Necks?johnosborneNo ratings yet
- Recent DevelopmentsDocument295 pagesRecent DevelopmentsGabriel PinheiroNo ratings yet